(UroToday.com) The 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting featured a prostate cancer session and a presentation by Dr. Hanbo Zhang discussing a real-world analysis of survival and fracture risk with radium-223 therapy in metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Radium-223 is a life-prolonging radionuclide therapy for men with bone-predominant mCRPC based on the phase 3 ALSYMPCA trial.1 This trial randomized 921 patients in a 2:1 fashion to receive six injections of radium-223 or matching placebo. The primary endpoint was overall survival and patients receiving radium-223 had significantly improved median overall survival (14.9 versus 11.3 months; HR 0.70, 95% CI 0.58 to 0.83). Radium-223 accumulates at sites of high bone turnover with emerging evidence suggesting use of radium-223 increases risk of pathologic fractures. Importantly, bone-protective agents, such as zoledronic acid and denosumab, reduce skeletal-related events including pathologic fractures in men with mCRPC. At the GU ASCO 2024 annual meeting, Dr. Zhang and colleagues evaluated real-world outcomes of patients treated with radium-223, including the effect of bone-protective agents use on pathologic fracture risk.
This study was a single institution retrospective cohort study that included patients with mCRPC treated with radium-223 in Manitoba, Canada from 2014 to 2021. Outcomes of interest included incidence of pathologic fracture, pain response, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) response, and overall survival. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for time-to-event outcomes and multivariable Cox regression models were used to adjust for covariates.
