(UroToday.com) On the second day of the American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Genitourinary Cancer Symposium 2023 focussing on urothelial cancer, the Poster Session B: Prostate Cancer and Urothelial Carcinoma included a presentation from Dr. James Catto highlighting an interim analysis of cohort 2 of the THOR-2 trial, assessing the efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG)-unresponsive, high-risk non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (HR-NMIBC) with FGFR3/2 alterations.
For patients that present with NMIBC who have carcinoma in situ (CIS), there is a high risk of disease progression. In more advanced bladder cancer FGFR inhibition has demonstrated benefits for those with FGFR3/2 alterations. Erdafitinib is an oral selective pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is approved for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer in adults with FGFR3/2 alterations who have progressed during or after at least 1 line of platinum-containing chemotherapy.
Thus, these authors postulated that patients with CIS who also harbor FGFR3/2 alterations and are unresponsive to first-line BCG may similarly benefit from FGFR inhibition. At the present time, there are relatively limited treatment options in this disease space. To test this hypothesis, they designed the THOR-2 trial (NCT04172675), a multi-cohort phase 2 study of erdafitinib in patients with HR-NMIBC. In this presentation, the authors report results from an exploratory cohort of patients with BCG-unresponsive CIS with FGFR3/2 alterations with or without papillary disease (Cohort 2).
In this phase 2 study, the authors included adult patients (age 18 years and older) with histologically confirmed, BCG-unresponsive HR-NMIBC with FGFR3/2 alterations (by local/central testing) who presented with CIS, with or without a papillary tumor and who refused or were not eligible for cystectomy. In this cohort, patients received continuous oral erdafitinib 6 mg once daily without up-titration in 28-day cycles (dose selected to improve tolerability while maintaining activity to prevent disease recurrence, for this population). Treatment with erdafitinib was discontinued if no complete response (CR) was observed within 3 months. Exploratory efficacy end points are CR rates at the Cycle 3 Day 1 (C3D1) disease evaluation and the Cycle 6 Day 1 (C6D1) disease evaluation; safety was a key secondary endpoint.

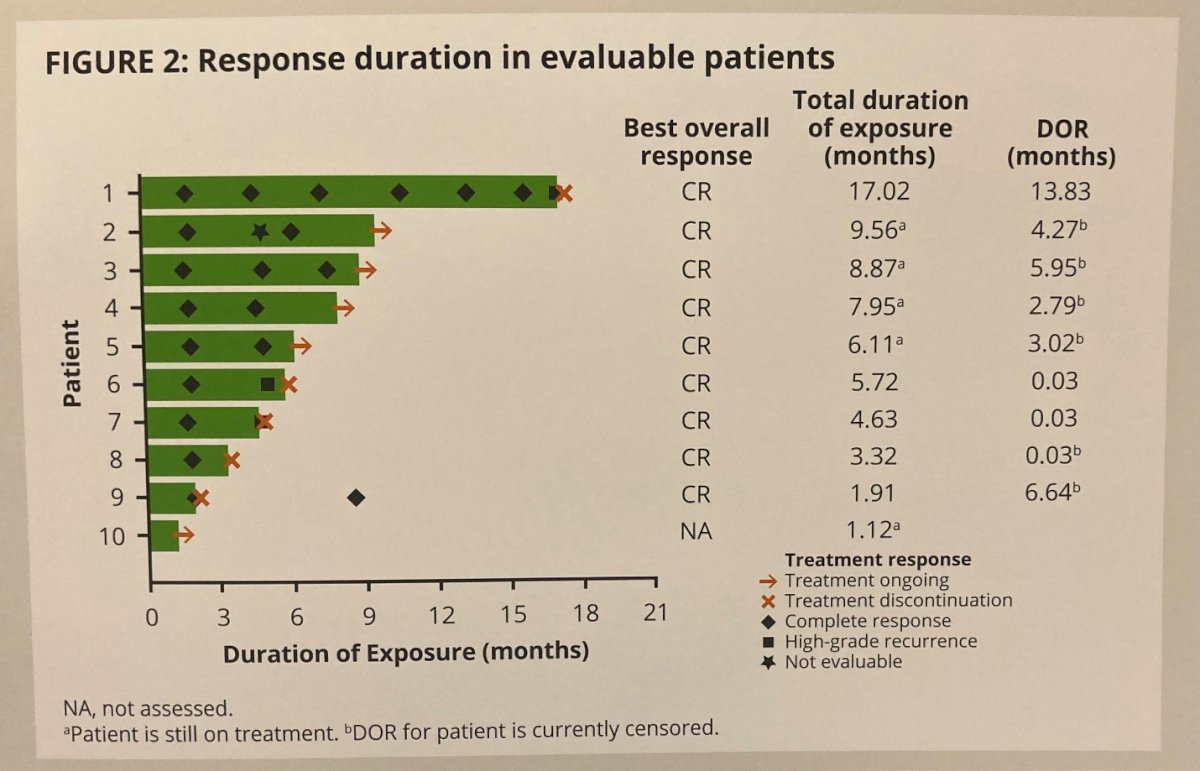
With a data cut-off of September 2022, 10 patients with a median age of 72 y [range 52-83] were treated with erdafitinib. Notably, 90% had CIS while one patients with Ta was mis-enrolled. Patients received erdafitinib for a median duration 5.9 months (range 1.1-17.0). Of 10 enrolled patients, the CR rates at first evaluation (C3D1) and second evaluation (C6D1) were 100% (9/9 evaluable patients) and 75% (6/8 evaluable patients), respectively. Over a median follow-up of 10 months, the median duration of response was 3.0 months.
