The first set of papers focused on neoadjuvant immunotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin-based combinations is associated with improved disease-free survival and overall survival in MIBC. In contrast, non-cisplatin treatment in the perioperative setting has no proven benefit. Dr. Grivas discussed two studies that evaluated immunotherapy in the neoadjuvant setting for MIBC with an emphasis on biomarker analyses in these cohorts.
PURE-01 was an open-label, single-arm, Phase II study that evaluated neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in men with MIBC with variant histologies.1 Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates were significantly higher in patients with non-predominant variant histology (53%) than pure urothelial carcinoma (39%) or predominant variant histology (16%). Notably, in most histologic subtypes, high tumor mutational burden (TMB) and PD-L1 expression were both associated with higher rates of pCR.
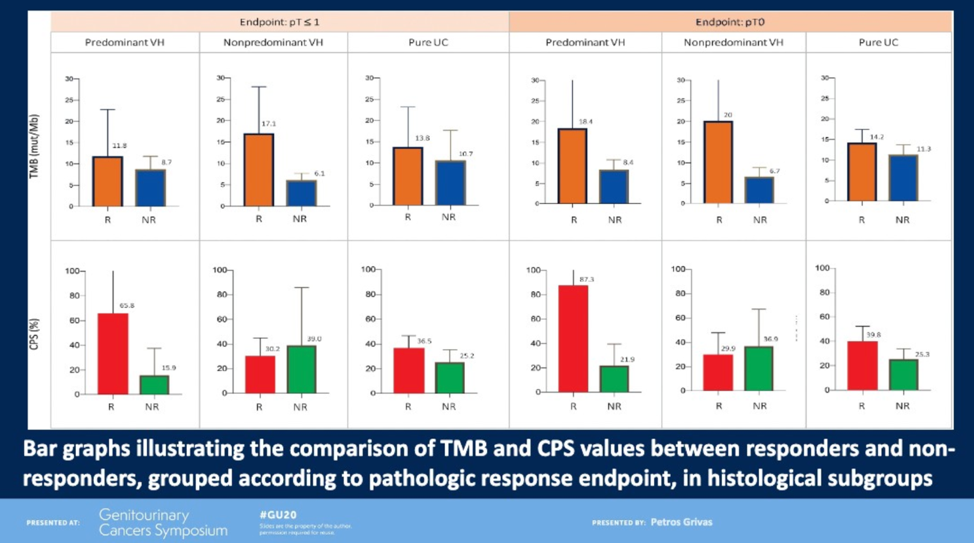
ABACUS was a single-arm Phase II study that evaluated neoadjuvant atezolizumab in men with MIBC.2 Twenty-nine percent of patients experienced a pCR. Interestingly, in this cohort, neither TMB nor PD-L1 were significantly associated with pCR, whereas CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was (p = 0.04).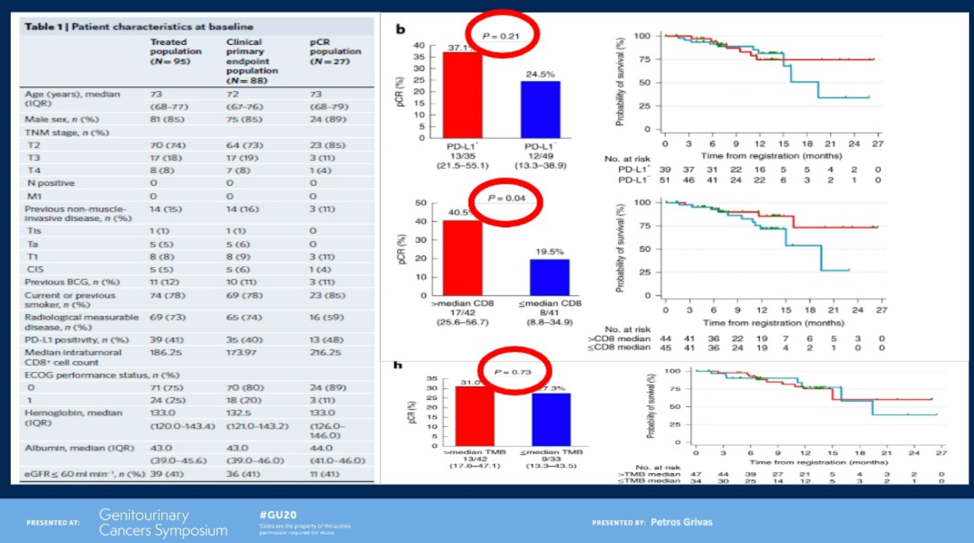
Dr. Grivas highlighted potential explanations for the discrepant biomarker results from these two studies including different patient populations (cisplatin-eligible versus cisplatin-ineligible, different proportion of variant histology), different clinical-stage, different therapy (anti-PD1 versus anti-PD-L1 and two versus three doses), different biomarker assays, and an unmeasured selection and confounding bias.
