(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) cancers symposium held in San Francisco, CA between January 25th and 27th was host to a trial in progress renal cell, adrenal, penile, urethral, and testicular cancers poster session. Dr. Elshad Hasanov presented a phase 1b/2 study of combination 177Lu girentuximab plus cabozantinib and nivolumab for treatment naive patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
Complete response (CR) remains a rare event in patients with advanced ccRCC. The combination of nivolumab plus cabozantinib was recently approved for the 1st line treatment of ccRCC based on the CheckMate 9ER phase 3 study demonstrating improved progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rate (ORR), compared to sunitinib. However, the CR rate was only 9%.1 Since the anti-tumor effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors are dependent on the presence of activated tumor-infiltrating T cells, drugs that have a synergistic mechanism of action with T-cells may allow for improved anti-tumor activity and, thus, improved CR rates.
Activation of the cGAS-STING pathway, the master regulator of anti-tumor immunity activated by radiation-induced DNA damage, is one of the promising mechanisms that has been investigated. Numerous studies have shown that radiation treatment augments immune checkpoint inhibition. However, it is not always possible to radiate all metastatic lesions. Therefore, targeted peptide receptor radionuclide therapies have been developed by conjugating radioisotopes to receptor binding analogs targeting specific cancer cell surface proteins, thereby delivering targeted radiation to cancer cells in the body with minimal damage to surrounding healthy cells (Figure 1).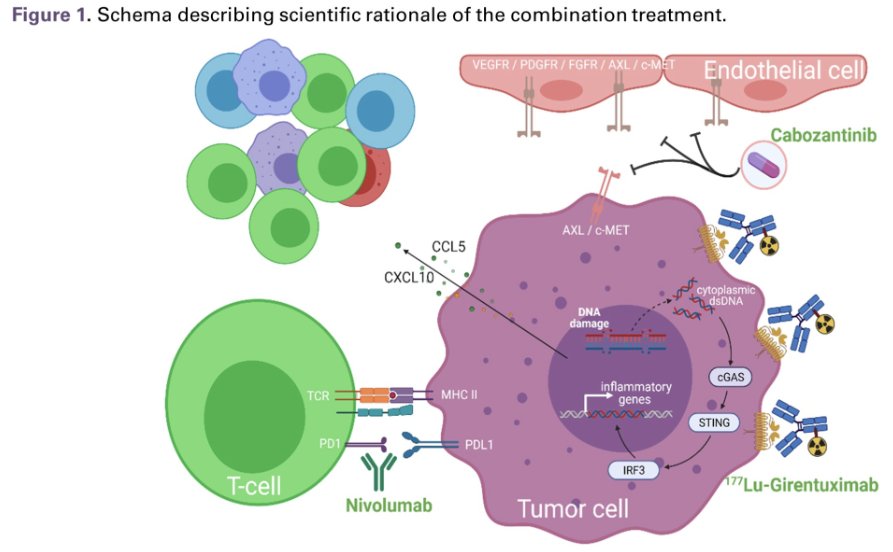
177Lu girentuximab is the first antibody-radioisotope designed for ccRCC, targeting carbonic anhydrase IX-expressing cells, expressed by >90% of ccRCC.2 177Lu girentuximab has been tested in metastatic ccRCC as a single agent and shown to be safe and effective in stabilizing disease in 57% of patients.3
This is a single arm, phase 1b/2 study that will test the hypothesis that adding 177Lu girentuximab to cabozantinib plus nivolumab will increase the CR of therapy, compared to the ‘historical’ reference with nivolumab plus cabozantinib (9%), in patients with predominantly clear cell histology. The primary objective of the study is to determine the safety and CR rate of combination 177Lu girentuximab plus nivolumab and cabozantinib in subjects with previously untreated ccRCC.
