(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting featured a session on prostate cancer, and a presentation by Dr. Johann De Bono discussing baseline ctDNA analyses and associations with outcomes in taxane-naive patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 versus change of androgen receptor pathway inhibitor in PSMAfore.
Initially presented as ESMO 2023, 177Lu-PSMA-617 prolonged radiographic progression-free survival versus androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change in taxane-naive patients with mCRPC. In this exploratory analysis presented at ASCO 2024, associations between baseline circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and outcomes were assessed.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to 177Lu-PSMA-617 (7.4 GBq every 6 weeks; 6 cycles) or androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change (abiraterone or enzalutamide). Patients known to have actionable mutations (ie. BRCA) were excluded. The primary endpoint was radiographic progression-free survival and the trial design is as follows:
Baseline plasma ctDNA was analyzed using a customized 585-gene sequencing assay, and the ctDNA fraction was assessed in all samples passing quality control. The design for the exploratory ctDNA analysis was as follows: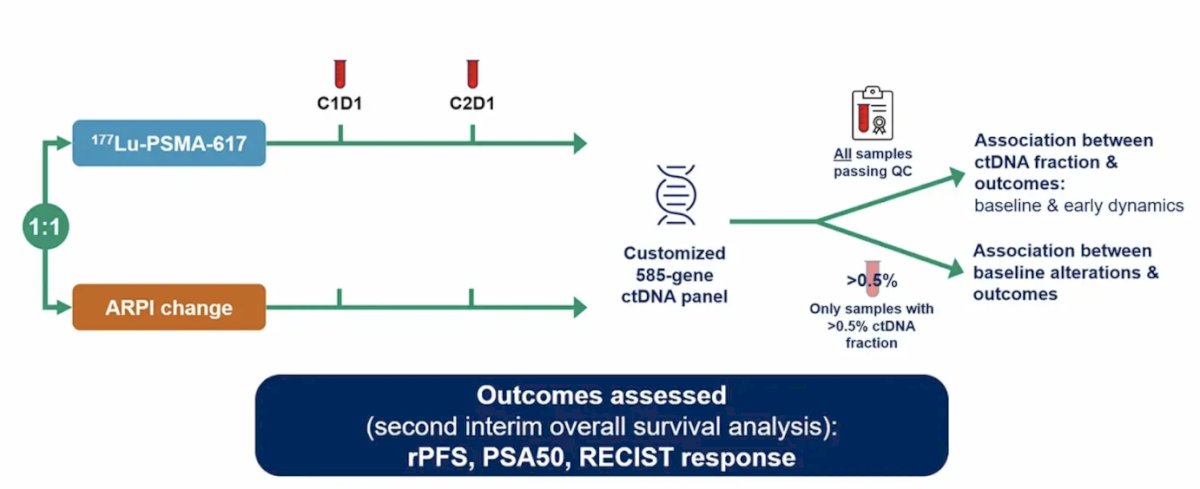
Alterations in key prostate cancer drivers (prevalent in >10% of participants) were assessed in samples with ctDNA fraction >0.5%. Univariate Cox regression (reference: androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change) was used to assess the association of ctDNA fraction or alterations with radiographic progression-free survival, PSA response (≥50% decline; PSA50), and RECIST response at the June 21, 2023 data cutoff.