Next, Dr. Grivas discussed a paper that evaluated the efficacy of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis for early detection of metastatic relapse and monitoring of therapeutic efficacy in 68 patients with localized urothelial MIBC.3 The investigators collected cfDNA before and during neoadjuvant chemotherapy, after completion of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and after cystectomy. At all timepoints, undetectable circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) was associated with a significant improvement in relapse-free survival and overall survival. Additionally, undetectable ctDNA pre-cystectomy was associated with higher rates of pCR (79%) compared to 0% of patients with detectable ctDNA. Dr. Grivas cautioned that, while exciting, these results will need to be prospectively validated before being implemented into clinical practice for prognostication and decision making.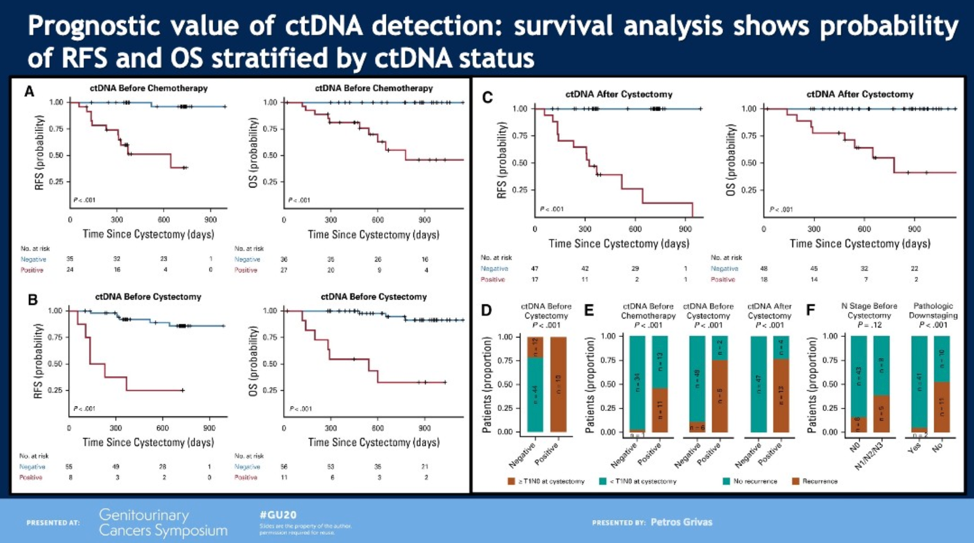
Erdafitinib is an FGFR inhibitor that was evaluated in an open-label Phase II study of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer (UC) with pre-specified FGFR alterations.4 All patients had received prior chemotherapy; prior immunotherapy was allowed. The primary endpoint was overall response rate, which was observed in 40% of patients (3% complete response; 37% partial response). Of note, 88% had progressed or relapsed after chemotherapy, 43% had received two or more lines of systemic therapy, and 79% had visceral metastases. Hyperphosphatemia was the most common adverse event, observed in 77% of patients. Other common adverse events included stomatitis, diarrhea, and dry mouth. Patients were analyzed by FGFR alteration status with 49% response rate in patients with FGFR3 mutations and 16% response rate in patients with FGFR2/3 fusions.
