(UroToday.com) The 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting featured a urothelial carcinoma rapid oral abstract session, including a presentation by Dr. Matthew Young discussing the predictive value of dynamic changes in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and baseline biomarkers with neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial. ctDNA is being explored in the neoadjuvant setting in multiple prospective trials, and dynamic changes may be a surrogate marker of pathological complete response. ABACUS was a multi-center, single-arm, phase II trial investigating two cycles of atezolizumab before cystectomy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial cancer who were ineligible for or refused neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy:1
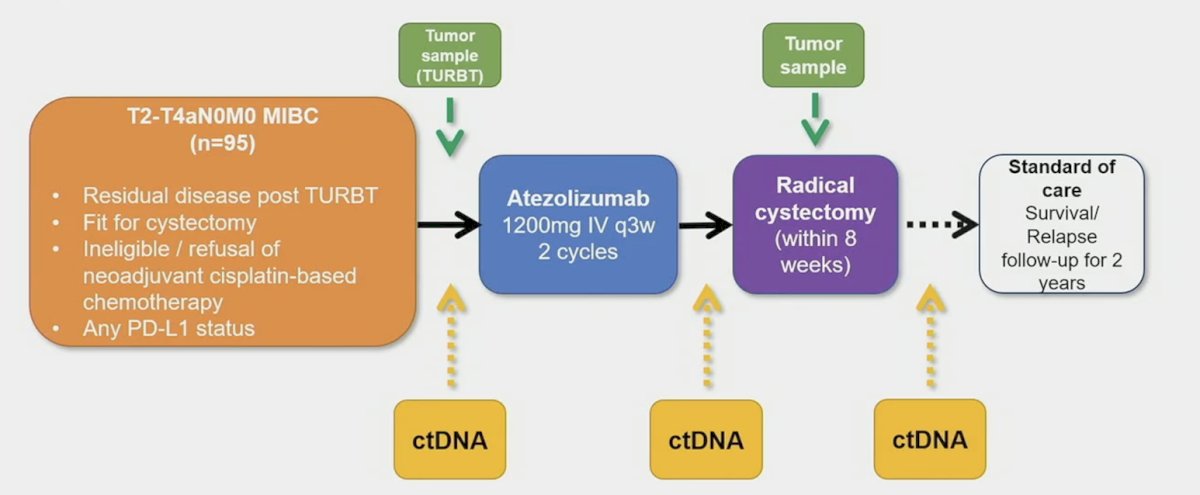
Results of primary and secondary endpoints have been previously published. Among 95 patients enrolled, the primary endpoint of pathologic complete response was 31% (95% CI 21-41%). At the 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting, Dr. Young and colleagues performed an exploratory biomarker analysis using different definitions of ctDNA response and assessed correlation with tissue response at time of cystectomy in the ABACUS trial. They also assessed how these definitions of response correlate with baseline biomarker expression.
Patients with baseline PDL-1, CD8, tumor mutational burden, and sequential ctDNA measurements (baseline and at cystectomy) were included. ctDNA analysis was performed using the Signatera assay, PD-L1 positivity was defined as ≥5% of immune cell staining, tumor mutational burden was assessed using the FoundationOne CDx assay and CD8 measurement was performed via immunohistochemistry analyses. Two definitions of ctDNA response were used:
- ctDNA clearance
- 50% reduction (or greater) in ctDNA variant allele frequency
Results were correlated with pathological complete response rate at time of cystectomy and relapse-free survival.
