(UroToday.com) The 2022 ASCO annual meeting featured a session on kidney and bladder cancer, including a presentation by Dr. Neil Shah discussing healthcare resource utilization and costs for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) receiving first-line pembrolizumab + axitinib or ipilimumab + nivolumab. Approval of immuno-oncology agents has changed the treatment paradigm for metastatic RCC patients. While immuno-oncology-based therapies have demonstrated improved survival, these can be associated with considerable healthcare resource utilization and costs necessitating their examination in real-world practice. The objectives of this study were to examine (i) baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of mRCC patients initiating pembrolizumab + axitinib or ipilimumab + nivolumab in the first-line setting, and (ii) all-cause healthcare resource utilization and costs among these patients.
This retrospective claims analysis utilizing Optum Research Database included adult patients with a metastatic RCC diagnosis from July 2017 to August 2020 that received pembrolizumab + axitinib or ipilimumab + nivolumab as first-line of therapy from January 2018 to May 2020 (first claim=index date). All eligible patients required continuous enrollment for a minimum of 6-months prior and 3-months post the index date unless death occurred. All-cause healthcare resource utilization counts and associated costs were examined during the first 90 days (first-line of therapy-90) and the entire first-line of therapy duration and reported as overall and per-patient-per-month estimates.
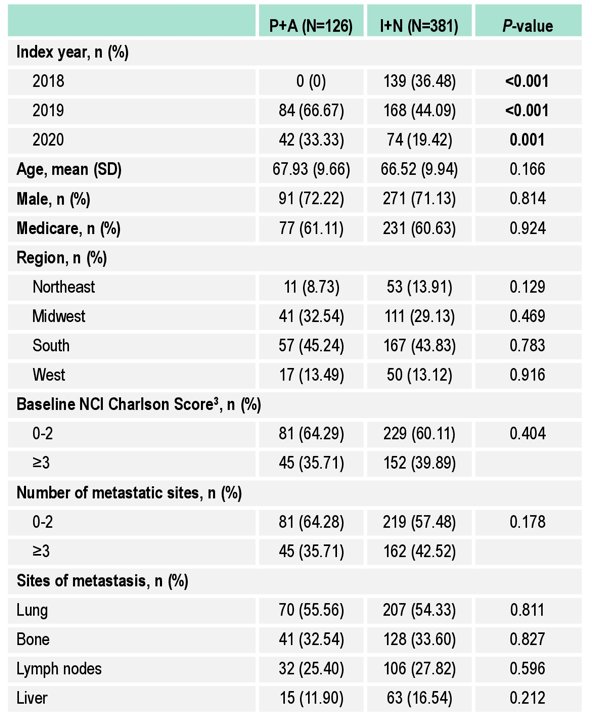
The study identified 507 patients (pembrolizumab + axitinib = 126, ipilimumab + nivolumab = 381). The average age of the entire cohort was 67 years, 71% were male, the mean NCI Charlson score was 2.4, and lung (55%) and bone (33%) were the most common metastatic sites. The mean time from metastatic RCC diagnosis to index date was 97 (SD 172) days. Patients with pembrolizumab + axitinib and ipilimumab + nivolumab had similar baseline characteristics:
The total percentage of patients with ambulatory visits was similar for pembrolizumab + axitinib and ipilimumab + nivolumab for first-line of therapy-90 and entire first-line of therapy (99.2% vs. 100.0%, p=0.082 for both). During first-line of therapy-90, there was a lower percentage of patients on pembrolizumab + axitinib with ER visits and inpatient stay compared to ipilimumab + nivolumab (34% vs. 48%, p=0.008; 19% vs. 38%, p<0.001, respectively). There was also an observed a shorter mean inpatient stay for pembrolizumab + axitinib vs. ipilimumab + nivolumab during first-line of therapy-90 (1.9 (SD 6.5) vs. 5.6 (SD 13.24) days, p<0.001). Similarly, pembrolizumab + axitinib had lower mean per-patient-per-month ambulatory visits, inpatient stay, and ICU stay during both first-line of therapy-90 and entire first-line of therapy. In addition, mean per-patient-per-month total (medical + pharmacy) and mean per-patient-per-month medical costs were lower for pembrolizumab + axitinib compared to ipilimumab + nivolumab, but mean per-patient-per-month pharmacy costs were higher for pembrolizumab + axitinib for both first-line of therapy-90 and entire first-line of therapy:

Dr. Shah concluded his presentation by discussing healthcare resource utilization and costs for patients with mRCC receiving first-line pembrolizumab + axitinib or ipilimumab + nivolumab with the following take-home messages:
- This is one of the first studies to comprehensively assess healthcare resource utilization counts and associated costs in newer immuno-oncology and TKI-based therapies of metastatic RCC patients in the real-world setting
- This study noted significantly higher healthcare resource utilization with ipilimumab + nivolumab including higher mean per-patient-per-month ambulatory visits, inpatient stays, and ICU stays compared to pembrolizumab + axitinib
- Although pembrolizumab + axitinib had higher mean per-patient-per-month pharmacy costs, the total medical plus pharmacy costs were significantly lower compared to ipilimumab + nivolumab
Presented by: Neil J. Shah, MBBS, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Co-Authors: Reshma Shinde, Kristin Moore, Amy Sainski-Nguyen, Lisa Le, Feng Cao, Rui Song, Puneet Singhal, Robert J. Motzer
Affiliations: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, Optum, Eden Prairie, MN
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Fri, June 3 – Mon, June 7, 2022.