177Lu-girentuximab 1,480 MBq/m2 (61% of single agent MTD) will be administered every 12 weeks for up to three treatment cycles (Figure 2). Starting with the second cycle, nivolumab (480 mg IV every 4 weeks) and cabozantinib (40 mg orally) will be administered at standard dose. To explore the effects of the combination therapy on inducing activated T-cell infiltration, patients will undergo pre- and post-treatment PET scan with [18F]F-AraG radiotracer, as well as biopsies for single cell, spatial transcriptomics, and proteomics studies.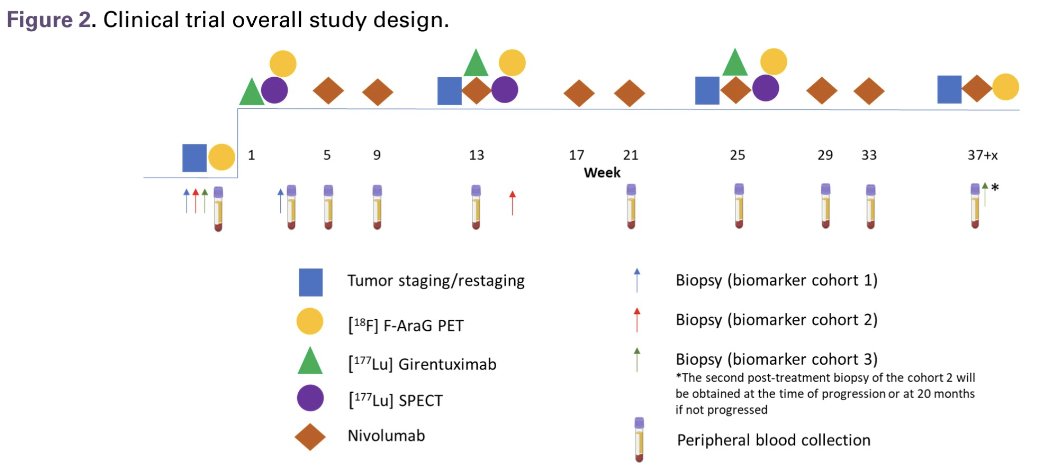
The study eligibility criteria are summarized below:
The study endpoints are as follows:
Primary Endpoints
- Safety defined by CTCAE v5.0 leading to discontinuation, immune-mediated adverse events, and worst grade clinical laboratory values
- CR rate by RECIST v1.1, per investigator assessment
- Objective response, progression-free survival, duration of response, durable stable disease, clinical benefit (ORR + stable disease) by RECIST 1.1 by investigator
- Tumor response (e.g., PR, CR, SD, PD) based on iRECIST 1.1 by investigator
- Overall survival
- Measures of pre-treatment and post-treatment tumor [18]F-AraG PET standardized uptake value (SUV) parameters and antitumor efficacy measures per RECIST 1.1, iRECIST.
- Measures of pre-treatment and post-treatment tumor SPECT 177Lu uptake and antitumor efficacy measures per RECIST 1.1, iRECIST.
- DNA, mRNA, and proteins involved in regulating immune response from tumor specimens and blood samples.
- DNA damage, cGAS-STING pathway activation, innate and adaptive immune cell infiltration from tumor specimens and blood samples.
- Resistance mechanisms related to DNA damage, cGAS-STING pathway activation, innate and adaptive immune cell infiltration from tumor specimens and blood samples
The planned sample size is 100 patients. The statistical design is summarized below:
Presented by: Elshad Hasanov, MD, PhD, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine/Medical Oncology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
References:- Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021 Apr 8;384(14):1289-1300.
- Stillebroer AB, Bperman OC, Desar IM, et al. Phase 1 radioimmunotherapy study with lutetium 177-labeled anti-carbonic anhydrase IX monoclonal antibody girentuximab in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2013;64(3):478-485.
- Muselaers CHJ, Boers-Sonderen MJ, van Oostenbrugge TJ, et al. Phase 2 Study of Lutetium 177-Labeled Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase IX Monoclonal Antibody Girentuximab in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2016;69(5):767-70.