The 2-year disease free survival and overall survival rates in ABACUS were 68% and 77%, respectively (n = 95). There were 40 patients that had sequential DNA analysis, including 43% (17 of 40) that had pathological complete response and 20% (8 of 40) that experienced relapse. Overall, 63% (25 of 40) patients were ctDNA positive at baseline, with 40% (10 of 25) having ctDNA response of 50% variant allele frequency reduction, and 8% (3 of 40) achieving ctDNA clearance. There were 30% (3 of 10) of patients who had variant allele frequency reduction that experienced relapse and 40% (4 of 10) that achieved pathological complete response. All patients with ctDNA clearance achieved pathological complete response and none relapsed:
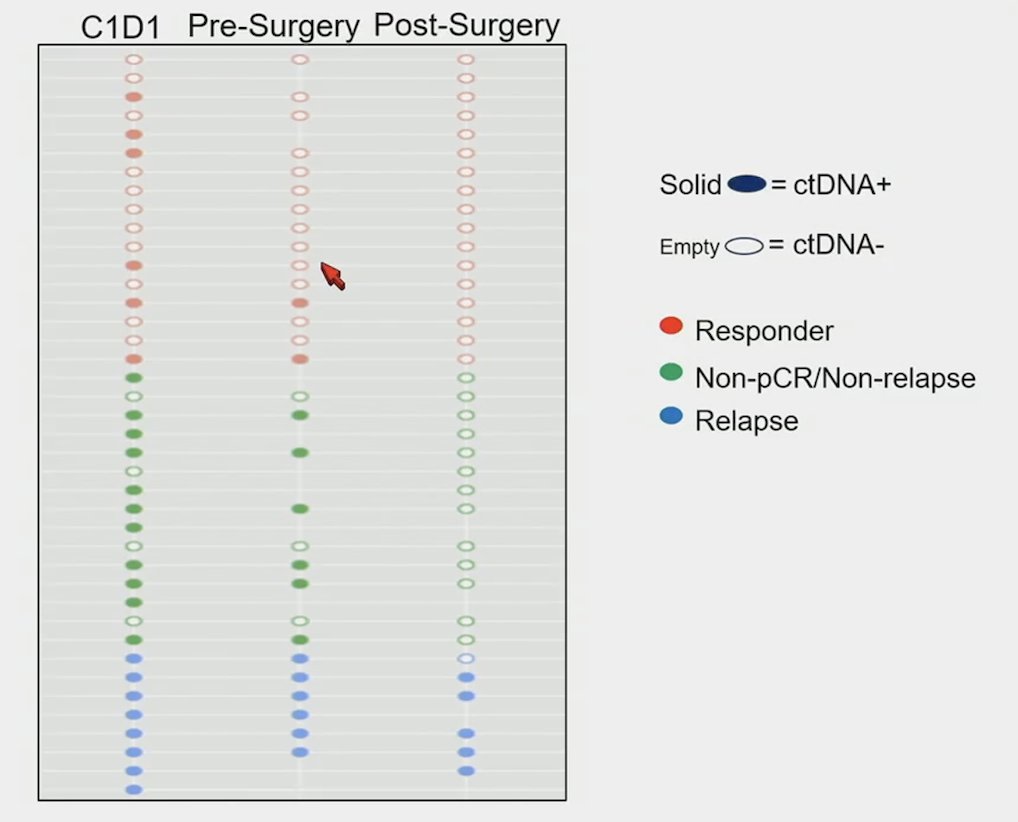
There was no association between variant allele frequency reduction of 50% and tissue response (pathological complete response) (p = 0.24). Additional analysis showed