(UroToday.com) The 2022 GU ASCO Annual meeting included a urothelial carcinoma session highlighting work from Dr. Amanda Young and colleagues presenting results of an exploratory analysis of the IMvigor-010 observation arm assessing molecular residual disease detection with a tissue comprehensive genomic profiling-informed personalized monitoring assay. There is compelling rationale that detection of molecular residual disease following curative therapy may identify patients at high risk of relapse requiring intensified adjuvant therapy. Combining molecular residual disease detection with comprehensive genomic profiling creates an opportunity to offer molecular residual disease-guided treatment with precision cancer therapeutics. At GU ASCO 2022, Dr. Young and investigators analyzed the observation arm of the IMvigor-010 study1 to understand the genomics of resected early stage bladder cancer and to validate comprehensive genomic profiling-informed personalized molecular residual disease detection in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).
Using the resected tumor, tissue comprehensive genomic profiling was performed retrospectively with a 300+ gene assay, followed by molecular residual disease detection using FoundationOne Tracker (F1T). Briefly, coding, synonymous, and non-coding variants were selected from tumor tissue sequencing using an optimized algorithm that filters out non-tumor derived variants (germline, clonal hematopoiesis derived, sequencing artifacts). Tumor-informed personalized multiplex PCR-next generation sequencing (Natera) assay was designed and used to detect and quantify variant allelic frequency (VAF) in ctDNA from 182 patients. ctDNA levels were reported in mean tumor molecules per mL of plasma. F1T, a tissue-informed personalized monitoring assay, was performed on plasma samples collected at a molecular residual disease time point a median of 11 weeks post-surgery.
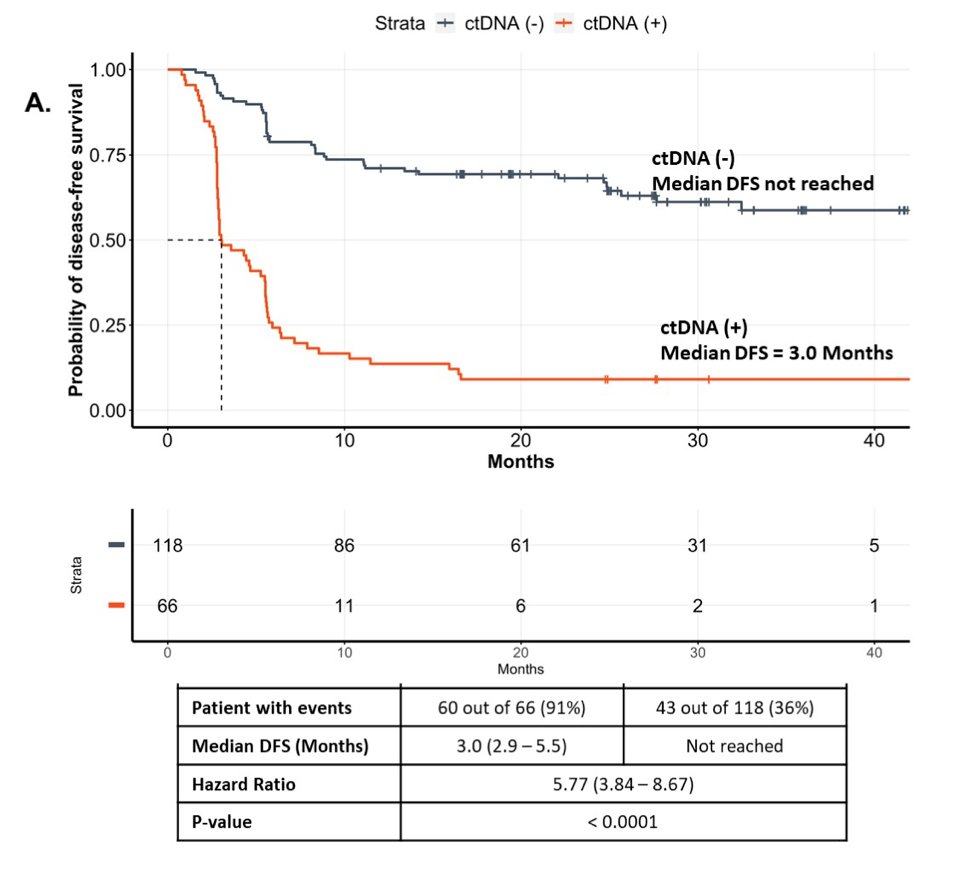
At the molecular residual disease time point, ctDNA was detected in 66/182 (36%) patients. Focusing on the 66 ctDNA-positive patients, 58 had relapsed (88% PPV) at time of analysis. Median disease-free survival (DFS) from randomization was 3 months (95% CI 2.9-5.5) in ctDNA-positive vs not reached in ctDNA-negative population (HR 5.77, 95% CI 3.84-8.67):
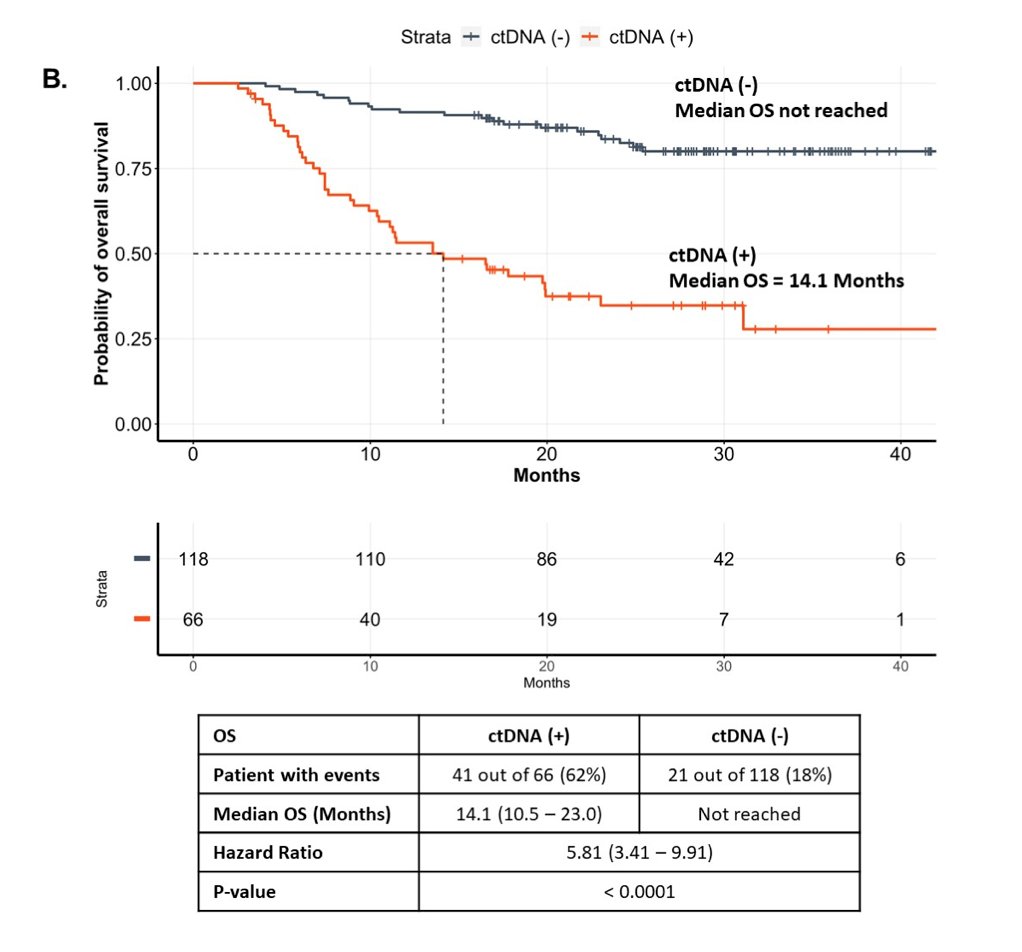
Median overall survival (OS) was 14.1 months (95% CI 10.5-23.0) in ctDNA-positive vs not reached in ctDNA-negative (HR 5.81, 95% CI 3.41-9.91):
Potentially actionable comprehensive genomic profiling findings included FGFR2/3 short variants (SVs) and fusions (13%), ERBB2 SVs and amplifications (13%), PIK3CA SVs (20%), CDKN2A SVs and losses (41%) and tumor mutational burden (TMB) ≥10 mutations/Mb (35%).
Dr. Young concluded her presentation with the following take home messages from this exploratory analysis of IMvigor-010:
- Tissue comprehensive genomic profiling-informed personalized molecular residual disease detection can detect low levels of residual ctDNA in patients with resected early stage bladder cancer, identifying a population with inferior DFS and OS
- This technologic approach, synergizing regulatory-grade actionable comprehensive genomic profiling with ctDNA-based molecular residual disease detection, creates new opportunities for precision adjuvant therapy across a range of high-risk cancer types.
Co-Authors: Halla Nimeiri, Russell Madison, Alexander D. Fine, Daniel Zollinger, Ole Gjoerup, Vasily N. Aushev, Hsin-Ta Wu, Alexey Aleshin, Nicole N. Davarpanah, Zoe Assaf, Sanjeev Mariathasan, Geoffrey R. Oxnard, Elise Renkonen, Thomas Powles, Priti Hegde
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, Thursday Feb 17 – Saturday Feb 19, 2022
References:
- Bellmunt J, Hussain M, Gschwend JE, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab versus observation in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor010): A multicentre, open-label, randomized, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021 Apr;22(4):525-537.


