(UroToday.com) The 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting held in Chicago, IL between June 2nd and June 6th was host to a kidney and bladder cancers poster session. Dr. David Braun presented the results of genomic and transcriptomic analysis from the HCRN GU16-260 study evaluating determinants of resistance to nivolumab monotherapy.
HCRN GU16-260 was a phase II trial that evaluated single agent nivolumab in patients with treatment-naïve, advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), with salvage nivolumab plus ipilimumab reserved for those with evidence of progressive disease or stable disease as best respose at 48 weeks treatment. The study design is summarized below:
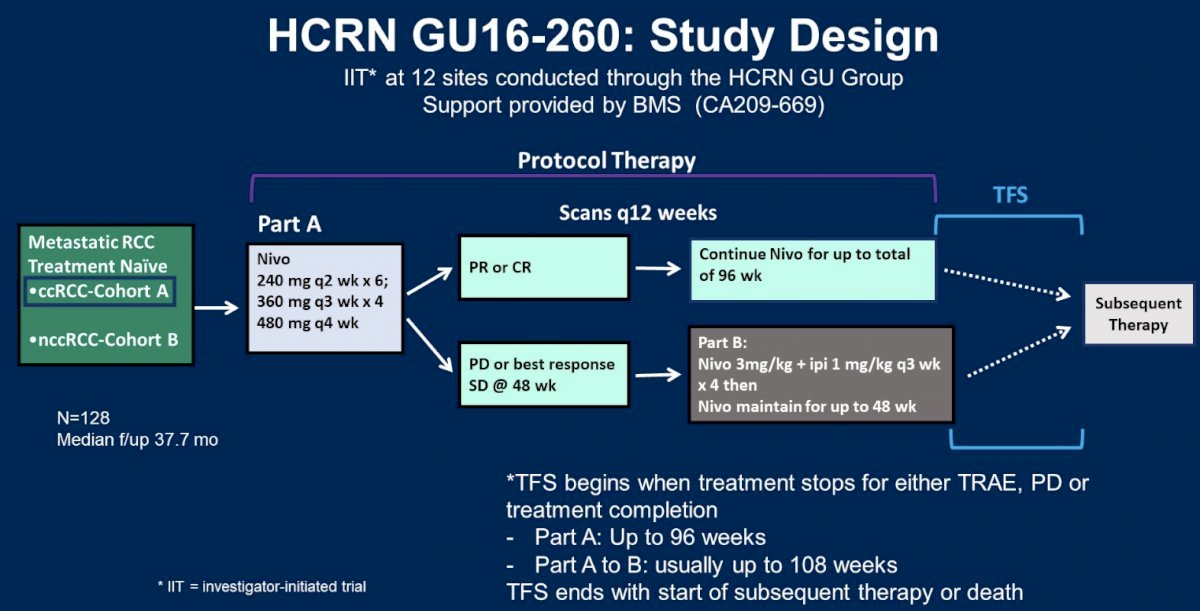
This treatment approach demonstrated an overall objective response rate (ORR) of 36% in patients with clear cell RCC (cohort A), with corresponding rates of 58%, 26% and 33% in IMDC favorable, intermediate, and poor-risk patients, respectively. Significantly, treatment-free survival rates with this approach ranged between 8 and 13 months. 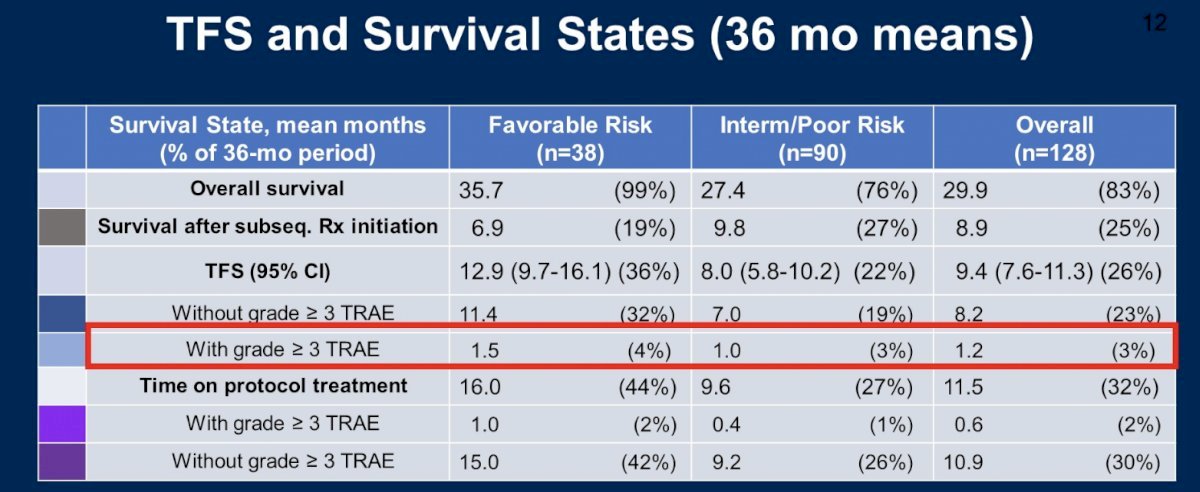
In this exploratory analysis, Dr. Braun and colleagues sought to characterize the tumor-immune microenvironmental determinants of effective anti-tumor immunity with nivolumab monotherapy using collected patient tumor samples from the HCRN GU16-260 trial.