The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were dry mouth (60%; n=6), hyperphosphatemia (50%; n=5), dysgeusia (50%; n=5), and diarrhea (50.0%; n=5). 1 patient (10%) had a grade 2 retinal detachment which led to treatment discontinuation and 1 patient (10%) had grade 1 subretinal fluid. By the end of follow-up, both of these adverse events were reported as resolved. Grade 3 or greater treatment-related TEAEs occurred in 3 patients (30%), and included dry mouth, stomatitis, nail disorder, onychomadesis, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, sepsis, and hypotension. One patient (10%) developed serious treatment-related TEAEs including dry mouth, hypotension, pneumonitis, acute kidney injury, and sepsis and 1 patient (10%) discontinued treatment due to a treatment-related TEAE. However, no treatment-related deaths were observed.
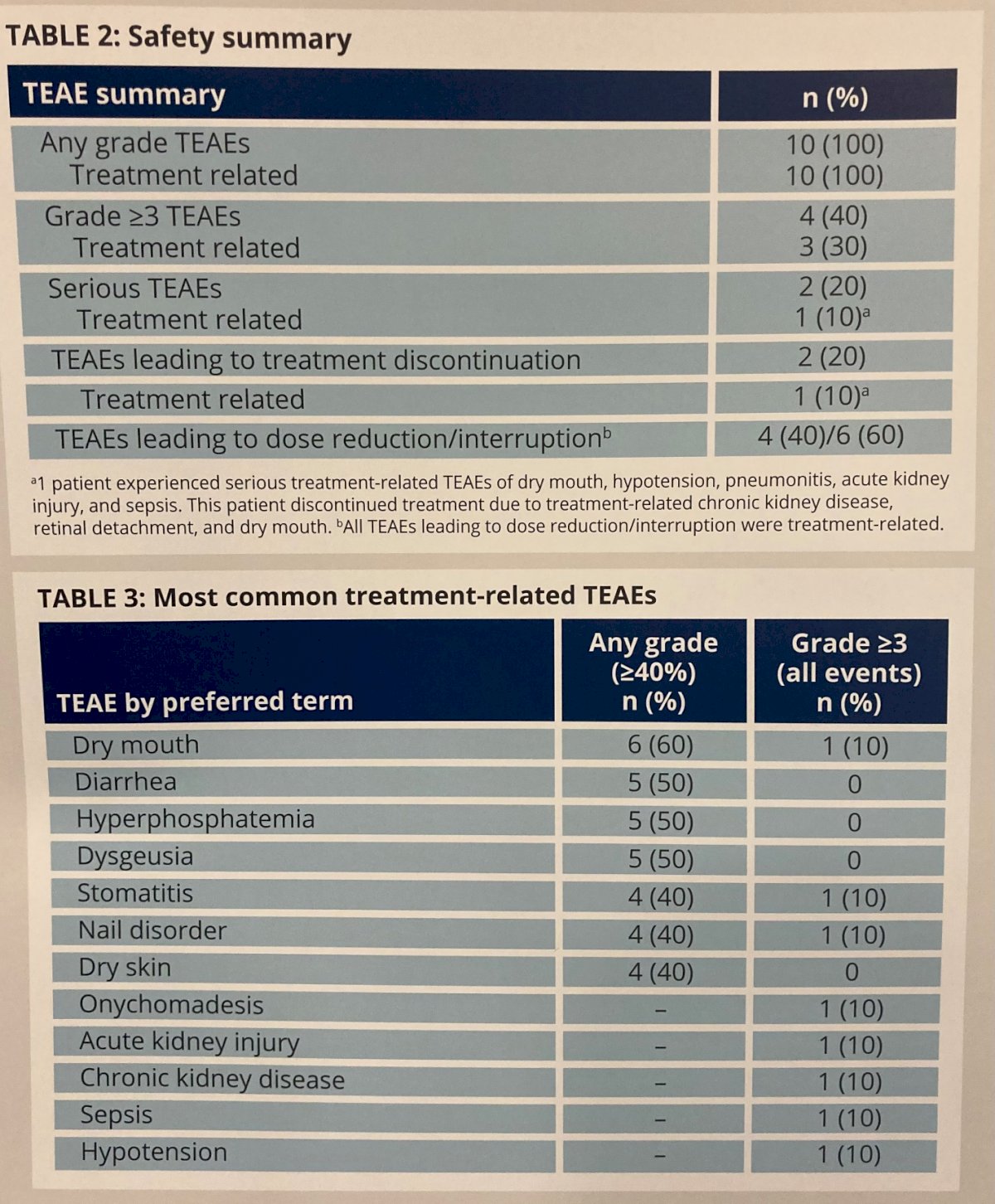
Thus, the authors conclude that these data from Cohort 2 of THOR-2 demonstrate the efficacy of erdafitinib for patients with HR-NMIBC with FGFR3/2 alterations at C3D1 and C6D1 evaluations without any new safety signals.
Presented by: James W.F. Catto, PhD, FRCS | University of Sheffield

