(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) cancers symposium held in San Francisco, CA was host to a prostate cancer poster session. Dr. Ken Herrmann presented the preliminary results of a predictive model for treatment outcomes with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), using data from the phase III VISION trial.
VISION is an international, open-label, phase 3 trial that evaluated 177Lu-PSMA-617 in patients with mCRPC previously treated with an androgen-receptor–pathway inhibitor (ARPI) and 1-2 taxane regimens and who had PSMA-positive 68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT scans. Between June 2018 and October 2019, 831 patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either 177Lu-PSMA-617 (7.4 GBq every 6 weeks for four to six cycles) plus protocol-permitted standard care or standard care alone. At a median follow-up of 20.9 months, 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus standard care significantly prolonged, as compared with standard care, both radiographic progression-free survival ([rPFS]; median: 8.7 versus 3.4 months; HR: 0.40, p<0.001) and overall survival ([OS]; median: 15.3 versus 11.3 months; HR: 0.62; 95% CI: 0.52 to 0.74, p<0.001).1
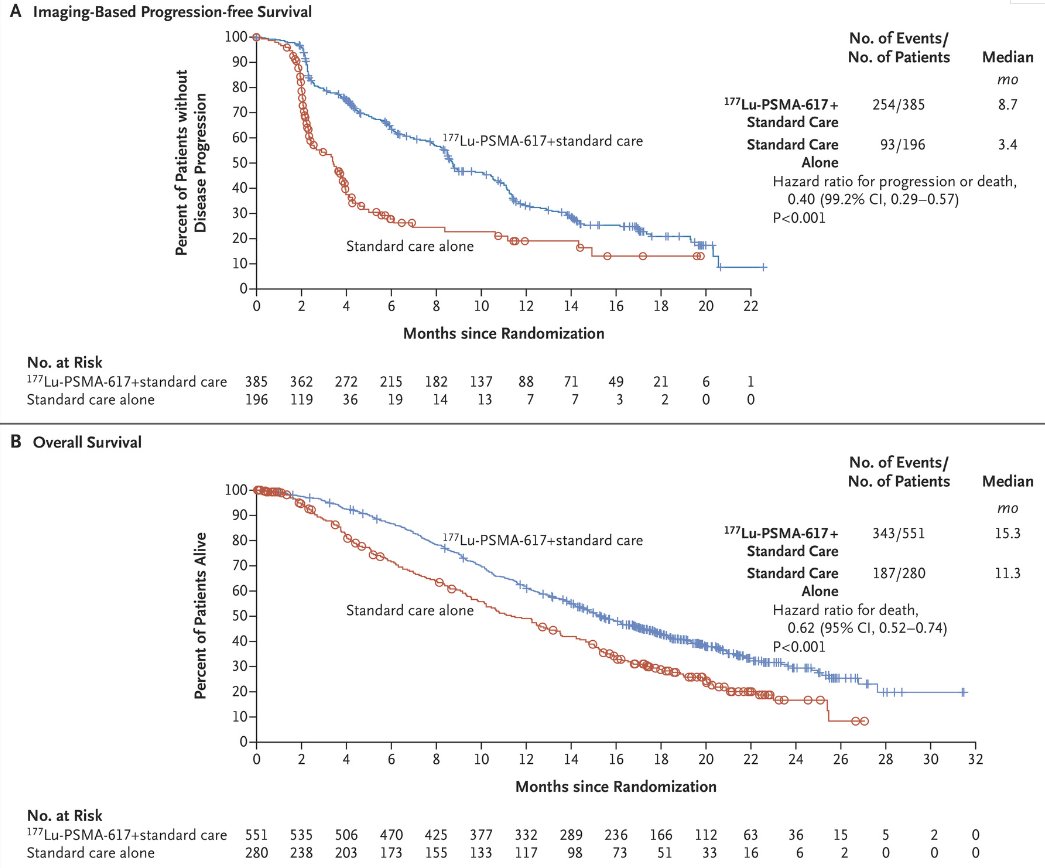
This ad hoc analysis of VISION data sought to build predictive models for clinical outcomes after 177Lu-PSMA-617 treatment. Twenty-nine baseline parameters were assessed for their prognostic and predictive values on OS, rPFS, and PSA50 response (i.e., ≥50% PSA reduction).

Univariable analyses using Cox proportional hazards model for the time-to-event outcomes (OS and rPFS) and logistic regression models for the binary outcome of PSA50 were used to identify potential prognostic/predictive biomarkers. Multiplicity was corrected by use of false discovery rate q values (alpha=0.05). Bayesian variable selection using horseshoe priors analysis was used to select parameters for inclusion in the multivariable models. Spearman correlation was performed to identify highly correlated parameters to reduce redundancy in the multivariable models.

Multivariate Cox proportional hazards (OS and rPFS) and logistic regression
(PS50) models were built with selected parameters using the 177Lu-PSMA-617 arm data only. Nomograms were subsequently constructed for visualization. The model performance was evaluated with C-index (for OS and rPFS) and receiver operating characteristic (ROC for PSA50) analyses, with confidence intervals calculated using the bootstrap method.
This analysis included a total of 831 VISION participants. Following univariable assessment of potential predictors, the authors performed the multivariable parameter selection and model building. Three parameter pairs were noted to be co-linear (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and pan-immune0inflammation; neutrophil count and white blood cell count; means SUV and whole body SUVmax). After removing co-linear parameters, all remaining parameters were subject to Bayesian horseshoe priors analysis for parameter selection. Selected parameters were used to build the multivariable models using 177Lu-PSMA-617 data only. The overall survival model included 10 parameters and had a C-index of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.70 to 0.76).

The multivariable model for rPFS included seven parameters and had a C-index of 0.68 (95% CI: 0.65 to 0.72).

The multivariable model for PSA50 included three parameters and the area under the ROC curve was 0.72 (95% CI: 0.68 to 0.77).

Dr. Herrmann concluded his presentation as follows:
- Bayesian modeling identified parameters that could be combined into a multivariable model to predict outcomes in good performance status patients treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus standard of care.
- More parameters were identified as having predictive value in these multivariable analyses than in previous models of outcomes after 177Lu-PSMA-617 treatment.
- A higher number of parameters were prognostic for OS and rPFS than for PSA50.
- The general health status of patients with mCRPC treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus standard of care appears to be more important in predicting mid-to-long-term outcomes, such as OS and rPFS, than shorter-term outcomes such as PSA50, which may be driven by PSMA expression (SUVmax and SUVmean).
Presented by: Ken Herrmann, MD, Department of Nuclear Medicine, West German Cancer Center, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
Related content: Predictive Markers in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Insights from the VISION Trial - Oliver Sartor
References:


