To briefly summarize as JAVELIN Renal 101 has previously been presented and published, this trial accrued patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma and randomized them in a 1:1 fashion to avelumab and axitinib or sunitinib. Patients were stratified according to IMDC risk group and, in this analysis, overall survival, progression-free survival, objective response rate, complete response rate, and duration of response are reported stratified by IMDC risk group.
The JAVELIN Renal 101 trial enrolled 886 patients with advanced RCC who, as of a data cut-off of April 2020, had a median follow-up of NR (42.2-NE) for those randomized to avelumab and axitinib and 37.8 (31.4-NE) months for those randomized to sunitinib. Stratified analyses demonstrated relatively consistent benefits of avelumab and axitinib, compared to sunitinib, across strata of IMDC risk groups. These effects were generally statistically significant for progression-free survival and objective response rate (apart from progression-free survival among patients with IMBC good risk disease), while the effect was statistically significant for overall survival only among those with IMDC intermediate/poor and poor risk disease.
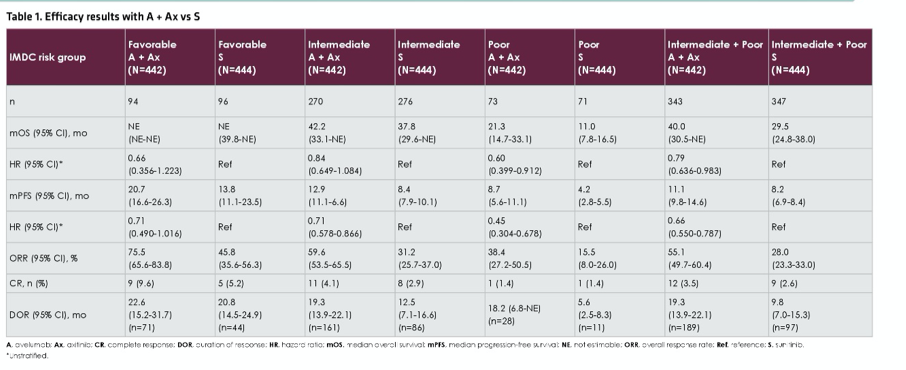
The effect of avelumab and axitinib were generally consistent across subgroups for both overall survival and progression-free survival.
The authors conclude that, in keeping with prior reports from this trial, avelumab and axitinib demonstrates consistent progression-free survival benefits compared to suntinib across IMDC risk groups though overall survival data remain immature.
Presented by: John B. Haanen, MD, PhD, Division of Molecular Oncology & Immunology, Netherlands Cancer Institute (NKI), Amsterdam
Written by: Christopher J.D. Wallis, Urologic Oncology Fellow, Vanderbilt University Medical Center Contact: @WallisCJD on Twitter at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Virtual Annual Meeting #ASCO21, June, 4-8, 2021


