(UroToday.com) The 2024 South Central AUA annual meeting included a session on lower genitourinary tract cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Peter Sullivan discussing financial toxicity in testicular cancer treatment. As our understanding of the long-term toxicities of chemotherapy evolves, the landscape for the management of testicular cancer is changing. Studies such as the SEMS1 and PRIMETEST2 trials are examining the utilization of Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) as the primary therapy for lower stage metastatic testicular cancer.
However, few studies have determined the financial toxicity associated with the various management strategies such as surveillance, RPLND, or systemic chemotherapy. Notably, artificial intelligence software can be used to predict costs associated with various treatment strategies (RPLND versus chemotherapy). At the 2024 South Central AUA annual meeting, Dr. Sullivan and colleagues described a novel approach to investigating the financial distress associated with these treatment options.
This study used a validated questionnaire, the COST-FACIT, developed to be distributed to patients prospectively to evaluate the perceived financial stress of patients undergoing treatment for testicular cancer:
A Markov model for stage IIa nonseminoma with various treatment outcomes was based on assumptions derived from the literature. Moreover, a large language model was utilized to apply these assumptions regarding outcomes and cost. Cost estimates were applied to the COST-FACIT questionnaire based on proportionality to identify potential financial stress and toxicity to patients associated. Assumptions for modeling are highlighted below: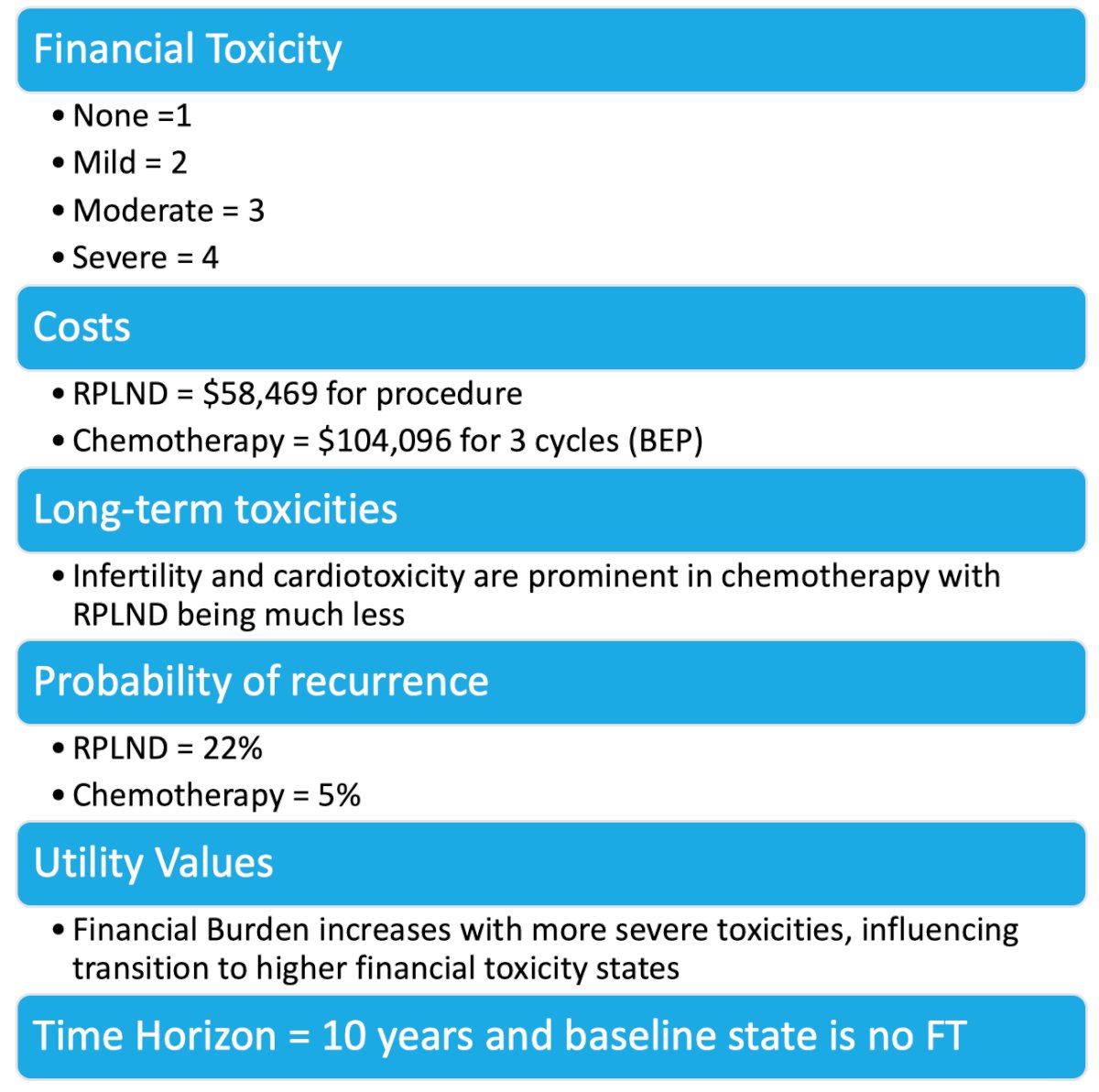
This study demonstrated the ability of the novel software program, TreeAge, to obtain financial data and performed a test case scenario to demonstrate the feasibility of correlating the software with the financial toxicity validated questionnaire. Results are highlighted by initial, mid, and long-term stages:
- Initial Stages (Year 1-3):
- RPLND: The majority of patients remain in the "No toxicity" or "Mild toxicity" states
- Chemotherapy: There is a noticeable progression towards "Mild" and "Moderate" toxicity, driven by the recurring costs of treatment cycles and side effects
- Mid Stages (Year 4-6):