The authors performed whole exome sequencing (WES) on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue collected within a year prior to the initiation of nivolumab monotherapy. For single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq), tumor biopsy tissue samples were obtained prior to and/or at the time of development of resistance to nivolumab monotherapy. RCC patients of all histologic subtypes were included. Gene expression signatures discovered through scRNA-seq were used to subsequently interrogate previously published bulk transcriptomic data of nivolumab in the treatment-refractory setting.
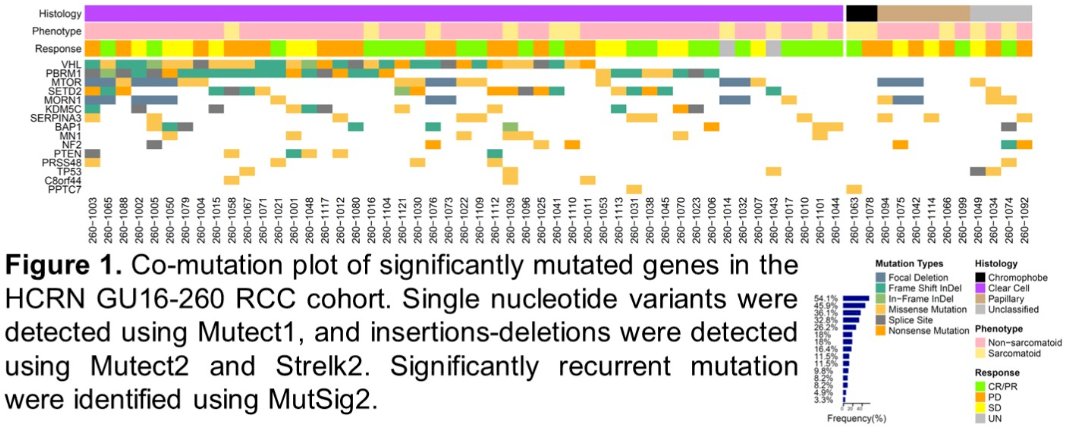
WES analysis of 96 tumors identified recurrent focal amplification within chromosome 11q13 (amp11q13). This was observed in:
- 6/18 (33.3%) tumor samples of patients with progressive disease (PD)
- 0/20 (0%) tumor samples of patients with complete (CR) or partial response (PR) (p for comparison=0.005)
Significantly, amp11q13 was associated with worse progression free survival (PFS; p = 0.008) and overall survival (OS; p = 0.010).
