Dr. Harada began by noting that muscle invasive disease accounts for approximately 15 to 30% of newly diagnosed bladder cancer cases. The current treatment paradigm for such patients includes radical cystectomy + neoadjuvant chemotherapy in cisplatin-eligible patients and trimodal therapy in select patients meeting strict eligibility criteria. It has been consistently demonstrated that pathologic lymph node involvement following neoadjuvant chemotherapy (ypN+) is a poor prognostic sign for patients with muscle invasive disease. Accordingly, a nomogram has been developed and validated for the prediction of ypN+ disease in patients with cN0 muscle invasive bladder cancer cohort treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by a radical cystectomy. Significantly, an increased nomogram probability of ypN+ disease has been shown to be associated with worse overall survival outcomes.
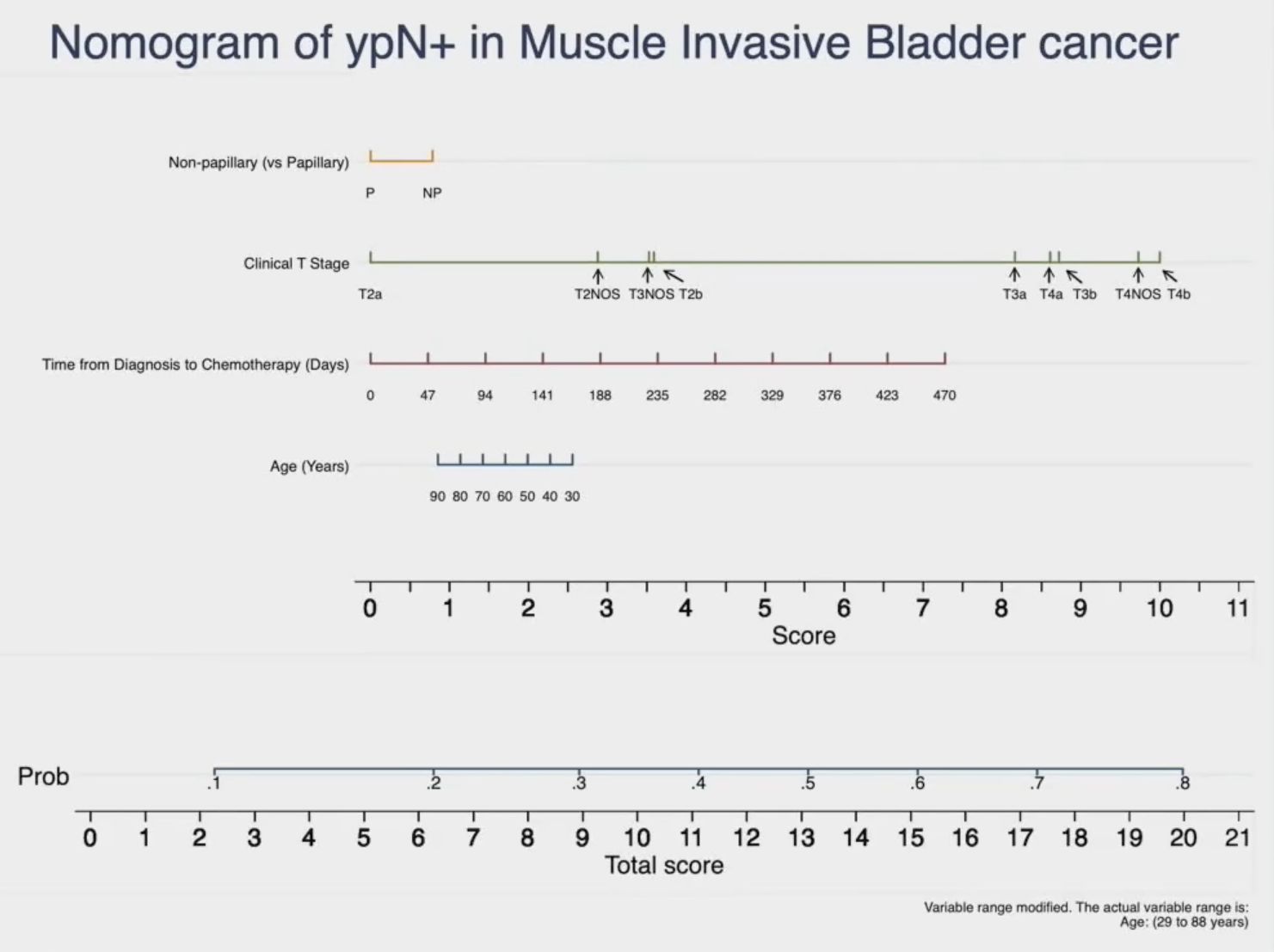
This nomogram has been trained and validated in the NAC/radical cystectomy cohort. As such, the external generalizability/validity of this nomogram to the trimodal/chemoradiotherapy cohort remains unknown. As such, the objective of this study was to determine if this nomogram can be used to prognosticate overall survival in patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy.