Among 360 samples from 468 patients, 255 passed quality control and 156 had ctDNA fraction >0.5% (median 5.85%; range 0–85). Median ctDNA fraction was consistent with profiles of patients with mCRPC at 1st and 2nd line: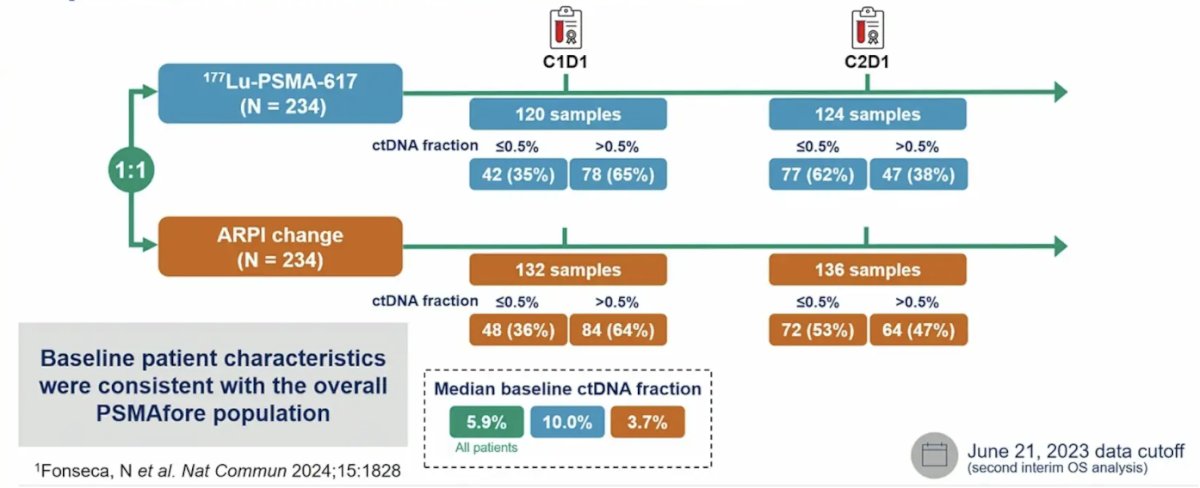
Higher baseline ctDNA fraction was associated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival regardless of treatment received:
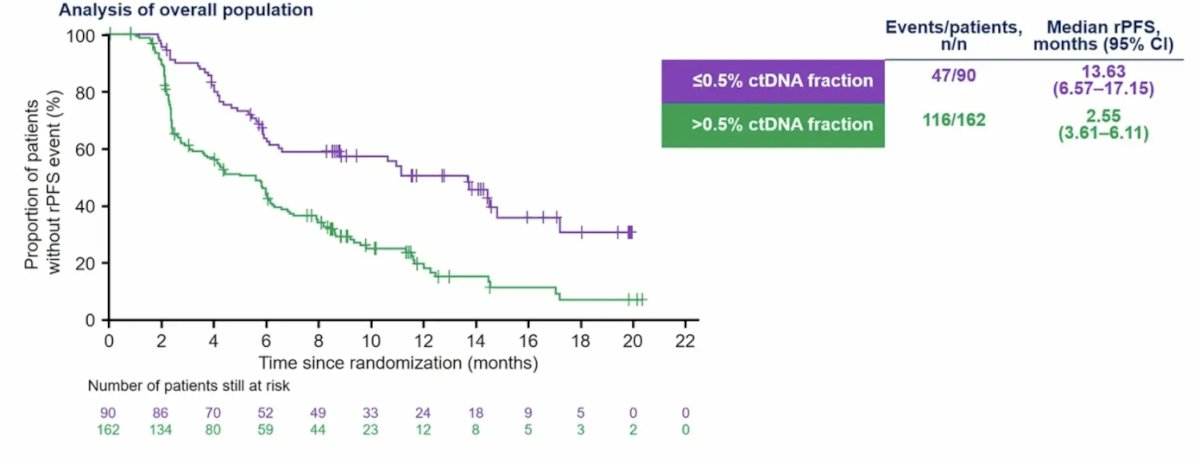
Additionally, 177Lu-PSMA-617 prolonged radiographic progression-free survival compared with androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change regardless of baseline ctDNA fraction:
Moreover, ctDNA fraction >0.5% was also associated with worse RECIST response and PSA50 response: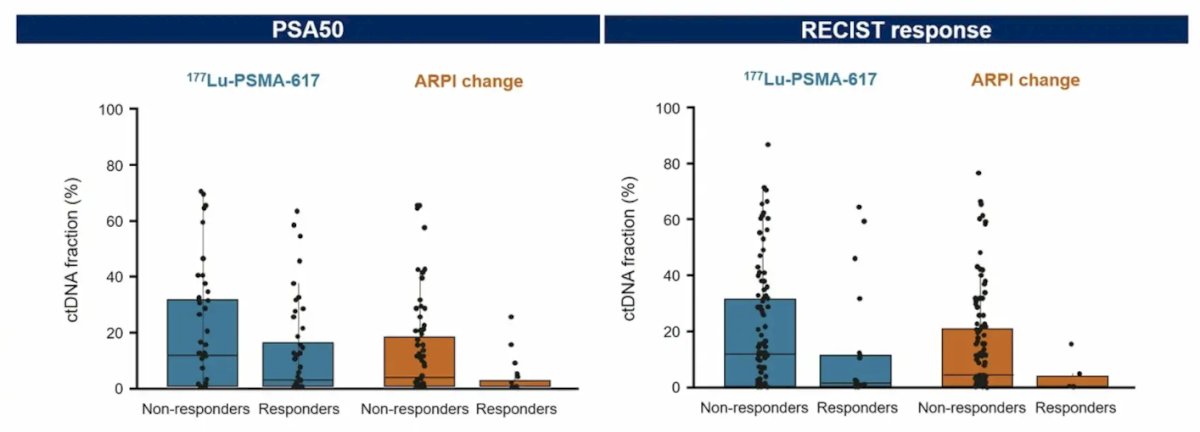
Interestingly, early ctDNA clearance was associated with longer radiographic progression-free survival:
Among the genomic analysis in the targeted sequencing panel (585 genes), 18 genes were selected for genomic features prevalent in >10% of patients. These included known prognostic biomarkers that may influence radiation sensitivity: AR amplification, chromosome 8q and MYC amplifications, TP53 deleterious alterations, and PI3K pathway alterations. The presence of 8q amplifications was associated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival: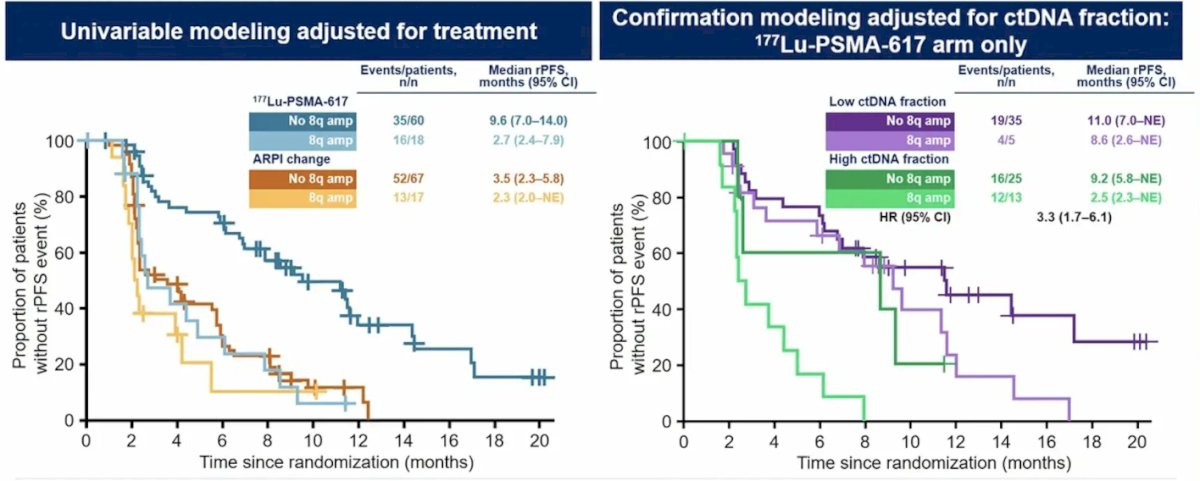
Additionally, the presence of AR amplification was also associated with radiographic progression-free survival: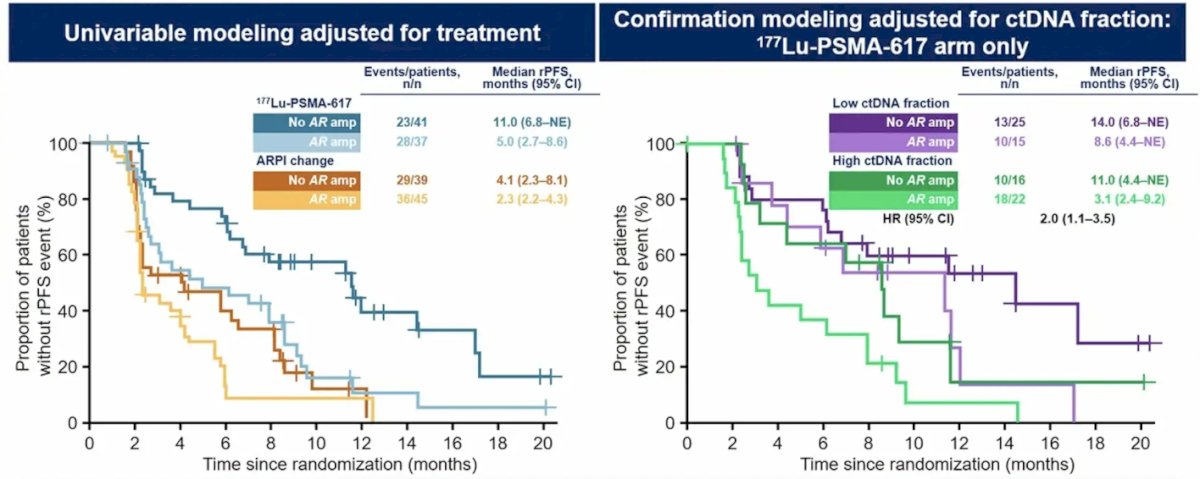
Finally, the presence of TP53 deleterious alterations was associated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival: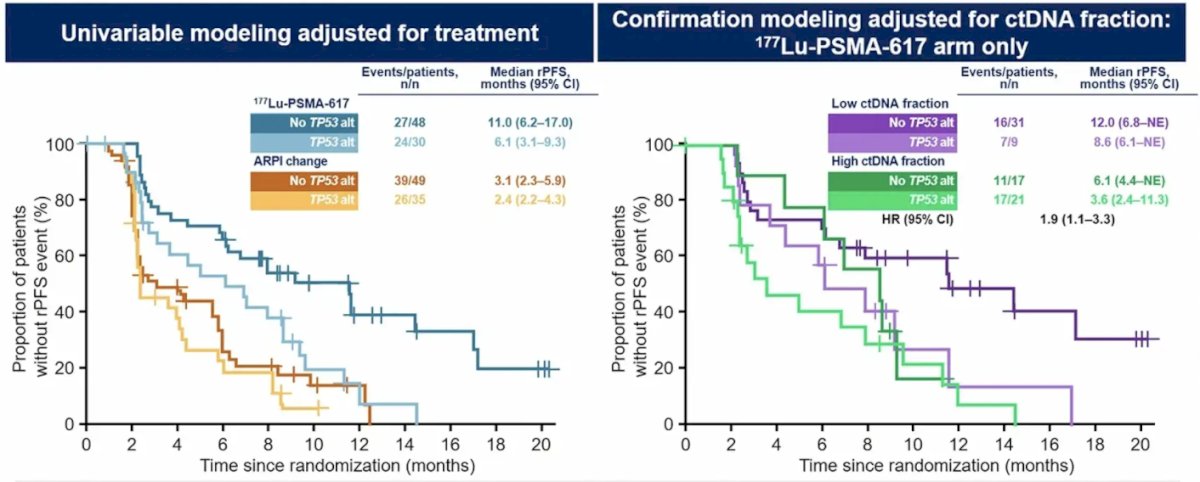
Dr. De Bono concluded his presentation discussing baseline ctDNA analyses and associations with outcomes in taxane-naive patients with mCRPC treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 versus change of androgen receptor pathway inhibitor in PSMAfore with the following take-home messages:
- Higher baseline ctDNA fraction was associated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival across both treatment arms
- Patients receiving 177Lu-PSMA-617 had longer progression-free survival compared with androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change, regardless of baseline ctDNA fraction
- Early ctDNA fraction dynamics informs on radiographic progression-free survival and tumor response
- 8q amplifications, AR amplifications, and TP53 deleterious alterations are prognostic biomarkers that were associated with shorter radiographic progression-free survival and decreased tumor response in the 177Lu-PSMA-617 arm
Presented by: Johann S. De Bono, MD, MSc, PhD, FRCP, FMedSci, Professor, The Institute of Cancer Research and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, Fri, May 31 – Tues, June 4, 2024.