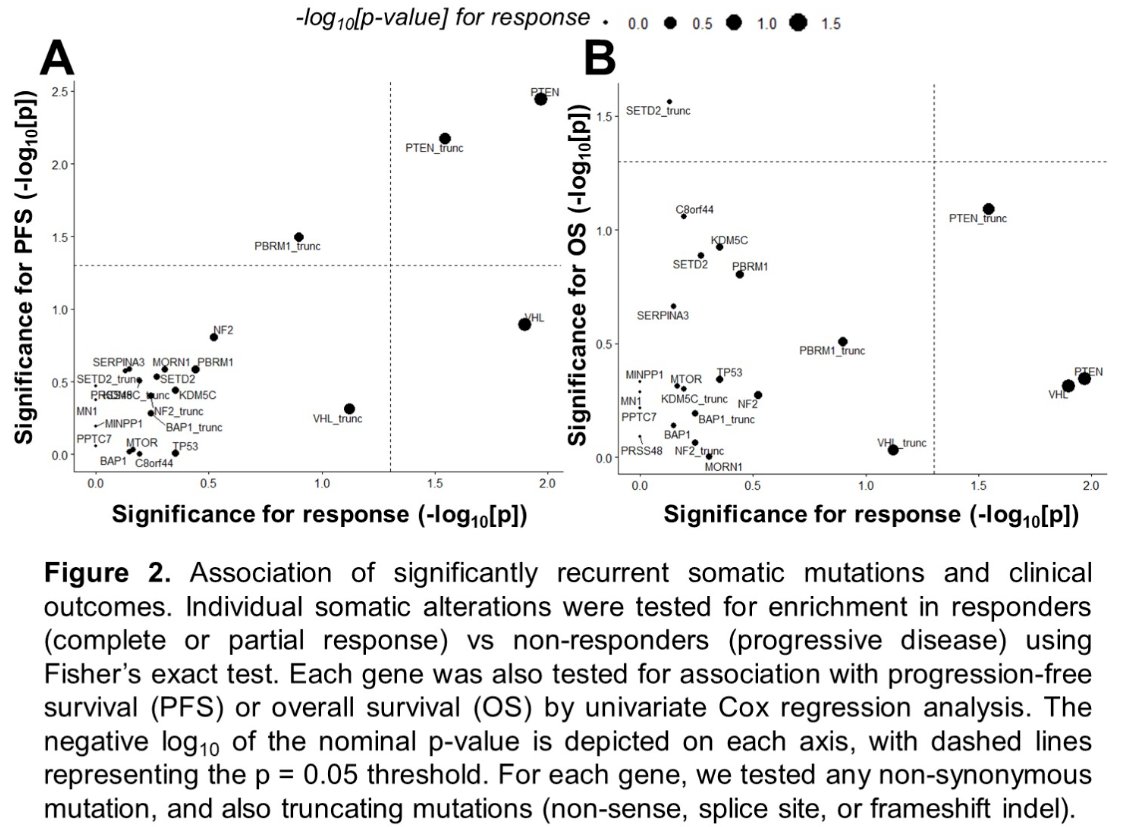
scRNA-seq was performed on tumors from 17 patients across 7 trial sites:
- 8 with baseline only tissue
- 7 with tissue post-progression
- 2 with paired baseline and post-progression samples

Trajectory inference analysis of tumor-infiltrating T cells revealed a bifurcating structure, starting with naïve T cells and ending either in terminally exhausted CD8+ T cells or SLAMF7+ CD8+ T cells. Interestingly, the SLAMF7+ T cell population expressed high levels of cytotoxic genes (including GZMA, GZMB, GNLY) and markers of tissue residency (ZNF683/HOBIT and ITGAE/CD103).

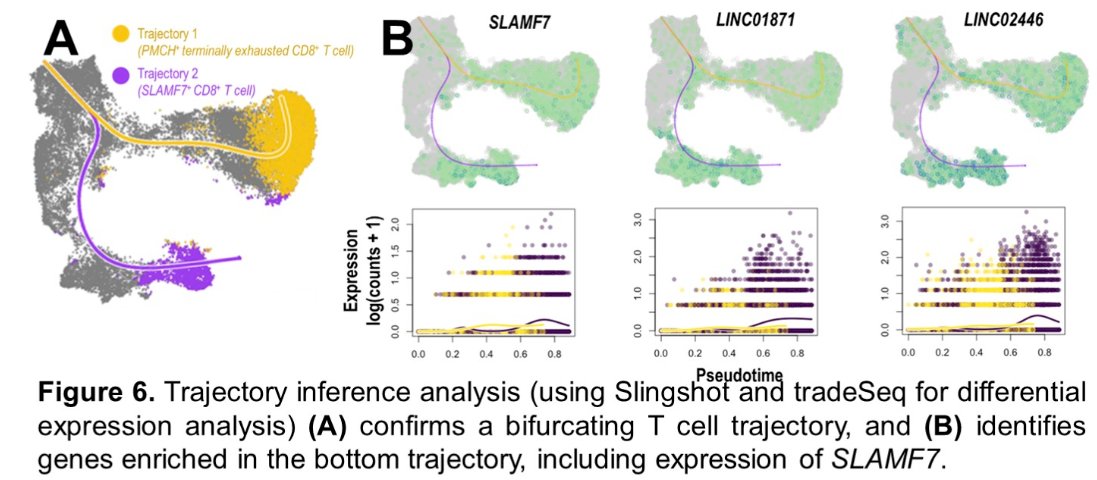
Of the 14 patients with at least 100 sequenced tumor-infiltrating T cells, the presence of a higher percentage of SLAMF7+ CD8+ T cells (relative to total T cells) was associated with primary resistance to nivolumab. The mean percentage of SLAMF7+ CD8+ T cells, relative to total T cells was as follows:
- PD (n=4): 33%
- SD (n=4): 9%
- CR/PR (n=6): 2.2% (p for CR/PR versus PD comparison=0.019)
Of 172 pre-treatment tumors from the nivolumab arms of the CheckMate-009/010/025 trials that were analyzed by bulk RNA-seq, a signature score derived using genes expressed in the SLAMF7+ CD8+ T cell trajectory branch was enriched in patients with PD, compared to those with CR/PR as best response (p=0.032).
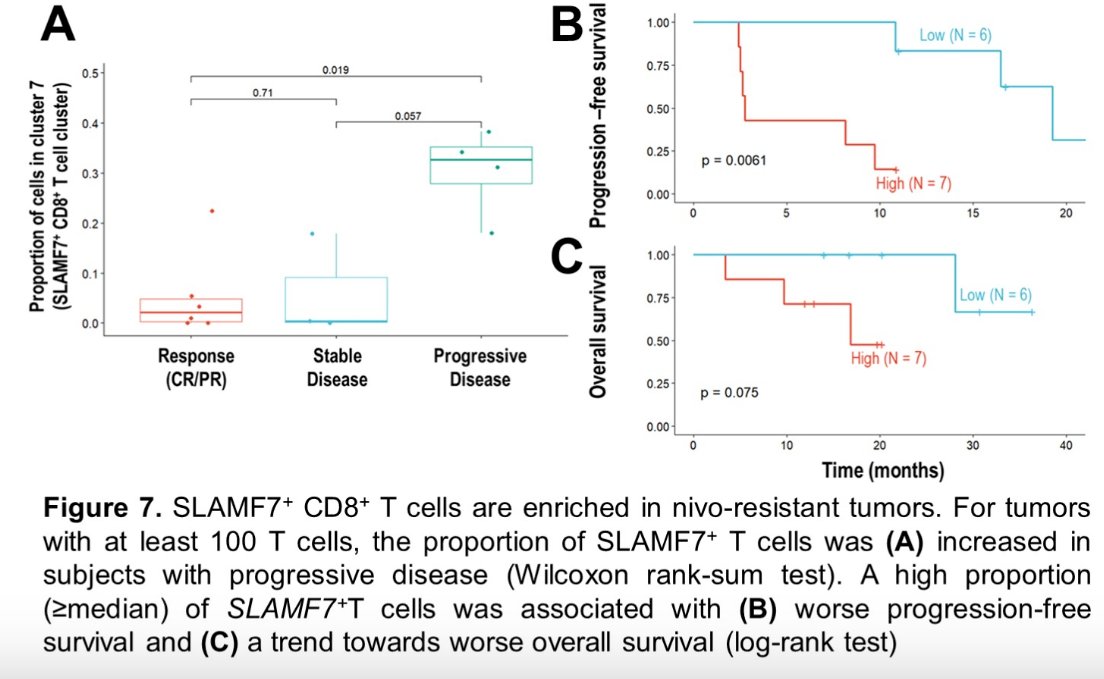
Dr. Braun and colleagues concluded that bulk genomic and single-cell transcriptomic analyses of patients with treatment-naïve, advanced RCC from the HCRN GU16-260 phase II trial revealed somatic alterations (amp11q13) and infiltrating T cell populations (SLAMF7+ CD8+) associated with resistance to frontline nivolumab monotherapy. Additional independent and functional validation studies are in currently in progress.
Presented by: David A. Braun, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine (Medical Oncology), Department of Medicine, Yale University, New Haven, CT
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Fri, June 2 – Tues, June 6, 2023.