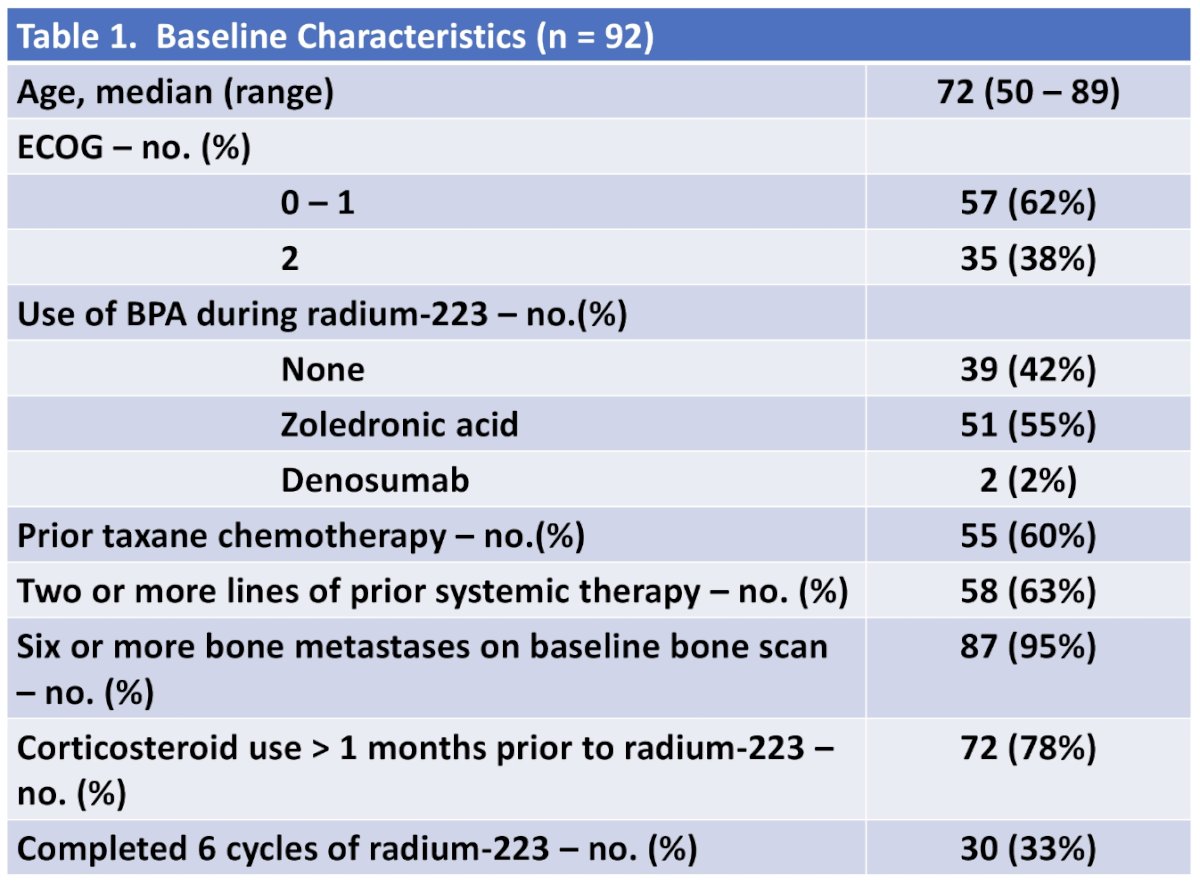
This study identified 92 patients who received radium-223 for mCRPC, including 30 patients (33%) who completed 6 cycles of radium-223:
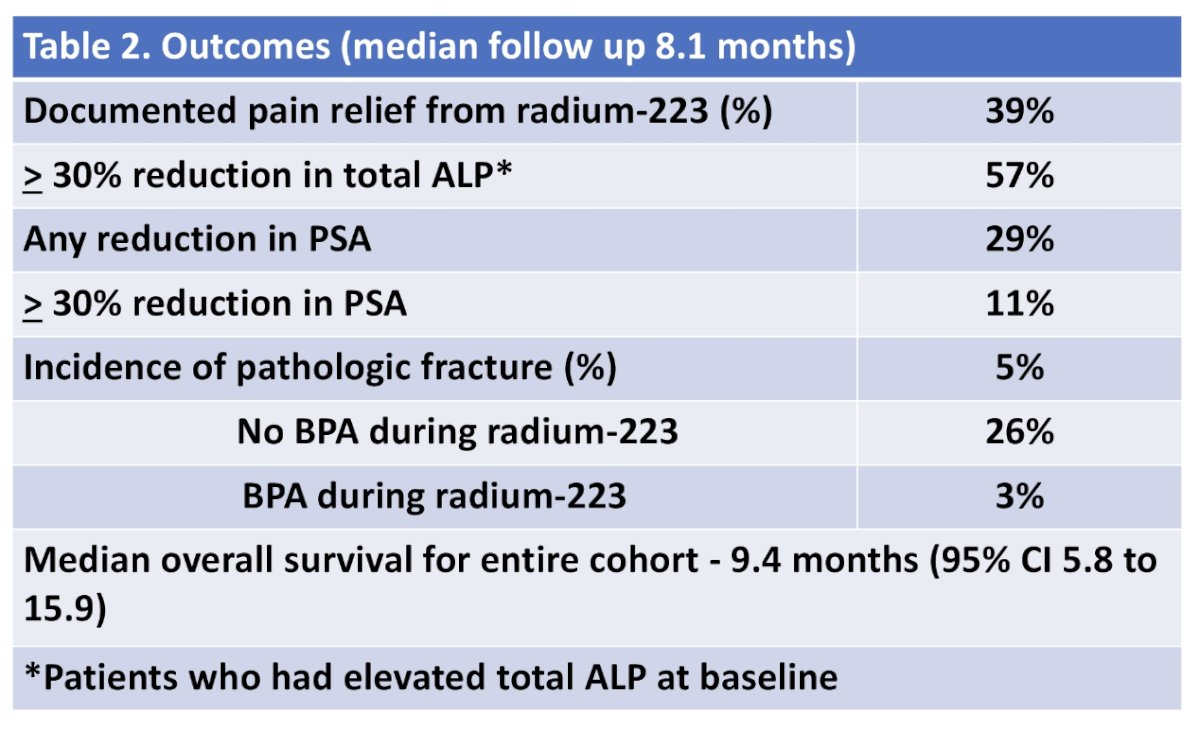
Documented pain relief occurred in 39% of patients. For those with elevated ALP at baseline (n = 46), 57% had at least 30% reduction in total ALP. PSA reduction occurred in 29% with 11% having at least 30% reduction in PSA. The median overall survival was 9.4 months (95% CI 5.8 to 15.9). Of those who did not receive concurrent bone-protective agents, 26% developed a pathologic fracture, compared to 3% who received concurrent bone-protective agents during a median follow up of 8.1 months:
Bone-protective agents use was associated with a significant delay in time to pathologic fracture (median not reached vs. 15.9 months; HR 0.20, 95% CI 0.05 – 0.76) after adjusting for number of bone metastases and corticosteroid use:

Dr. Zhang concluded his presentation discussing a real-world analysis of survival and fracture risk with radium-223 therapy in mCRPC with the following take-home points:
- In this real-world study, concurrent bone-protective agents use was associated with significant reduction in risk of pathologic fractures in mCRPC patients receiving radium-223
- Bone-protective agent administration should be considered for patients receiving radium-223
Presented by: Hanbo Zhang, MD, FRCPC, Medical Oncology and Hematology, University of Manitoba, CancerCare Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
References:
1. Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2013;369(3):213-223.


