(UroToday.com) The 2024 South Central AUA annual meeting included a session on bladder cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Amanda Myers discussing a contemporary US claims analysis assessing real-world treatments following BCG induction in patients with non muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Intravesical BCG is the guideline-recommended first-line treatment for high-risk NMIBC, including for CIS. However, a substantial number of patients experience treatment failure with BCG. Notably, there has been a recent surge in clinical trials focused on patients who have recurrent disease of their NMIBC after BCG. Due to ongoing BCG shortages and access to alternative agents, the true number of patients who are receiving BCG induction is unclear. At the 2024 South Central AUA annual meeting, Dr. Myers and colleagues presented results evaluating this question and elucidated alternative treatment agents that patients received from a contemporary US insurance claims database.
From the Komodo Health claims database (January 2018 to March 2023) with Medicare Advantage, Medicaid, Managed Medicaid, and commercially insured patients, they identified patients with NMIBC using the following algorithm: (i) presence of CIS, or (ii) presence of bladder cancer TURBT, followed by intravesical chemotherapy or immunotherapy or 12 months with no treatment and no evidence of muscle-invasive bladder cancer:
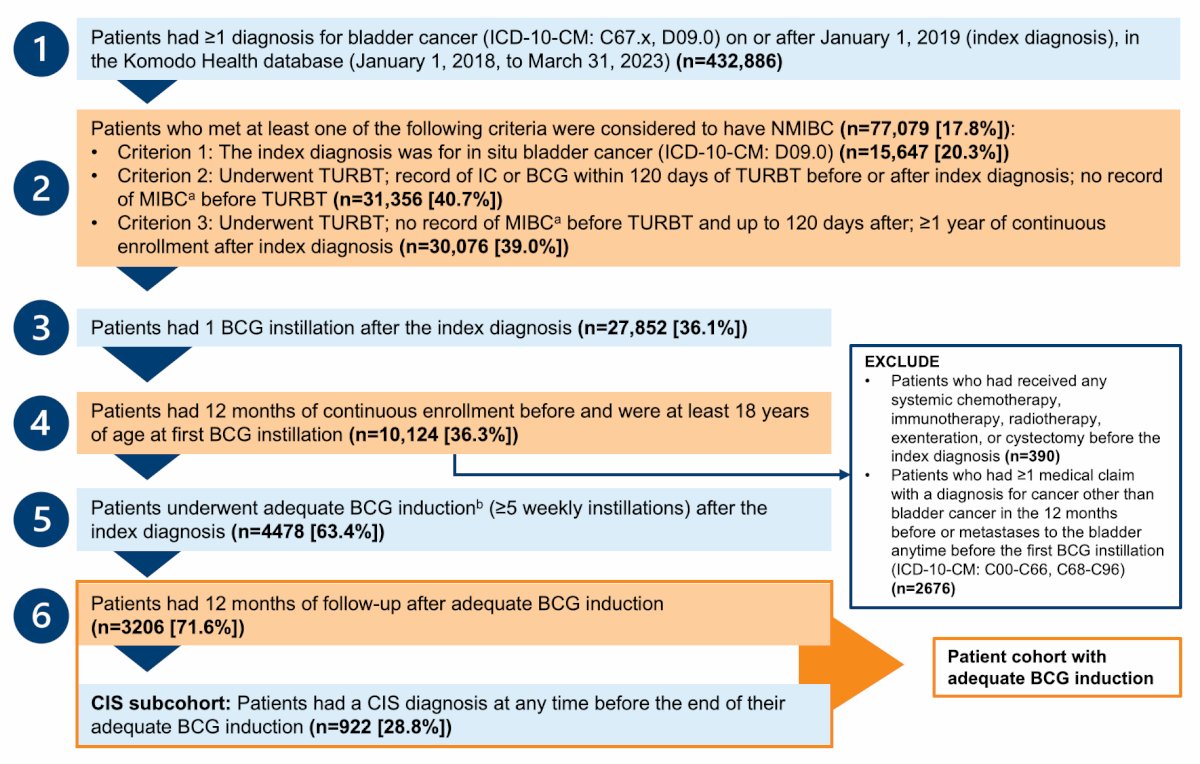
Patients were further queried to identify those who received adequate BCG induction (defined as ≥ 5 weekly instillations). They then summarized the distribution of this group and the treatments following BCG induction with ≥12 months of evaluable data for the overall population and the CIS subgroup.
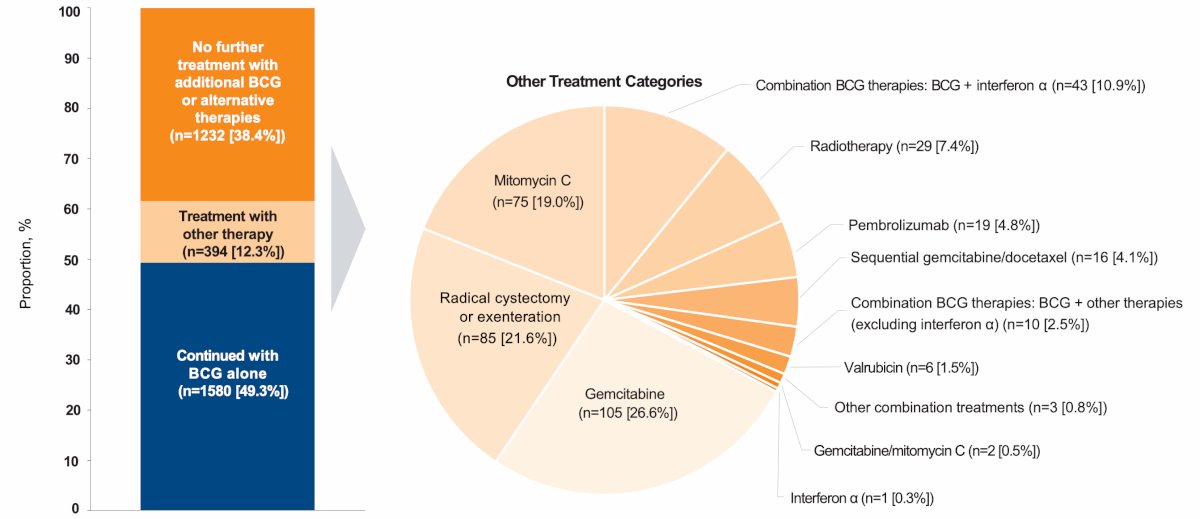
Among 7,058 patients with NMIBC receiving BCG, more than half (4,478, 63.4%) had adequate BCG induction. Of these patients, 3,206 had ≥ 12 months of data (including 28.8% of patients with CIS; n = 922). Following adequate BCG induction, 49.3% had further BCG and 24.9% had ≥2 doses of maintenance BCG. There were 38.4% of patients that had no further treatment, and 12.3% (394 patients) were treated with other therapies, including gemcitabine (26.6%), radical cystectomy or exenteration (21.6%), mitomycin C (19.0%), BCG + interferon-α (10.9%), radiotherapy (7.4%), and pembrolizumab (4.8%):
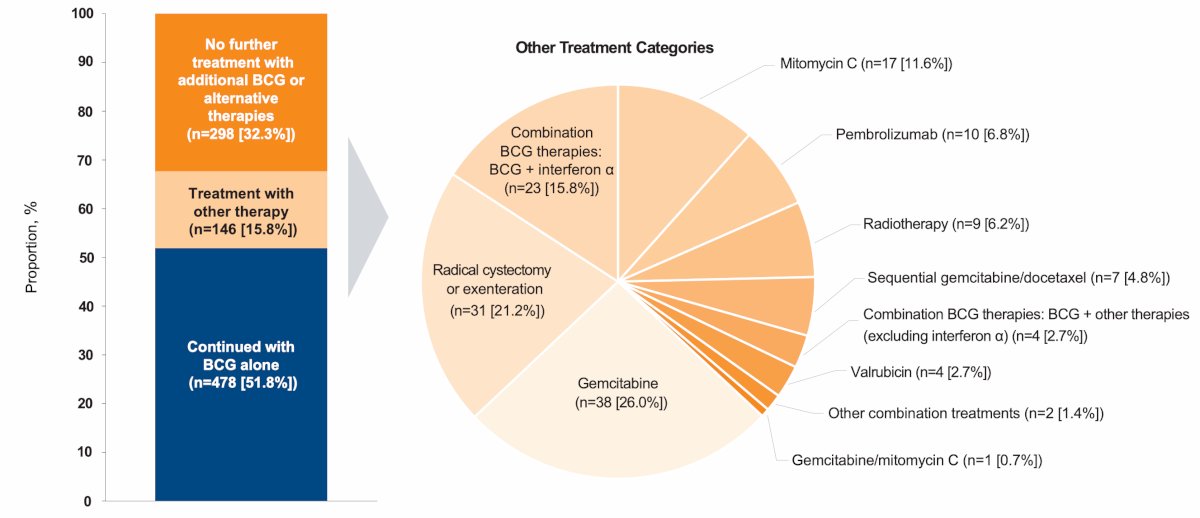
A similar distribution was observed in the CIS subgroup through BCG + interferon-α was the third most common treatment (15.8%):
Dr. Myers concluded her presentation by discussing a contemporary US claims analysis assessing real-world treatments following BCG induction in patients with NMIBC with the following take-home points:
- Approximately 2/3 of patients treated with BCG received adequate BCG induction, while only a quarter received adequate maintenance BCG
- There is significant treatment heterogeneity observed following adequate BCG induction
- Radical cystectomy rate remains low overall (2-3% among patients with adequate BCG induction) relative to bladder preserving therapies
- 4 patients were treated with bladder preserving therapies for every 1 patient undergoing radical cystectomy
- Follow-up studies are warranted to inform how treatment patterns shift when novel bladder preserving therapies are available and how patient outcomes are affected by current treatment patterns
Presented by: Amanda Myers, MD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 South Central American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Colorado Springs, CO, Wed, Oct 30 – Sat, Nov 2, 2024.


