(UroToday.com) The 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) cancers symposium held in San Francisco, CA between February 16th and 18th was host to a Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Challenging Renal Cell Carcinoma Cases session. Dr. Fabien Moinard-Butot presented the results of his group’s study evaluating the effect of treatment of residual disease after immunotherapy-based combinations on complete response rate in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Dr. Moinard-Butot began by highlighting that immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI)-based combinations are currently considered standard of care 1st line treatment for patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Numerous phase III trials have demonstrated improved overall survival and overall response rates with these combination, compared to sunitinib. Complete response rates per RECIST v1.1 criteria have varied from 10 to 16%.1,2,3,4 To date, no robust data are available for the effect of residual disease treatment after ICI-based combinations. The clinical question as to whether an ablative approach of residual disease post-ICI can increase CR rate and improve patient outcomes remains unanswered.
To address this clinical question, the investigators performed a single center, retrospective cohort study of patients at the Strasbourg Cancer Institute in France. They included patients with metastatic RCC diagnosed between May 2016 and May 2022 who received ICI-based treatment in the first line setting. They excluded patients with non-clear cell RCC or treated with single-agent TKI. The primary endpoint was CR rate following local treatments of residual disease (RECIST v1.1). Secondary endpoints included:
- Overall response rate with ICI-based regimen
- CR rate with systemic treatment alone
- Median time from starting systemic therapy to CR
- Duration of CR
- Discontinuation rate of systemic treatment
- Relapse rate
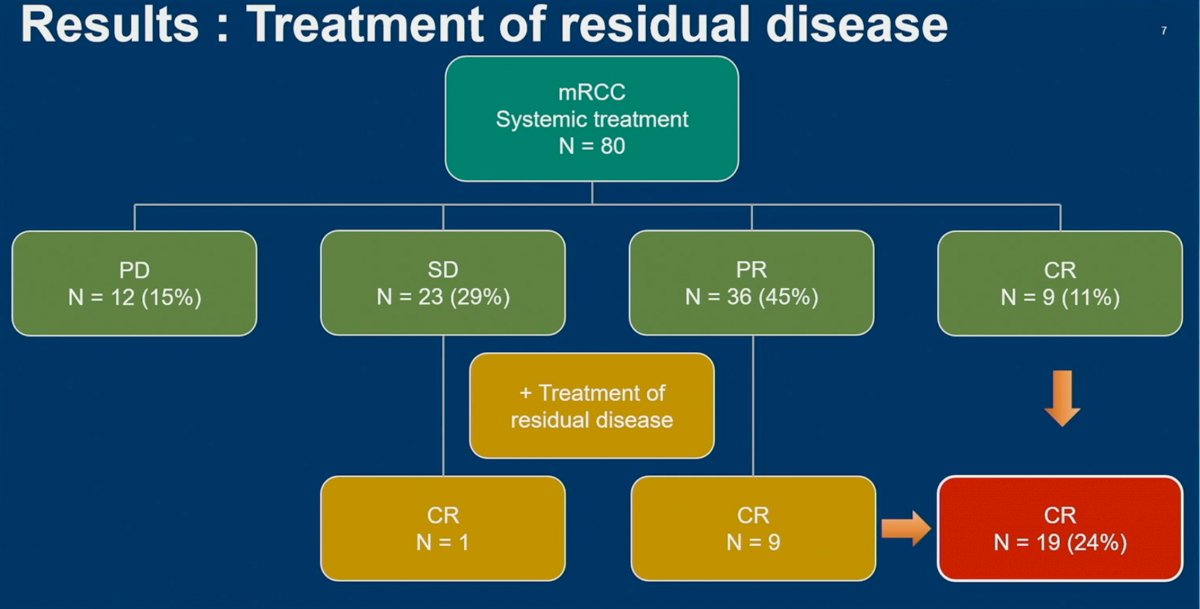
Efficacy results are demonstrated below. In the overall cohort (n=80), complete response was observed in 9 (11%) patients, partial response in 45%, and stable disease in 15%. The overall objective response rate was 56% (CR + PR). There were no statistically significant differences between patients receiving dual ICI therapy, ICI + TKIs, or other immunotherapy-based treatments.

Residual disease was locally treated in patients with either stable disease (n=23) or a partial response (n=36). 1/23 patients in the SD group had a CR, whereas 9/36 patients in the PR group had a CR. As such, 10 additional patients had a CR, for a total now of 19 patients (24%; 9 with systemic therapy, 10 additional with treatment of residual disease).
The most common type of local treatment was a nephrectomy in 6/10 patients (2 with RPLND).
Pathologic analysis revealed viable renal cell carcinoma for 7/9 patients with evaluable tissue. Notably, sarcomatoid features were reported in 3/9 samples.

At a median follow-up of two years, the median duration of a CR had not yet been reached. All 10 patients who had a CR following the additional local treatment had discontinued systemic treatment, and two (20%) had relapse or death at the time of analysis.

Dr. Moinard-Butot concluded as follows:
- Within the context of this single center retrospective study, the treatment of residual disease after ICI-based combinations increased the CR rate from 11% to 24%
- All patients discontinued systemic therapy after the treatment of residual disease
- The treatment of residual disease in metastatic RCC patients responding (SD/PR) to 1st line ICI-based treatment should be discussed in multidisciplinary tumor boards
- Longer follow-up is needed and prospective trials should be undertaken to further evaluate this
Presented by: Fabien Moinard-Butot, MD, Department of Medical Oncology, Institut de Cancérologie Strasbourg Europe, Strasbourg, France
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 Genitourinary (GU) American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, San Francisco, Thurs, Feb 16 – Sat, Feb 18, 2023.
References:- Motzer RJ et al. N Engl J Med 2018; 378(14):1277-1290.
- Rini B et al. N Engl J Med 2019;380(12):1116-1127.
- Motzer R, et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(14):1289-1300.
- Choueiri TK et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(9):829-841.
Analyzing the Impact of Residual Disease Treatment on Complete Response Rate in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma - Fabien Moinard-Butot


