(UroToday.com) At the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting held in Chicago and virtually, the poster session focused on Kidney and Bladder cancers on Saturday afternoon included a presentation from Dr. Tianxin Lin examining novel neoadjuvant treatment approaches for patients with localized muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).
Currently, for those who are eligible, cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to radical cystectomy is the standard of care for patients with localized MIBC. However, despite this multimodality treatment approach, disease relapse and cancer-related mortality are common. Thus, there is a need to improve this treatment paradigm. The authors, therefore, sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tislelizumab combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin as neoadjuvant therapy for patients with clinical T2-T4aN0M0 (cT2-T4aN0M0) MIBC.
To do so, they performed a multicenter, open-label, single arm phase II study which enrolled patients eligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy (ChiCTR2000037670). Eligible patients received tislelizumab 200 mg on day 1, cisplatin 70 mg/m2 on day 2, and gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 of every 21 days cycle for four cycles. Patients then underwent radical cystectomy (RC) within 6 weeks after last dose of cycle four.
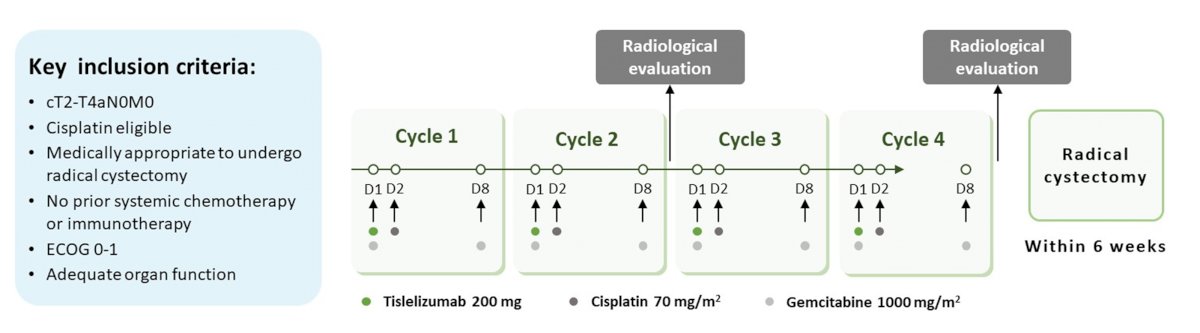
The primary endpoint was pathologic complete response (pCR, pT0N0M0) while secondary endpoints were pathologic downstaging (≤pT1N0M0), event free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS), and safety.
In this single-arm, phase II study, the authors used a Simon two-stage design: if more than 5 patients achieved pCR in the first stage (n = 22), the study would proceed to the second stage and enroll 33 additional patients. At the completion of the second stage, if more than 18 of 55 patients achieved pCR, the study would have been deemed to have met the primary endpoint.
In this analysis, the author report results of the first-stage of this trial with 23 eligible patients enrolled as of October 2021. Among these 23 patients, 18 had completed neoadjuvant therapy. The median age was 62 (48-72) years and 8 (44.4%) patients had PD-L1 positive tumors. Among the 18 who had completed neoadjuvant therapy, 17 patients underwent RC and one declined RC. In this subset of patients, pre-operative staging was cT2 in 12 cT2, cT3 in 3, and cT4a in 2.