- RPLND: Most patients have progressed to the "Mild" or "Moderate" toxicity states, but the proportion in "Severe toxicity" remains low
- Chemotherapy: A significant portion of patients have now reached "Moderate" toxicity, with a growing proportion in "Severe toxicity" due to continued expenses, treatment for long-term toxicities, and other complications
- Long-Term (Year 7-10):
- RPLND: The probability of remaining in "Moderate toxicity" is higher, but only a smaller group moves to "Severe toxicity." Patients who experience recurrence require additional treatments, but overall, RPLND remains a more cost-effective strategy
- Chemotherapy: A higher number of patients end up in the "Severe toxicity" state by year 10 due to accumulated financial burdens from long-term side effects and the cost of managing complications like infertility and cardiovascular toxicity
Dr. Sullivan concluded his presentation discussing financial toxicity in testicular cancer treatment with the following take-home points:
- Using large language modeling software applied to a Markov model associated with the various outcome scenarios associated with the treatment of Stage 2a nonseminoma, financial toxicity can be predicted
- From this model, RPLND is generally a more favorable option in terms of long term financial toxicity. Although the initial costs are high, the subsequent financial burden remains lower over time.
- Chemotherapy results in higher cumulative financial toxicity due to ongoing treatment costs, risk of side effects, and the need for more intensive management toxicities
- Further prospective studies regarding financial toxicity are necessary
Presented by: Peter Sullivan, DO, UT Houston, Houston, TX
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 South Central American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Colorado Springs, CO, Wed, Oct 30 – Sat, Nov 2, 2024.
References:
- Daneshmand S, Cary C, Masterson T, et al. Surgery in early metastatic seminoma: A phase II trial of retroperitoneal lymph node dissection for testicular seminoma with limited retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy. J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun 1;41(16):3009-3018.
- Hiester A, Che Y, Lusch A, et al. Phase 2 Single-arm Trial of Primary Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection in Patients with Seminomatous Testicular Germ Cell Tumors with Clinical Stage IIA/B (PRIMETEST). Eur Urol. 2023; Jul;84(1):25-31.