The final study discussed evaluated enfortumab vedotin in patients with advanced UC who had previously received platinum chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Of note, 90% had visceral disease, including 40% with liver involvement, and the median number of prior lines of therapy was three. In spite of this high-risk, heavily-pretreated cohort, the objective response rate was 44%. The swimmer plot demonstrates durable responses (>9 months) in a large subset of patients. All subgroups analyzed benefited, including those with liver involvement. Notable adverse events included peripheral sensory neuropathy (40%) and maculopapular rash (22%).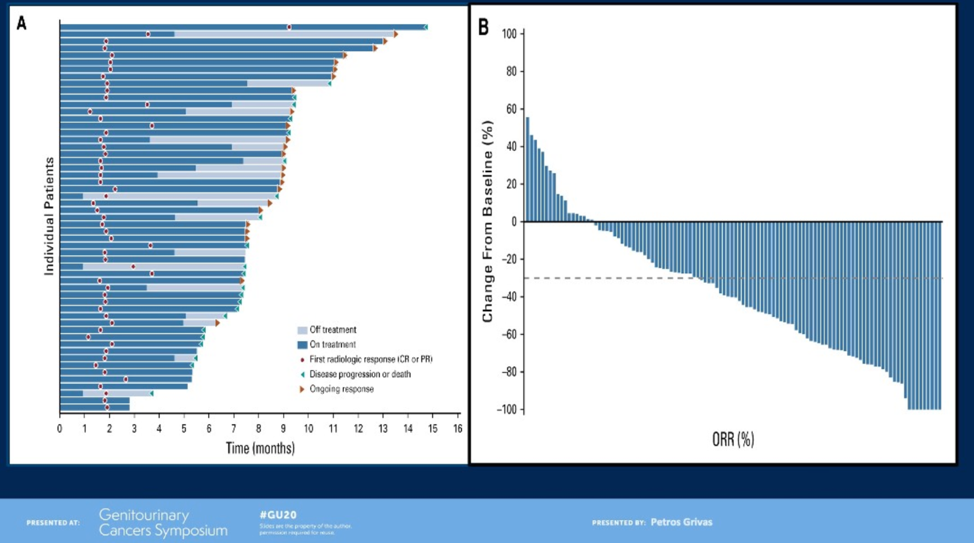
Dr. Grivas concluded with a treatment algorithm for UC incorporating the latest clinical data: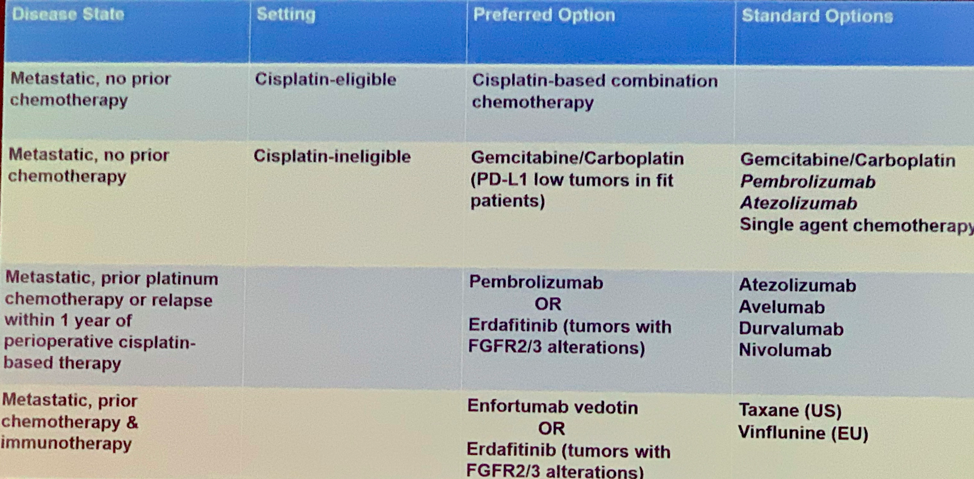
Presented by: Petros Grivas, MD, PhD, Medical Oncologist, Associate Professor, University of Washington School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle Washington
Written by: Jacob Berchuck, MD, Medical Oncology Fellow at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, Twitter: @jberchuck at the 2020 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium, ASCO GU #GU20, February 13-15, 2020, San Francisco, California
References:
1. Necchi, Andrea, Daniele Raggi, Andrea Gallina, Russell Madison, Maurizio Colecchia, Roberta Lucianò, Rodolfo Montironi et al. "Updated Results of PURE-01 with Preliminary Activity of Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab in Patients with Muscle-invasive Bladder Carcinoma with Variant Histologies." European urology (2019).
2. Powles, Thomas, Mark Kockx, Alejo Rodriguez-Vida, Ignacio Duran, Simon J. Crabb, Michiel S. Van Der Heijden, Bernadett Szabados et al. "Clinical efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial." Nature medicine 25, no. 11 (2019): 1706-1714.
3. Christensen, Emil, Karin Birkenkamp-Demtröder, Himanshu Sethi, Svetlana Shchegrova, Raheleh Salari, Iver Nordentoft, Hsin-Ta Wu et al. "Early detection of metastatic relapse and monitoring of therapeutic efficacy by ultra-deep sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma." Journal of Clinical Oncology 37, no. 18 (2019): 1547-1557.
4. Loriot, Yohann, Andrea Necchi, Se Hoon Park, Jesus Garcia-Donas, Robert Huddart, Earle Burgess, Mark Fleming et al. "Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma." New England Journal of Medicine 381, no. 4 (2019): 338-348.
5. Rosenberg, Jonathan E., Peter H. O’Donnell, Arjun V. Balar, Bradley A. McGregor, Elisabeth I. Heath, Evan Y. Yu, Matthew D. Galsky et al. "Pivotal trial of enfortumab vedotin in urothelial carcinoma after platinum and anti-programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy." Journal of Clinical Oncology 37, no. 29 (2019): 2592.