no association between a ctDNA reduction of 75% (rather than 50%) and pathological complete response (p = 0.24). Baseline PDL-1, tumor mutational burden was not predictive of pathological complete response (p = 0.18, p = 0.77, p = 0.10, respectively) or ctDNA response (p = 0.54, p = 0.77, p = 0.74) to neoadjuvant atezolizumab:
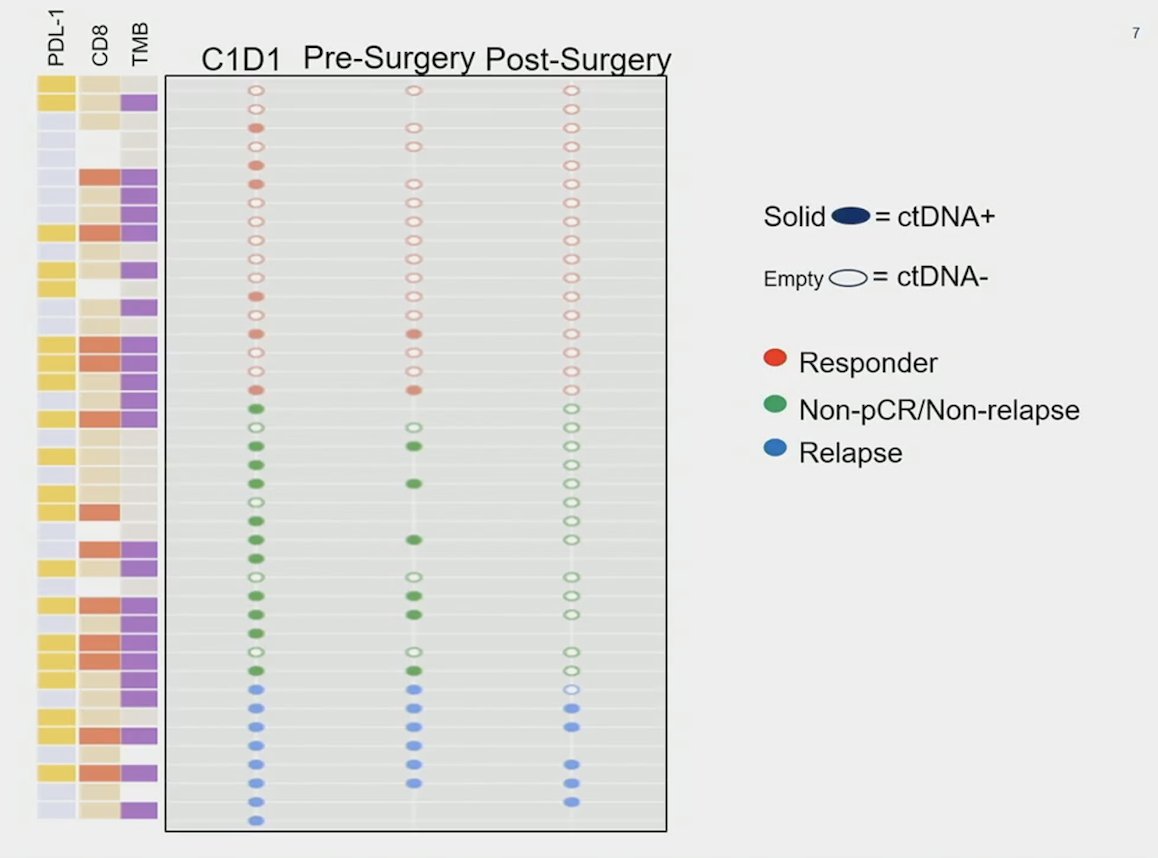
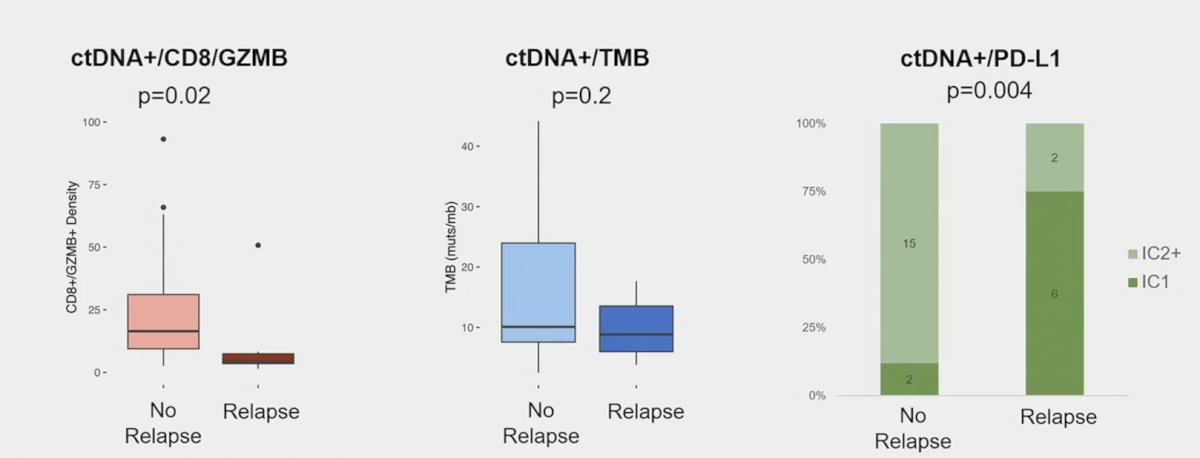
Importantly, combining ctDNA with baseline biomarkers enriches predictive value:
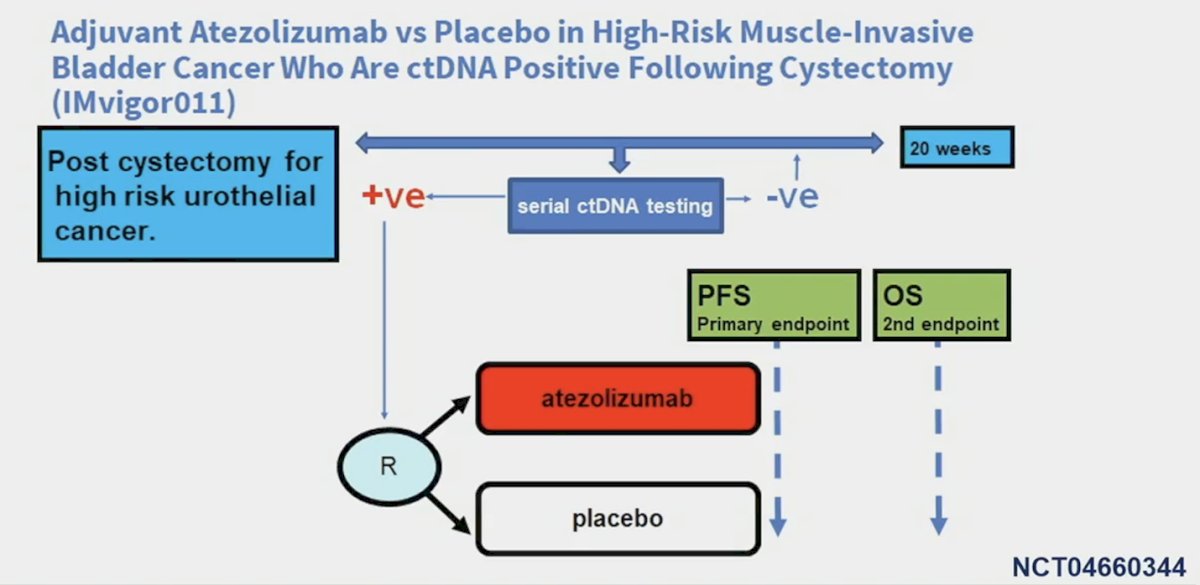
Dr. Young notes that use of atezolizumab in ctDNA positive patients post cystectomy is being explored in the phase III IMvigor011 trial:
Dr. Young concluded his presentation discussing the predictive value of dynamic changes in ctDNA and baseline biomarkers with neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial with the following take-home points:
- ctDNA clearance appears more accurate than 75% or 50% reduction in variant allele frequency to predict response/relapse
- Combining ctDNA and tissue based biomarkers improved biomarker accuracy
- Increases innate and adaptive immune signals was observed in ctDNA positive patients at baseline
- In ctDNA positive patients, increased immune signals appears to be associated with better outcomes with atezolizumab
- Combining immune and circulating biomarkers may be required to accurately predict response to therapy
Presented by: Matthew N. Young, MD, Barts Cancer Institute, London, UK
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the Genitourinary (GU) American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, Thurs, Jan 25 – Sat, Jan 27, 2024.
References:
- Powles T, Kockx M, Rodriguez-Vida A, et al. Clinical efficacy and biomarker analysis of neoadjuvant atezolizumab in operable urothelial carcinoma in the ABACUS trial. Nat Med. 2019 Nov;25(11):1706-1714.


