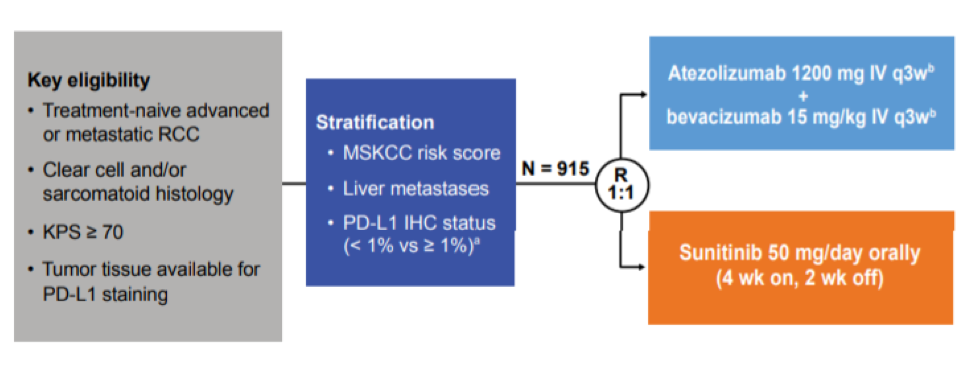
A total of 142 patients (16%) from IMmotion 151 had tumors with some component of sarcomatoid histology. Baseline characteristics are below.

In the sarcomatoid population, the objective response rate was significantly higher for patients receiving atezo/bev than sunitinib (49% vs 14%) and the CR rate was 10% in the atezo/bev arm compared with 3% in the sunitinib arm. This CR rate is comparable to the CR rate seen with Pembro/Axi in Keynote 426 (as described during ASCO 2019 (Abstract 4500)) and data from the ipi/nivo sarcomatoid cohort also shows a very impressive CR rate at (18%).2 Gene expression profiles demonstrated higher T-effector gene expression in sarcomatoid vs non-sarcomatoid (54% vs 40%) and PD-L1+ was more common in sarcomatoid as well (63% vs 39%).

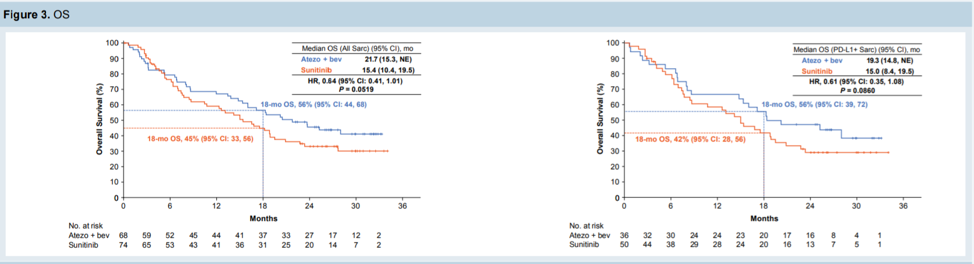
In terms of overall survival, patients with sarcomatoid features had increased OS with atezo+bev vs sunitinib, regardless of PD-L1 status.
Biomarker data revealed that patients with sarcomatoid features had a higher percentage of Angiolow expression (66%) compare with patients with non-sarcomatoid features (35%) and patients with sarcomatoid features also had a higher rate of PD-L1 expression (63%) compared with non-sarcomatoid tumors (39%).

Patients with mRCC with sarcomatoid features had improved survival, objective response rate, and progression-free survival with combination atezolizumab/bevacizumab compared with sunitinib. Combination tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and checkpoint inhibitor is now a proven strategy for patients with mRCC, with both axitinib/avelumab and pembrolizumab/avelumab approved in the United States. This data shows that for patients with mRCC with sarcomatoid features, atezo/bev shows similar efficacy compared to the other two options. However, without an OS benefit for all patients, at this time, this combination is unlikely to be chosen as a frontline therapy for patients with mRCC.
Presented by: Brian I. Rini, MD, FACP, Hematology and Medical Oncology, Cleveland Clinic Main Campus, Cleveland, OH
Written by: Jason Zhu, MD, Fellow, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Duke University, @TheRealJasonZhu at the 2019 ASCO Annual Meeting #ASCO19, May 31- June 4, 2019, Chicago, IL USA
References:
- Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 2019.
- Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2018;378:1277-90.
- Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 2019.