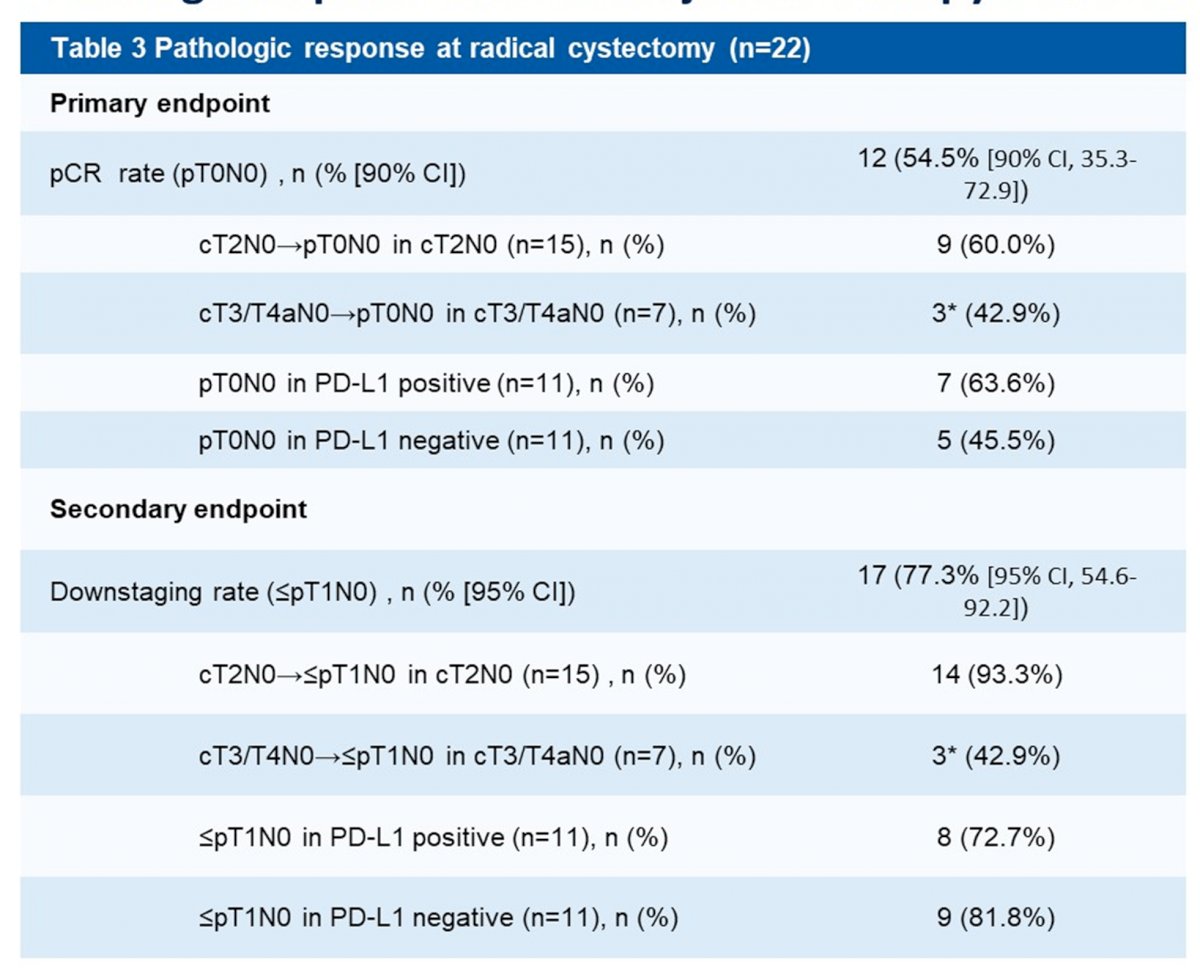
At the data cut off, among the 22 evaluable patients who had undergone radical cystectomy, 12 (54.5% [90% CI, 35.3-72.9]) patients achieved pCR and 17 (77.3% [95% CI 54.6-92.2]) achieved pathologic downstaging. There were no significant differences seen in terms of pCR (63.6% vs. 45.5%) or downstaging (72.7% vs. 81.8%) rates between patients with PD-L1 positive versus PD-L1 negative tumors.
Among the 18 patients who completed neoadjuvant therapy, patients were able to receive 71/72 cycles of tislelizumab, 68/72 cycles of cisplatin, and 135/144 cycles of gemcitabine therapy. The rate of dose reduction (all due to AEs) of cisplatin and gemcitabine therapy was 25.0% (17/68 cycles) and 23.7% (32/135 cycles), respectively. The relative dose intensity of tislelizumab, cisplatin, and gemcitabine were 93.6%, 84.5%, and 85.9%, respectively.
The most common neoadjuvant therapy related adverse events (AEs) of any grade were hematologic toxicities (94.4%), nausea (72.2%), vomiting (61.1%), decreased appetite (55.6%), fatigue (27.8%), pruritus (22.2%) and ALT/AST increase (22.2%). Grade ≥3 neoadjuvant therapy related AEs included neutropenia (n = 6), thrombocytopenia (n = 4), anemia (n = 2) and decreased lymphocyte count (n = 1). Eight patients experienced grade 1-2 immune related AEs, including pruritus (n = 4), rash (n = 2), ALT/AST increased (n = 4), GGT increased (n = 2), CPK increased (n = 1), hyperthyroidism (n = 1), hypothyroidism (n = 1) though there were no high grade immune related adverse events.
The authors, therefore, concluded that neoadjuvant tislelizumab combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin showed promising anti-tumor activity with high pCR and good tolerability in patients with MIBC. Based on these favourable results from the first-stage, this trial is continuing enrollment.
Presented by: Tianxin Lin, Department of Urology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China


