(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) cancers symposium held in San Francisco, CA between January 25th and 27th was host to a prostate cancer trials in progress poster session. Dr. Evan Yu presented the rationale and study design of KEYNOTE-365 (Cohort 1), a phase 1b/2 study of pembrolizumab plus platinum/etoposide and platinum/etoposide for neuroendocrine metastatic prostate cancer.
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer is an aggressive form of prostate cancer that can arise either de novo or secondary to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) exposure in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Nearly 20% of patients treated with hormonal therapies for prostate adenocarcinoma develop treatment-emergent neuroendocrine mCRPC. Treatment-emergent neuroendocrine or de novo neuroendocrine prostate cancer is often treated with platinum-based chemotherapy, but, currently, there is no established standard-of-care treatment. As such, more efficacious treatment options are needed
The PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab has shown anti-tumor activity and manageable safety in patients with mCRPC previously treated with docetaxel and targeted endocrine therapy in the phase 2 KEYNOTE-199 trial.1 In cohort I of the open-label, multicohort, phase 1b/2 KEYNOTE-365 trial (NCT02861573), the safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab + carboplatin + etoposide (arm 1) and carboplatin + etoposide (arm 2) are being evaluated in patients with treatment-emergent neuroendocrine mCRPC.
The study design is illustrated below:
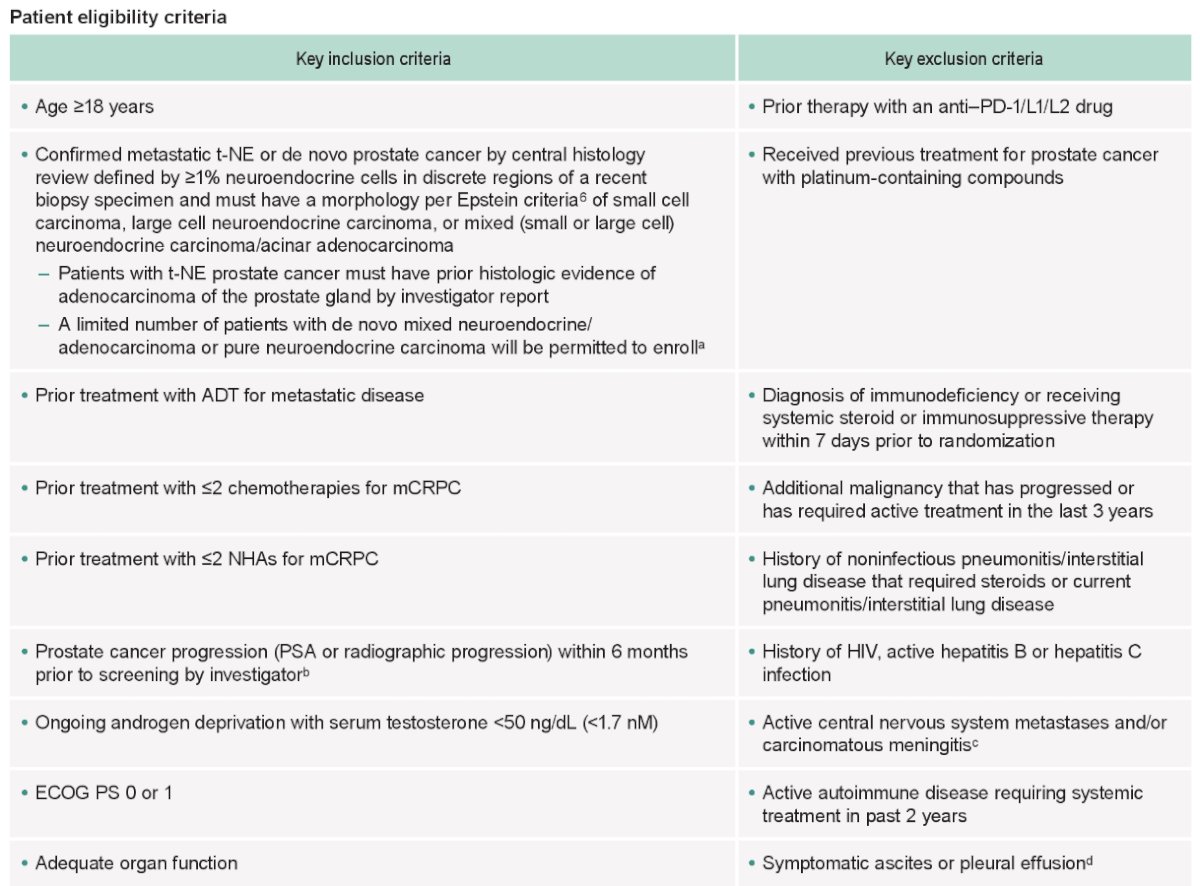
With regards to key eligibility criteria, patients were required to have treatment-emergent neuroendocrine mCRPC, confirmed by central histology review, progressive disease within 6 months prior to screening, prior treatment with ADT for metastatic disease, ≤2 prior chemotherapies for mCRPC, ≤2 prior novel hormonal agents for mCRPC, and ECOG performance status of 0 – 1. The remaining eligibility criteria are as follows:
The study objectives are as follows:
- Primary
- To evaluate the following for the pembrolizumab + carboplatin + etoposide and carboplatin + etoposide combinations:
- Safety and tolerability
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response rate (reduction in the PSA level ≥50% from baseline measured twice 23 weeks apart)
- Objective response rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 by blinded independent central review (BICR)
- Secondary
- To evaluate the following for the pembrolizumab + carboplatin + etoposide and carboplatin + etoposide combinations:
- Time to PSA progression (time from the first day of study treatment to the date of PSA progression)
- ORR and radiographic progression-free survival (rFS) per Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3 (PCWG3)-modified RECIST v1.1 by BICR
- Duration of response (DOR) and disease control rate (DCR) per RECIST v1.1 and per PCWG3-modified RECIST v1.1. both by BICR
- Overall survival (OS)
The study assessment and follow-up are as follows:
The current status of enrollment for KEYNOTE-365 is illustrated below:
Presented by: Evan Yu, MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Washington and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary (ASCO GU) Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA, January 25th – January 27th, 2024
References: