As background, sacituzumab govitecan (SG) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) with accelerated FDA approval for advanced urothelial carcinoma (aUC) which is refractory to platinum-based chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI).
At this time, Enfortumab Vedotin (EV) is the most commonly used ADC. Unfortunately, SG activity and efficacy in patients previously treated with EV and biomarkers of response to SG in that setting are not well described. As their targets are slightly different, the authors hypothesized that SG would continue to have antitumor activity despite prior EV utilization.
The authors used the established UNITE Urothelial Cancer Network to Investigate Therapeutic Experiences) is a large multi-institutional retrospective cohort study of patients with aUC treated with novel agents and encompasses 16 centers and 592 patients to-date. Their initial experience with using EV was published in 2021.1
Patients treated with SG monotherapy who also had next-generation sequencing (NGS) were identified in the retrospective UNITE study.
They only included patients who had at least one SG cycle. They focused on observed response rate as their primary outcome. But, in patients who had NGS testing, they also evaluated potential biomarkers of response – including tumor mutational burden, somatic gene alterations (alt) in ≥ 10% of pts, and presence of ≥1 DNA damage response (DDR) mutations.
Secondary analyses included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) from SG start.
They identified 90 patients treated with SG at 9 US sites. Of these, 78 had available NGS data.
Demographics can be found below:
Of note, 60 (67%) had primary bladder tumor, and 67 (74%) ECOG PS 0/1. NGS testing included multiple modalities, but the predominant was Foundation Medicine.
Most (n=84, 93%) received SG after EV. This was also a heavily pretreated population with 33 (37%) had ≥4 prior therapies for advanced UC.
Looking at primary outcome, the ORR with SG was 23% (15/66) – despite prior EV therapy and other prior lines of therapy. Of these patients, 24% ORR was seen in patients with prior response (CR/PR/SD) to EV and 14% ORR in patients who had progressive disease on EV. Interesting response rates were higher if the patients also responded to EV.
Median follow-up from SG start was 8.7 mos, PFS and OS were 3.5 mos and 6.0 mos.
In pts with NGS, ORRs to SG were higher in MTAP altered pts (50% vs 19%; p = 0.05).
On univariate analysis, low neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), high Hgb, no prior smoking history, < 3 prior therapies, as well as BRCA2 and DDR alts were associated with longer OS (p<0.05 for all).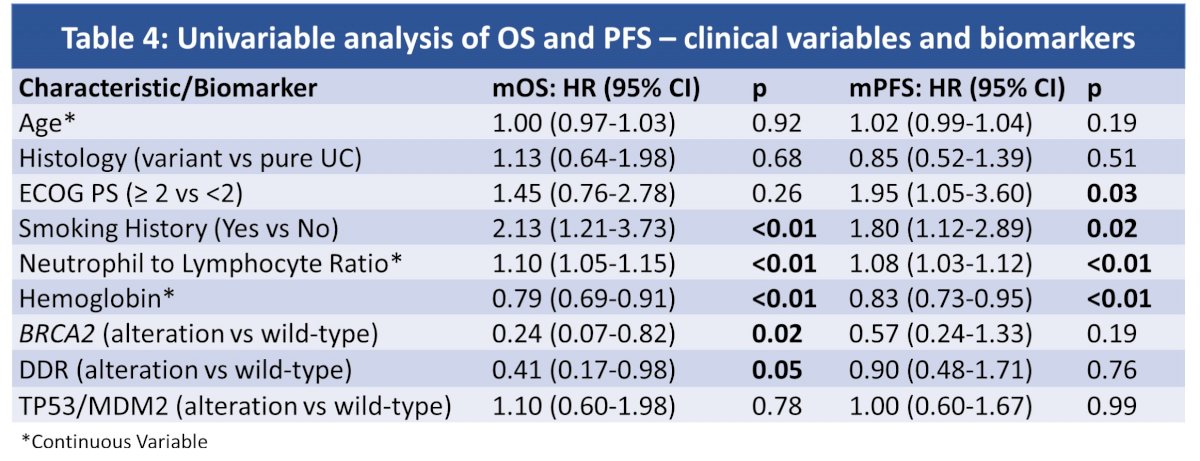
On multivariate analysis, patients with alterations in either TP53 or MDM2 had longer OS.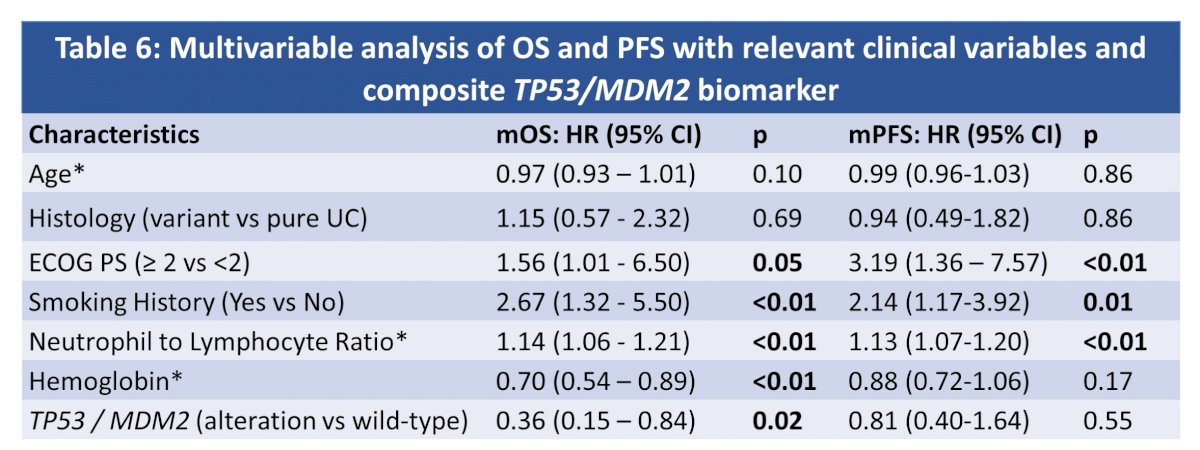
Some key takeaways from this study:
- SG continues to have good efficacy following EV therapy, comparable to Phase 2 trial data following post-platinum or ICI therapy alone. EV therapy does not seem to generate a resistant to SG therapy.
- Some potential important biomarkers of response may help predict response to SG that can be used to select therapy
- Including TP53/MDM2 alterations
- Clinical biomarkers, including smoking history, NLR, hemoglobin and ECOG status
Written by: Thenappan (Thenu) Chandrasekar, MD – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, University of California, Davis, @tchandra_uromd @UCDavisUrology on Twitter during the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Fri, June 2 – Tues, June 6, 2023.
Reference:

