(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting featured an oral abstract session on kidney cancer, and a presentation by Dr. Brian Rini discussing biomarker analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 study of pembrolizumab + axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Previously, pembrolizumab + axitinib established an improved overall survival, progression-free survival, and objective response rate over sunitinib in first-line advanced RCC in KEYNOTE-426.1-2
Moreover, the 18-gene T-cell inflamed gene expression profile is associated with response to pembrolizumab in multiple tumor types, including clear cell RCC. Molecular subtypes that are predictive of survival have also been identified in phase 3 studies of advanced RCC: IMmotion151 for atezolizumab + bevacizumab versus sunitinib and JAVELIN Renal 101 for avelumab + axitinib versus sunitinib. At the 2024 ASCO annual meeting, Dr. Rini and colleagues presented exploratory biomarker results including RNAseq, WES, and PD-L1.
Patients in KEYNOTE-426 with treatment-naive advanced renal cell carcinoma were randomly assigned 1:1 to pembrolizumab + axitinib or sunitinib: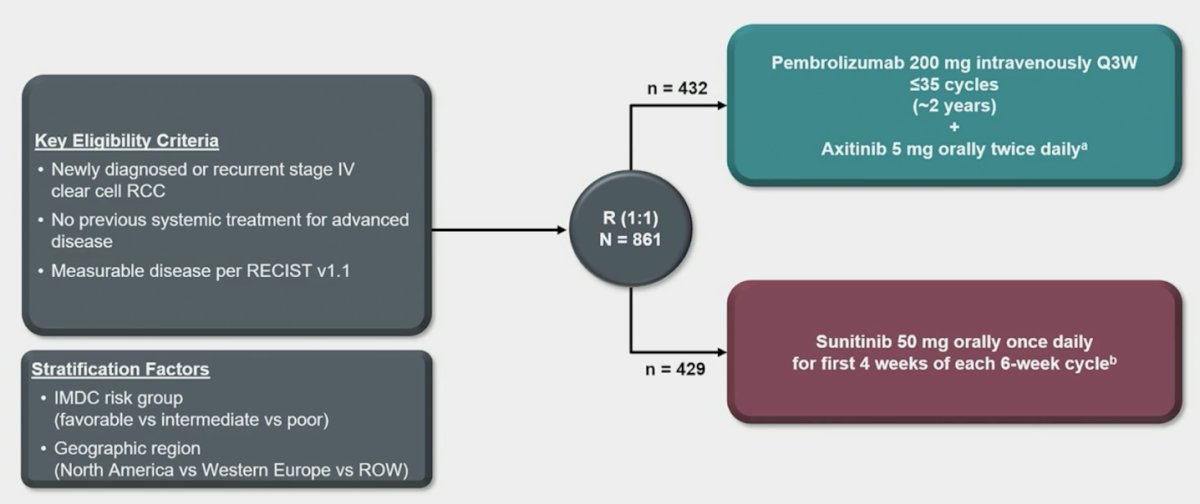
Association between T-cell–inflamed gene signature, angiogenesis gene signature (RNAseq), and PD-L1 CPS with clinical outcomes were tested at prespecified α = 0.05. Other RNA signatures [3] and molecular subtypes, based on clustering identified from IMmotion151 [4], were tested at prespecified α = 0.10 after multiplicity adjustment. DNA mutations (VHL, PBRM1, SETD2, and BAP1) by WES were tested at prespecified α = 0.10 after multiplicity adjustment.
Among 861 patients, 369 (pembrolizumab + axitinib) and 361 (sunitinib) had archival samples for RNAseq; 347 (pembrolizumab + axitinib) and 351 (sunitinib) had WES samples: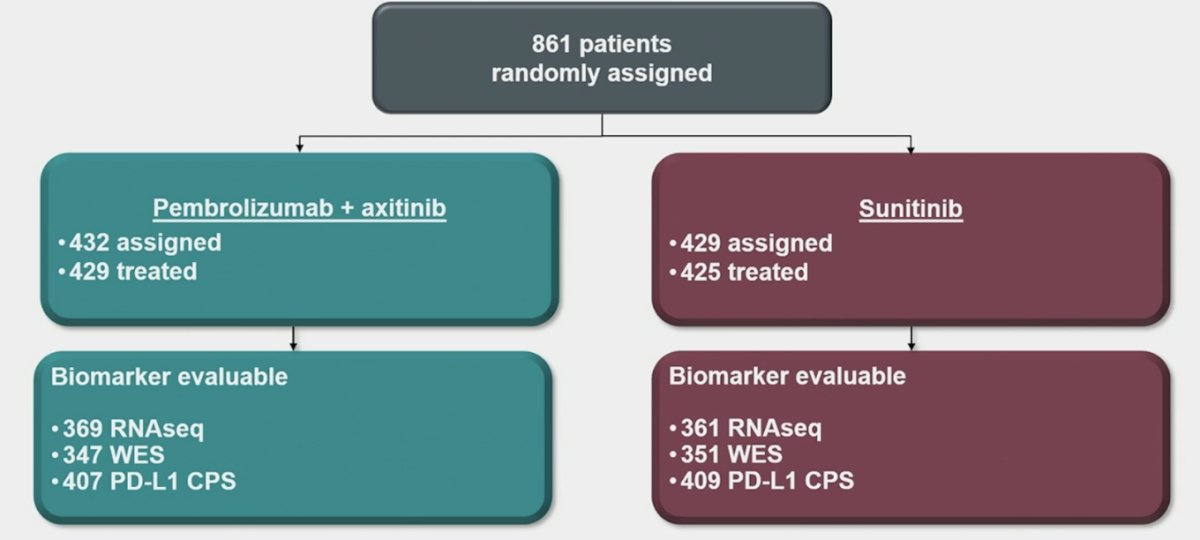
The baseline characteristics stratified by available RNAseq and WES are as follows: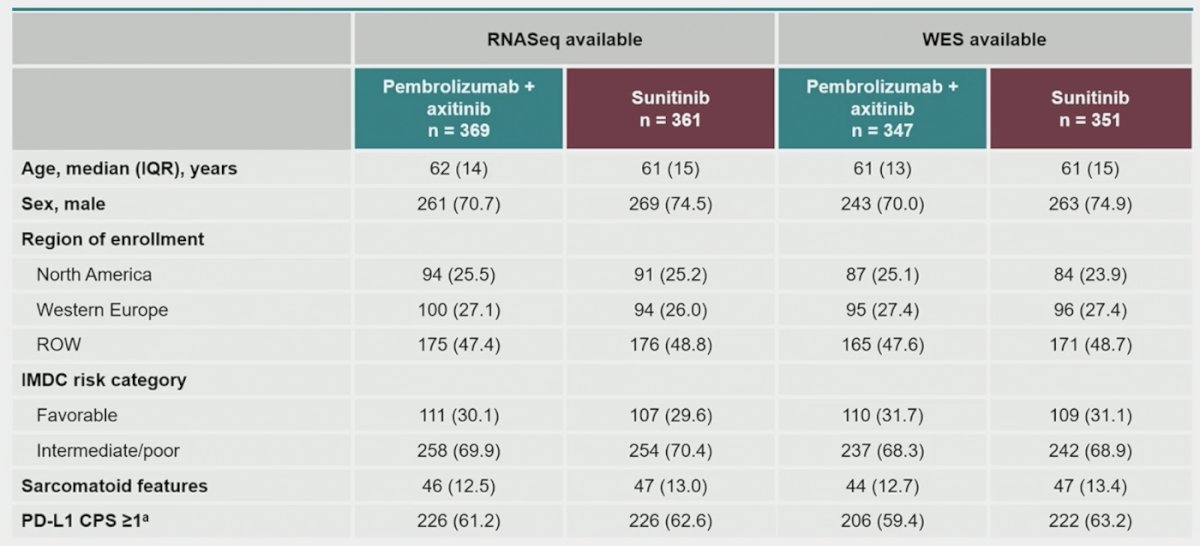
PD-L1 CPS was negatively associated with overall survival (p = 0.013) for sunitinib. There was a strong positive association of T-cell–inflamed gene signature with overall survival (p = 0.003), progression-free survival (p < 0.0001), and objective response rate (p < 0.0001) for pembrolizumab + axitinib. Angiogenesis was positively associated with overall survival (p = 0.013) for pembrolizumab + axitinib, and there was a strong positive association with overall survival (p < 0.0001), progression-free survival (p < 0.001), and objective response rate (p = 0.002) for sunitinib: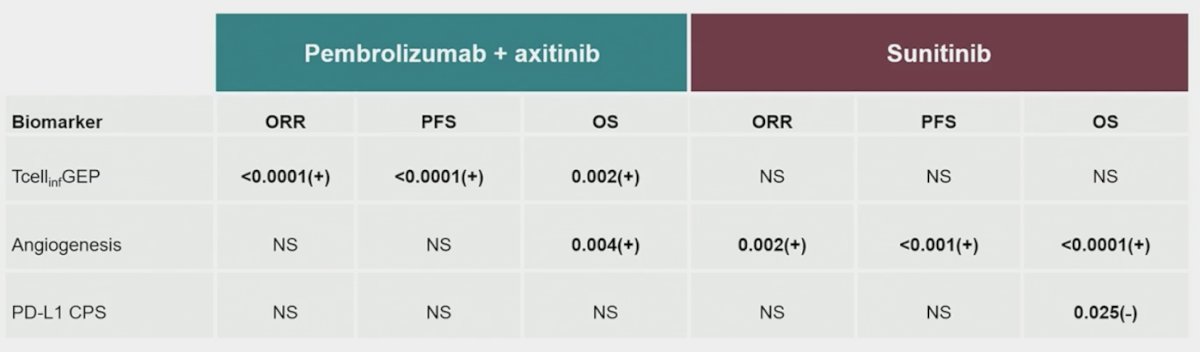
The comparison of T-cell inflamed gene expression profile and clinical outcomes is highlighted below: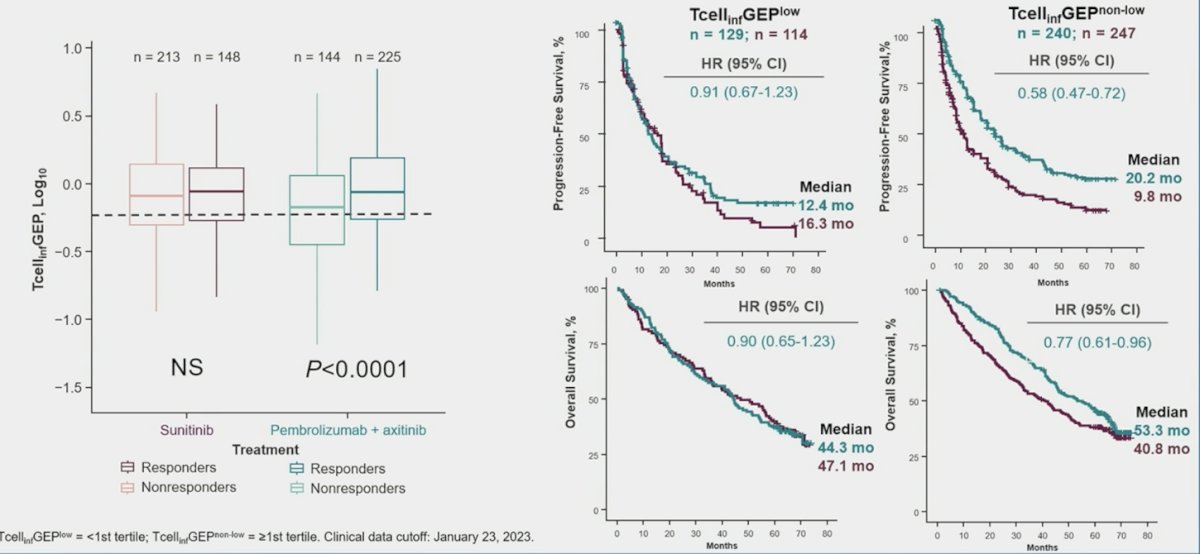
For other RNA signatures, positive association with monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells was found for progression-free survival (p = 0.018) and objective response rate (p = 0.093) with pembrolizumab + axitinib. For sunitinib, positive association was found with hypoxia (overall survival, p = 0.034; objective response rate, p = 0.071) and negative associations with MYC (overall survival, p < 0.001; progression-free survival, p = 0.012) and proliferation (overall survival, p = 0.002):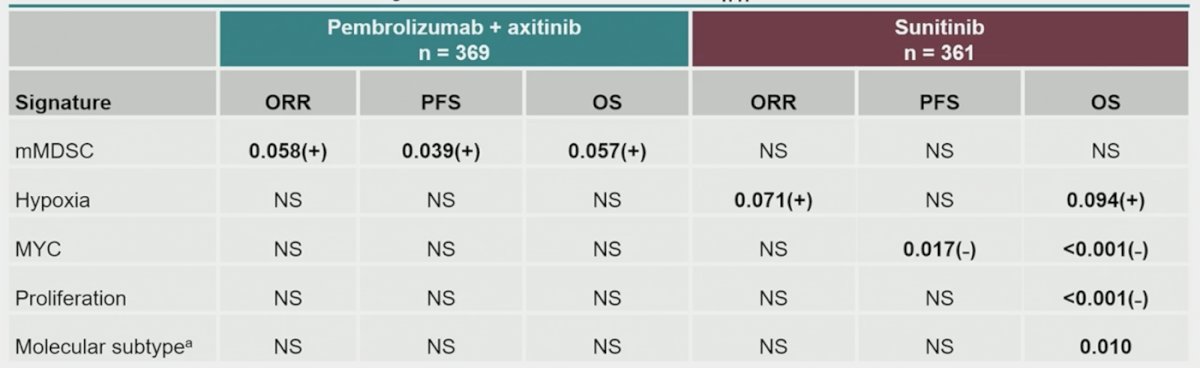
Across all molecular clusters, objective response rate favored pembrolizumab + axitinib over sunitinib, with the highest pembrolizumab + axitinib objective response rate in the immune/proliferative cluster: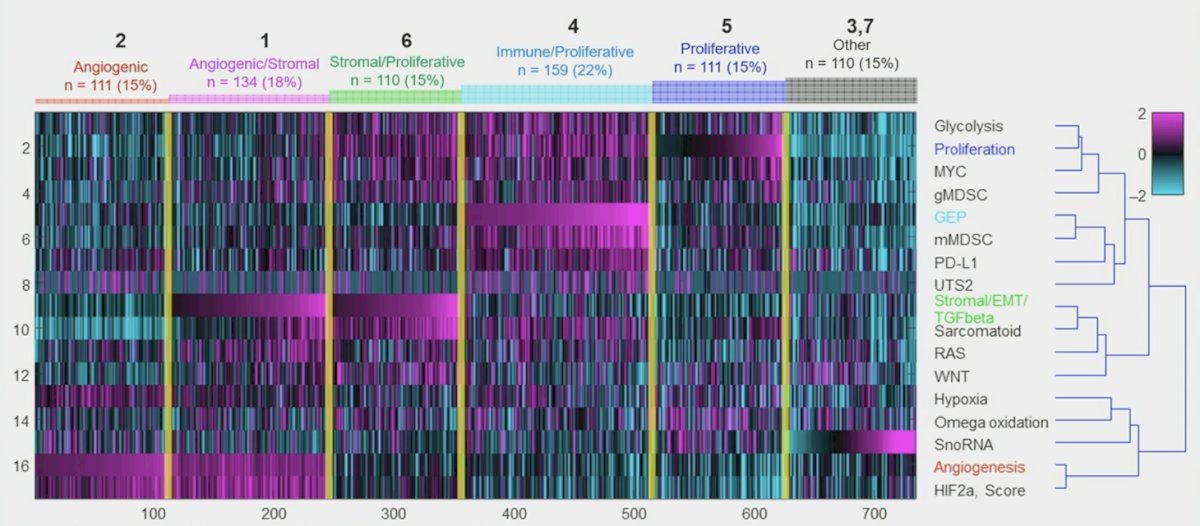
By WES, PBRM1 mutation had positive association with objective response rate (p = 0.004) and progression-free survival (p = 0.079) for pembrolizumab + axitinib. For sunitinib, positive associations were observed with overall survival for VHL (p = 0.073) and PBRM1 (p = 0.001) mutations, and a negative one observed for BAP1 mutation (p = 0.046). Pembrolizumab + axitinib improved objective response rate over sunitinib regardless of mutational status.
Dr. Rini concluded his presentation discussing biomarker analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 study of pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma with the following take-home messages:
- In this exploratory analysis of KEYNOTE-426, higher T-cell inflamed gene expression profile values were positively associated with clinical outcomes for pembrolizumab + axitinib, and angiogenesis had a positive association with clinical outcomes for sunitinib
- PD-L1 CPS was not associated with clinical outcomes for pembrolizumab + axitinib
- Pembrolizumab + axitinib showed improved objective response rate versus sunitinib across molecular subtypes
- Within the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm, the objective response rate was highest in the immune/proliferative subtype, and within the sunitinib arm, the objective response rate was highest in the angiogenic subtype
- Additional correlative data and further prospective clinical investigation are needed for biomarker-directed treatment
Presented by: Brian I. Rini, MD, Chief of Clinical Trials, Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center, Nashville, TN
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Fri, May 31 – Tues, June 4, 2024.
References:
- Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019;380(12):1116-1127.
- Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulieres D, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): Extended follow-up from a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020 Dec;21(12):1563-1573.
- Cristescu R, Nebozhyn M, Zhang C, et al. Transcriptomic determinants of response to pembrolizumab monotherapy across solid tumor types. Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 14;28(8):1680-1689.
- Motzer RJ, Banchereau R, Hamidi H, et al. Molecular subsets in renal cancer determine outcome to checkpoint and angiogenesis blockade. Cancer Cell. 2020 Dec 14;38(6):803-817.


