(UroToday.com) The 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting featured a prostate cancer session and a presentation by Dr. Dana Rathkopf discussing patient-reported outcomes from the MAGNITUDE study. MAGNITUDE, an international phase 3 randomized double-blind study, demonstrated that metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients with BRCA1/2 alterations receiving niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone had significantly improved radiographic progression-free survival, and clinically relevant prolongations in time to symptomatic progression and time to cytotoxic chemotherapy compared with placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone.1
At the 2024 GU ASCO annual meeting, Dr. Rathkopf and colleagues reported patient reported outcome results, specifically pain, health-related quality of life, and side effect bother, in the BRCA1/2 subset of mCRPC patients in the final analysis of MAGNITUDE.
Patients were screened prospectively for HRR gene alterations. Eligible patients had ECOG status ≤1 and a Brief Pain Inventory–Short Form (BPI-SF) worst pain score ≤3 (scale of 0-10), and were randomized 1:1 to niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone or placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone orally daily in 28-day cycles. Patient reported outcome assessments on day 1 of specified cycles included BPI-SF and FACT-P. Time to deterioration in pain (BPI-SF worst, average, pain interference, and FACT-P pain-related scale) were compared between treatment arms using proportional hazards regression models. Changes from baseline in health-related quality of life (FACT-P total, scale of 0-156) were compared using repeated measures analysis, and side-effect bother was assessed in both arms as a single item from FACT-P (GP5).
Patient reported outcome compliance for FACT-P and BPI-SF was >85% in 225 patients with BRCA1/2-altered mCRPC across all treatment visits and assessments. At baseline, mean BPI-SF pain scores was 1.09 (SD, 1.57) in niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone and 1.35 (SD, 1.98) in placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone. Mean FACT-P Total in niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone and placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone was 116.33 (SD, 18.42) and 114.8 (SD, 18.9), respectively:
Median time to deterioration in BPI-SF worst pain, pain interference, average pain, and FACT-P pain-related scale were numerically longer for niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone vs. placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone: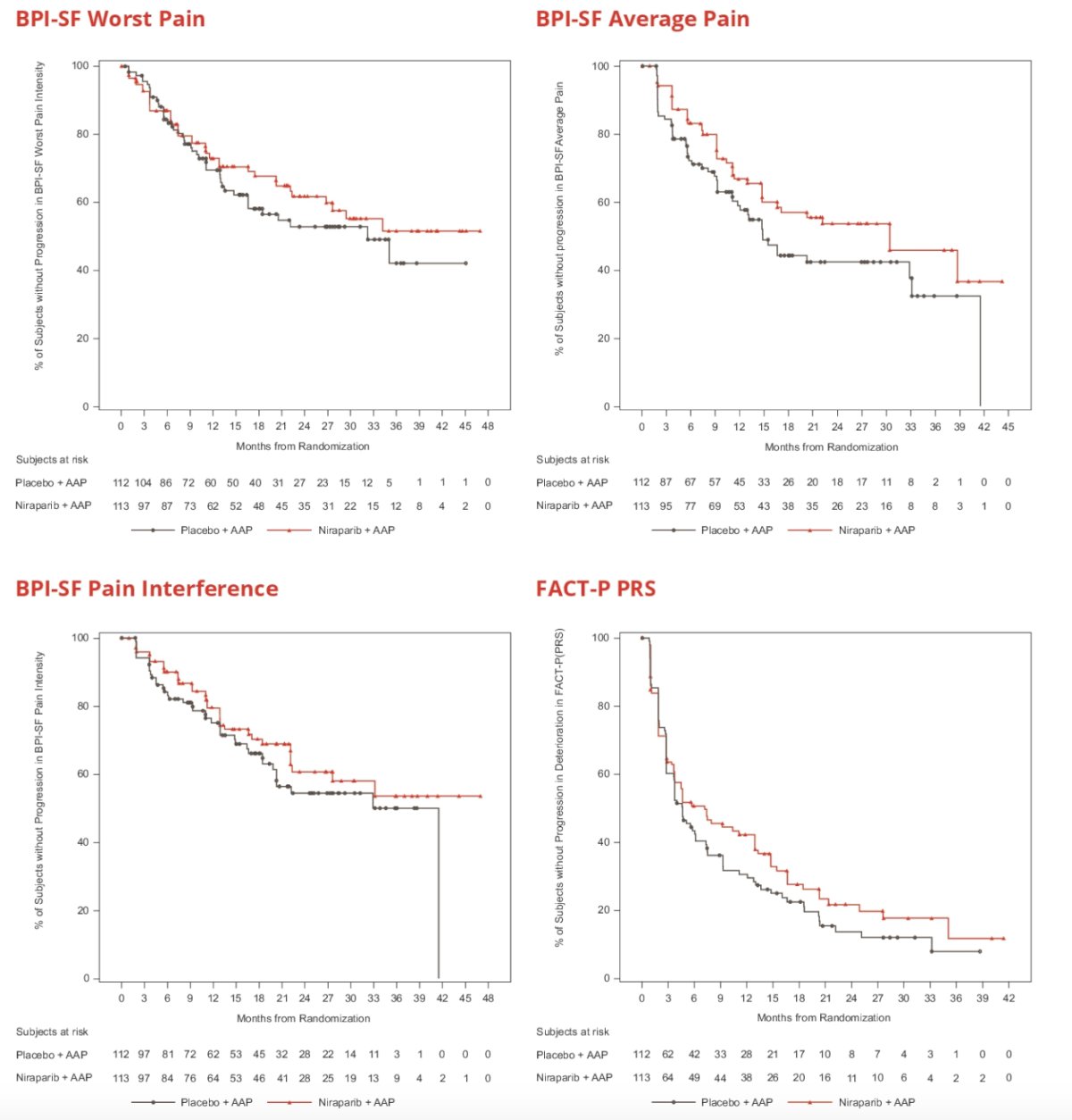
Repeated measures results showed health-related quality of life was maintained on treatment for the BRCA subgroup with no clinically meaningful differences in the FACT-P total score over time or between treatment arms: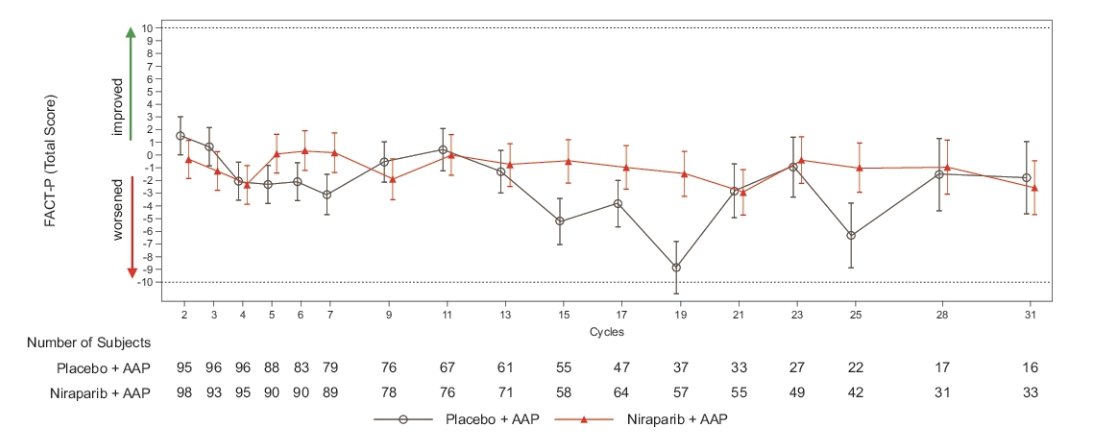
Analysis of FACT-P item GP5 in the BRCA subset showed side effect bother was rated “not at all” or “a little bit” by 87% of niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone and 92% of placebo + abiraterone acetate and prednisone subjects across treatment cycles: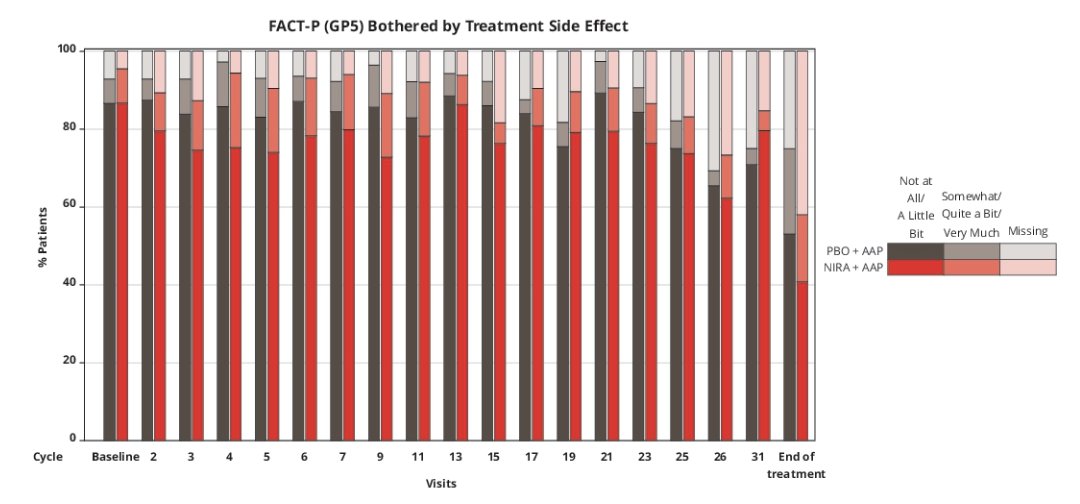
In both treatment groups, a greater proportion of patients reported that side effect bother remained stable or improved rather than worsened during treatment: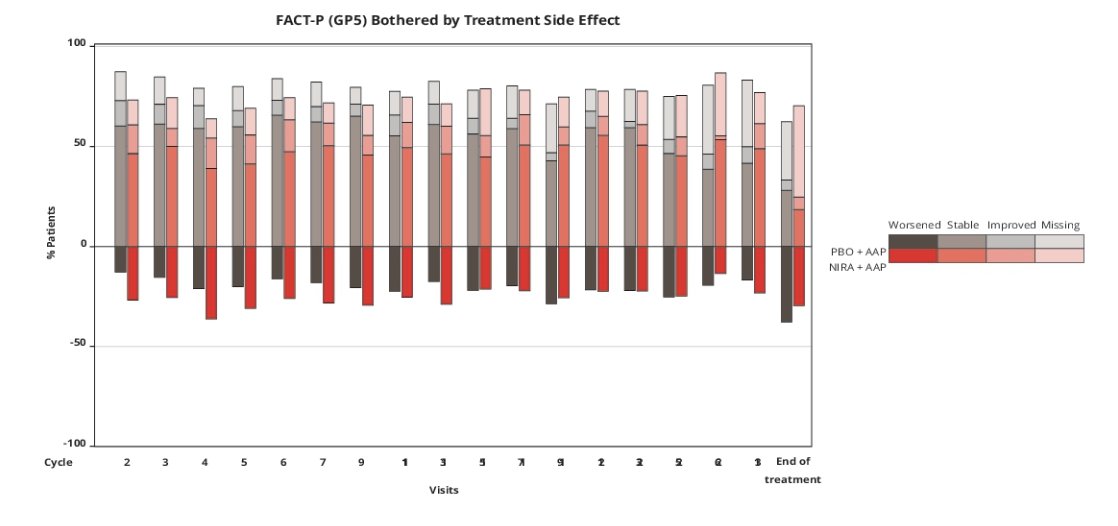
Dr. Rathkopf concluded her presentation discussing patient-reported outcomes from the MAGNITUDE study with the following take-home points:
- Niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone showed a trend of longer time to pain progression, with results consistent across pain scores
- Overall health related quality of life was maintained on niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone in mCRPC patients with BRCA1/2 alterations
- Side-effect bother was minimal, and remained stable or improved with niraparib + abiraterone acetate and prednisone
Presented by: Dana E. Rathkopf, MD, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the Genitourinary (GU) American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, Thurs, Jan 25 – Sat, Jan 27, 2024.
Reference:
- Chi KN, Rathkopf D, Smith MR, et al. Niraparib and abiraterone acetate for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun 20;41(18):3339-3351.


