(UroToday.com) The 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting featured a session on the management of renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid features or variant histologies and a presentation by Dr. Rana McKay discussing the impact of immunotherapy-based regimens in primary renal tumors. Although clear cell RCC makes up 80% of cases, there are many variant histologies with varying degrees of genetic mutations and survival outcomes:
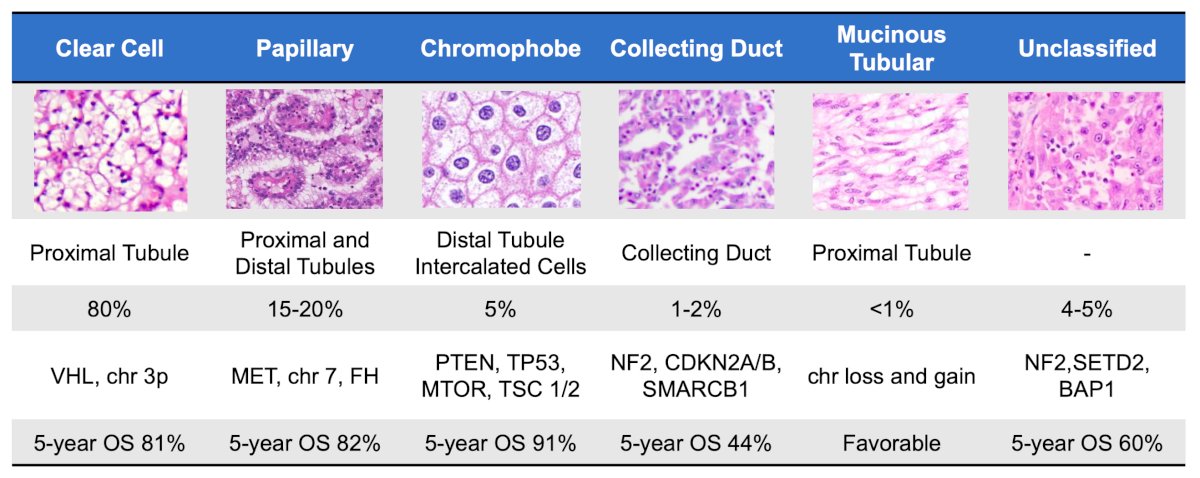
Dr. McKay notes that there is an expanding list of renal tumors, and based on the 2022 World Health Organization Classification there are several new entities (as well as the removal of papillary type 1 and 2):
- Eosinophilic solid and cystic RCC
- TFEB-altered RCC
- ELOC-mutated RCC
- Fumarate hydratase-deficient RCC
- ALK-rearranged RCC
- SMARCB1-deficient medullary-like RCC
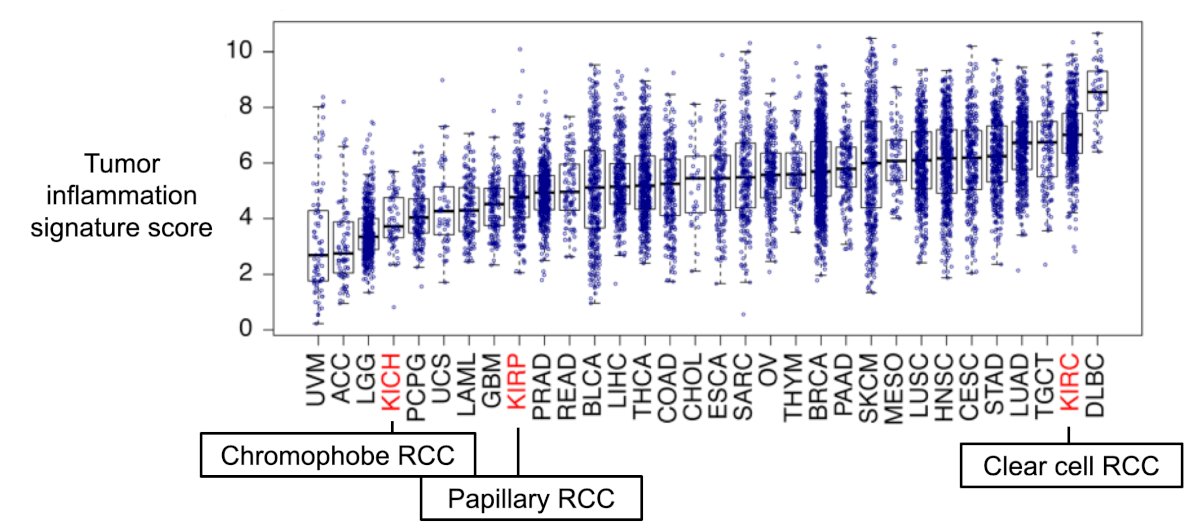
Dr. McKay notes that sarcomatoid-differentiated RCC is a molecularly and immunologically distinct entity that can occur in any RCC histology and is associated with stage IV disease in 20% of instances. Sarcomatoid histology occurs as a result of EMT, and has enrichment in BAP1, NF2 alterations, EZH2 amplifications, CDKN2A/B deletion, and MYC transcriptional programs. It generally has an immune-inflamed phenotypic, which includes activation of immune pathways, increased expression of antigen presentation machinery genes, increased cytotoxic immune infiltration, and high PDL1 protein expression in tumor cells. Indeed, tumor inflammation varies across RCC histologies:
The following table is an overview of pure immunotherapy regimens in variant RCC:
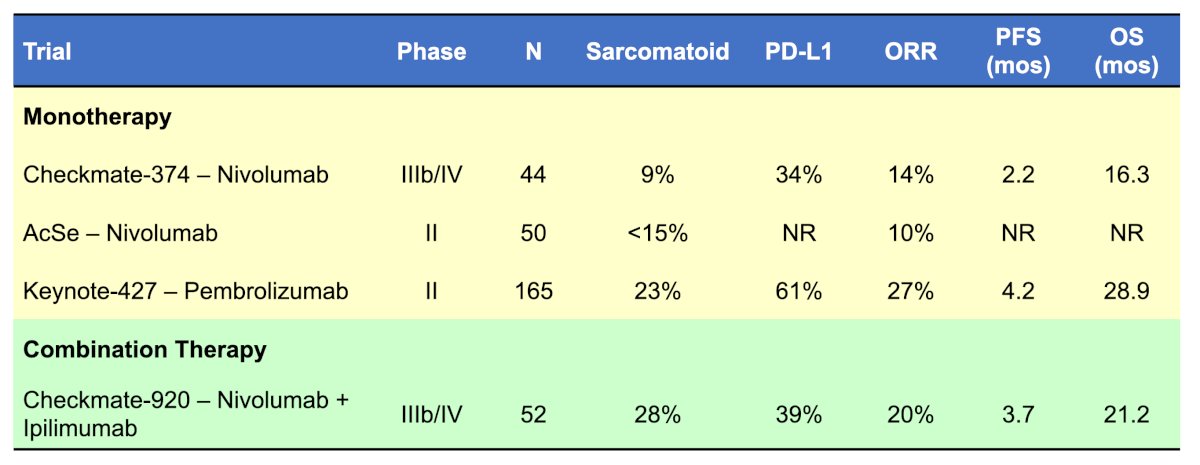
The first trial Dr. McKay discussed was the CheckMate-374 trial assessing monotherapy nivolumab in a phase IIIb/IV trial among variant histology RCC [1]. This study had 44 patients, including 24 with papillary RCC, 7 with chromophobe, 8 with unclassified, and 5 with other histology. Over a median follow-up of 11 months (range 0.4-27), the objective response rate was 13.6% (95% CI 5.2-27.4), with 1 complete response (chromophobe) and 5 partial responses (papillary [n = 2], chromophobe [n = 1], collecting duct [n = 1], and unclassified [n = 1] histology). The median PFS was 2.2 months (95% CI 1.8-5.4) and median overall survival was 16.3 months (95% CI 9.2-NE).
The KEYNOTE-427 trial cohort B assessed pembrolizumab in the first line setting among patients with metastatic non-clear cell RCC [2]. There were 165 patients that received pembrolizumab 200 mg IV Q3W for 35 cycles (~2 year) or until progressive disease, unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal. Histology was as follows: papillary 71% (n = 118), chromophobe 13% (n = 21), and unclassified 16% (n = 26). At a median follow-up duration of 11.1 months (range 0.9-21.3), 56% of patients discontinued pembrolizumab due to progressive disease or clinical progression. The overall objective response rate was 26.7%, which included 8 patients with a complete response, and 33 with a partial response. When objective response rate was assessed by histologic type, objective response rate was 28.8% for papillary, 9.5% for chromophobe, and 30.8% for unclassified non clear cell RCC. The median PFS was 4.2 months and the median overall survival was 28.9 months.
With regards to combination therapy trials, Dr. McKay noted the CheckMate-920 trial assessing nivolumab + ipilimumab among 52 patients. Over a minimum follow-up of 24.1 months, the objective response rate was 19.6% (4.3% complete response rate), median progression free survival was 3.7 months, and median overall survival was 21.2 months.
The following table highlights the treatment efficacy of pure immunotherapy for sarcomatoid RCC:
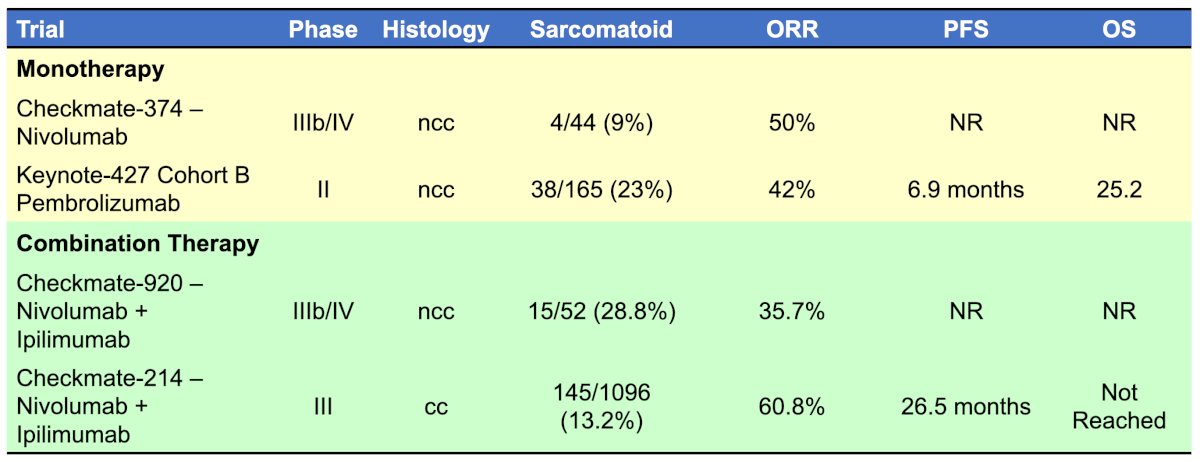
The phase III CheckMate-214 trial evaluating nivolumab + ipilimumab in the first line setting included 145 (among 1,096) patients with pure sarcomatoid variant histology [3]. With a 42 month minimum follow-up in 139 patients with intermediate/poor-risk disease, the median overall survival favored nivolumab + ipilimumab (not reached, 95% CI 25.2-not estimable) versus sunitinib (14.2 months, 95% CI 9.3-22.9; HR, 0.45, 95% CI, 0.3-0.7):
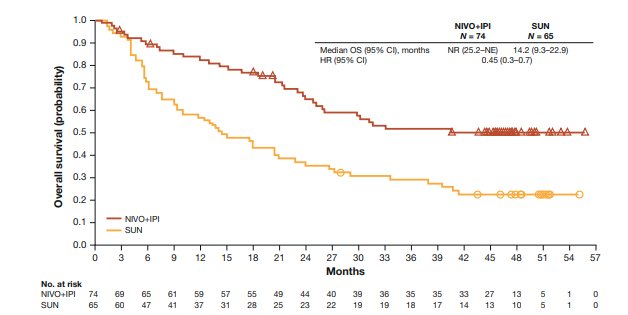
Similar PFS benefits with nivolumab + ipilimumab were also observed (HR 0.54, 95% CI 0.33-0.86). The confirmed objective response rate was 60.8% with nivolumab + ipilimumab versus 23.1% with sunitinib, with complete response rates of 18.9% versus 3.1%, respectively.
The following data summarizes the IO-VEGF combinations for sarcomatoid RCC, highlighting objective response rates ranging from 46%-60%:

Finally, Dr. McKay highlighted that based on lessons learned from the lung cancer literature, we need to integrate biomarkers into treatment selection for these RCC patients:

Dr. McKay concluded her presentation discussing the impact of immunotherapy-based regimens in primary renal tumors with the following take-home points:
- The list of RCC histologies continues to expand with a growing list of molecularly defined entities
- Treatment of variant histology RCC represents an unmet need as clinical trials have excluded or lumped variant tumors into a single trial
- Immunotherapy (PD-1/L1 and CTLA-4 targeting agents) has heterogeneous responses across variant histologies with pronounced responses in papillary and unclassified RCC, as well as RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation
- There is a need to move towards future trials that personalize therapy based on biomarkers of disease biology
Presented by: Rana R. McKay, MD, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
References:
- Vogelzang VJ, Olsen MR, McFarlane JJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Results from the phase IIIb/IV CheckMate 374 Study. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020 Dec;18(6):461-468.
- McDermott DF, Lee JL, Ziobro M, et al. Open-label, single-arm, phase II study of pembrolizumab monotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Mar 20;39(9):1029-1039.
- Tannir NM, Signoretti S, Choueiri TK, et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment of patients with advanced sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;27(1);78-86.