To this end, the authors conducted an analysis of the National Cancer Database (NCDB) between 2004 and 2020 of patients with cT2-4N0M0 papillary or non-papillary urothelial carcinoma who received definitive chemoradiotherapy, defined as those receiving:
- Radiotherapy (5,500 or 6,480 cGy) +/- pelvic lymph nodes
- Concurrent chemoradiotherapy (within 14 days of therapy initiation).
Following a 70:30 training and testing data split, variables were assessed for association with overall survival using the log-rank test, with those with p < 0.05 deemed eligible for inclusion within a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model. Patients were then stratified as high-, medium-, or low-risk for death using the hazard function’s prognostic index. The proportional hazards assumption was checked using Schoenfeld residuals and discrimination assessed using dynamic area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUC). Subsequent validation was performed within the NCDB training dataset and within an institutional cohort of 15 patients treated with chemoradiotherapy between 2014 and 2020.
This analysis included a total of 1,047 patients, with a median age of 78 years (IQR: 70 – 83). The median follow-up was 31.3 months. Cox regression analysis identified the following variables to be significantly associated with overall survival:
- Patient age (HR = 1.03; 95% CI = 1.02 – 1.04; p < 0.001)
- Charlson-Deyo Score
- Predicted probability of developing future lymphadenopathy (HR = 4.47; 95% CI = 1.83 – 10.93; p = 0.001)

The median overall survival by risk group was as follows:
- High: 34.2 months (IQR = 21.3 – 40.6 months),
- Medium: 38.9 months (IQR = 31.4 – 47.2 months)
- Low: 77.8 months (IQR = 56.1 – 100.3 months)
Similar discriminatory performance was seen within the testing cohort as well with significant differences between median overall survival across each group (AUC range = 0.580 – 0.726) (p < 0.001). Notably, among patients within the institutional cohort, only one patient stratified as high (N = 1/2; 50.0%) or medium risk (N = 0/5; 0.0%) remained alive at time of final follow-up, whereas 88.9% (N = 7/8) of low-risk patients survived (p = 0.051). Similarly, significant differences in overall survival were again seen between risk groups, with a median overall survival of 51.3 months and 19.9 months for high- and medium-risk patients, respectively, while median overall survival for low-risk patients was not reached (p=0.006).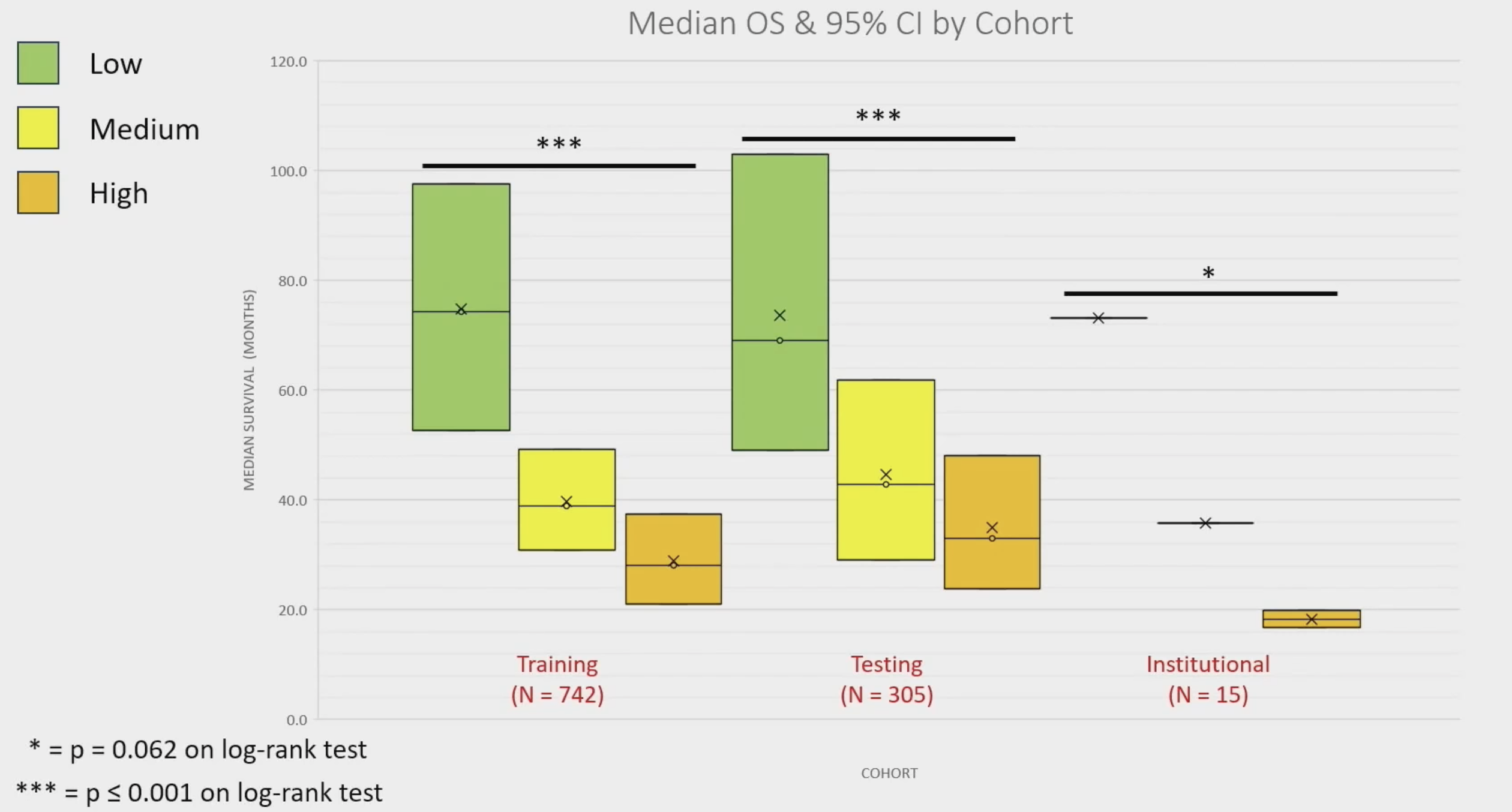
The model demonstrated excellent calibration performance in both the training and testing cohorts.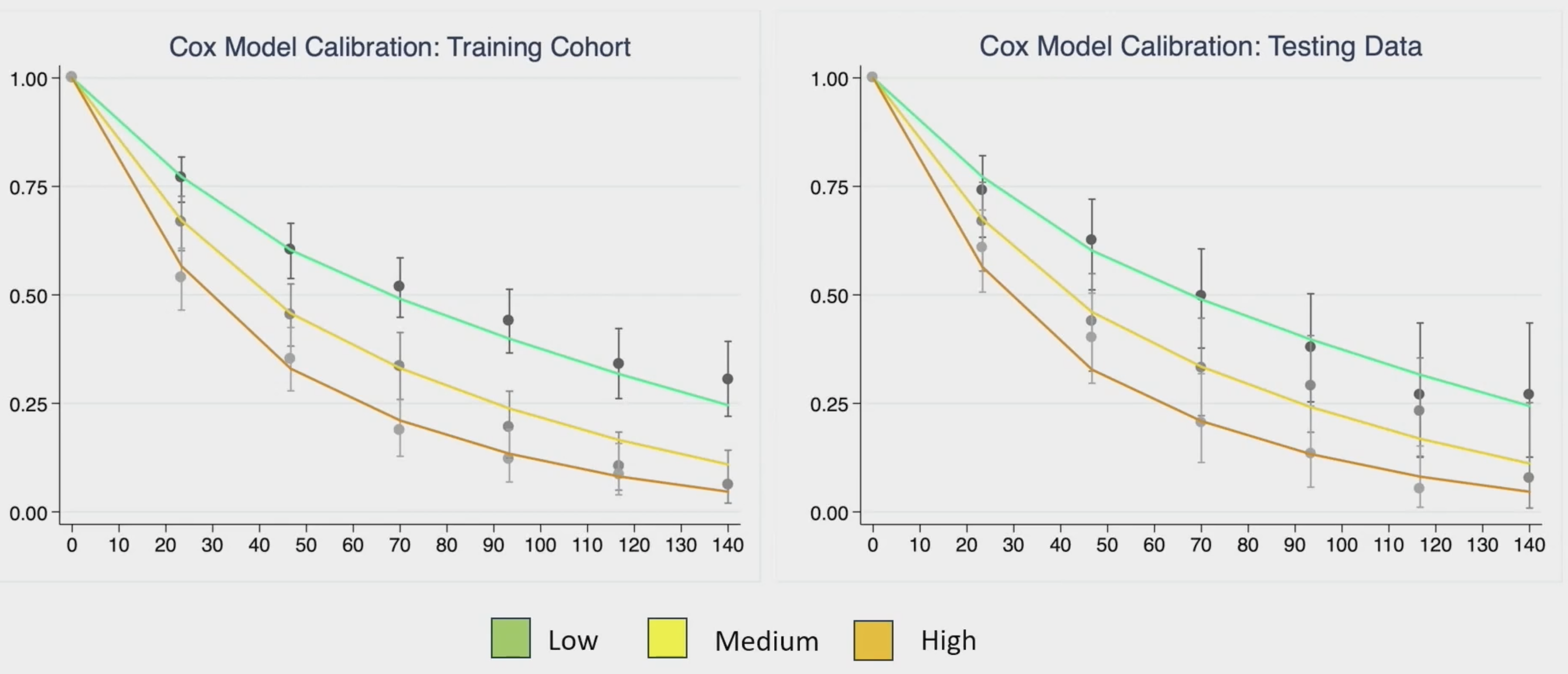
This model appeared to have ‘peak’ AUC prognostic performance at about 6 months, and then again at 10 years, as demonstrated below: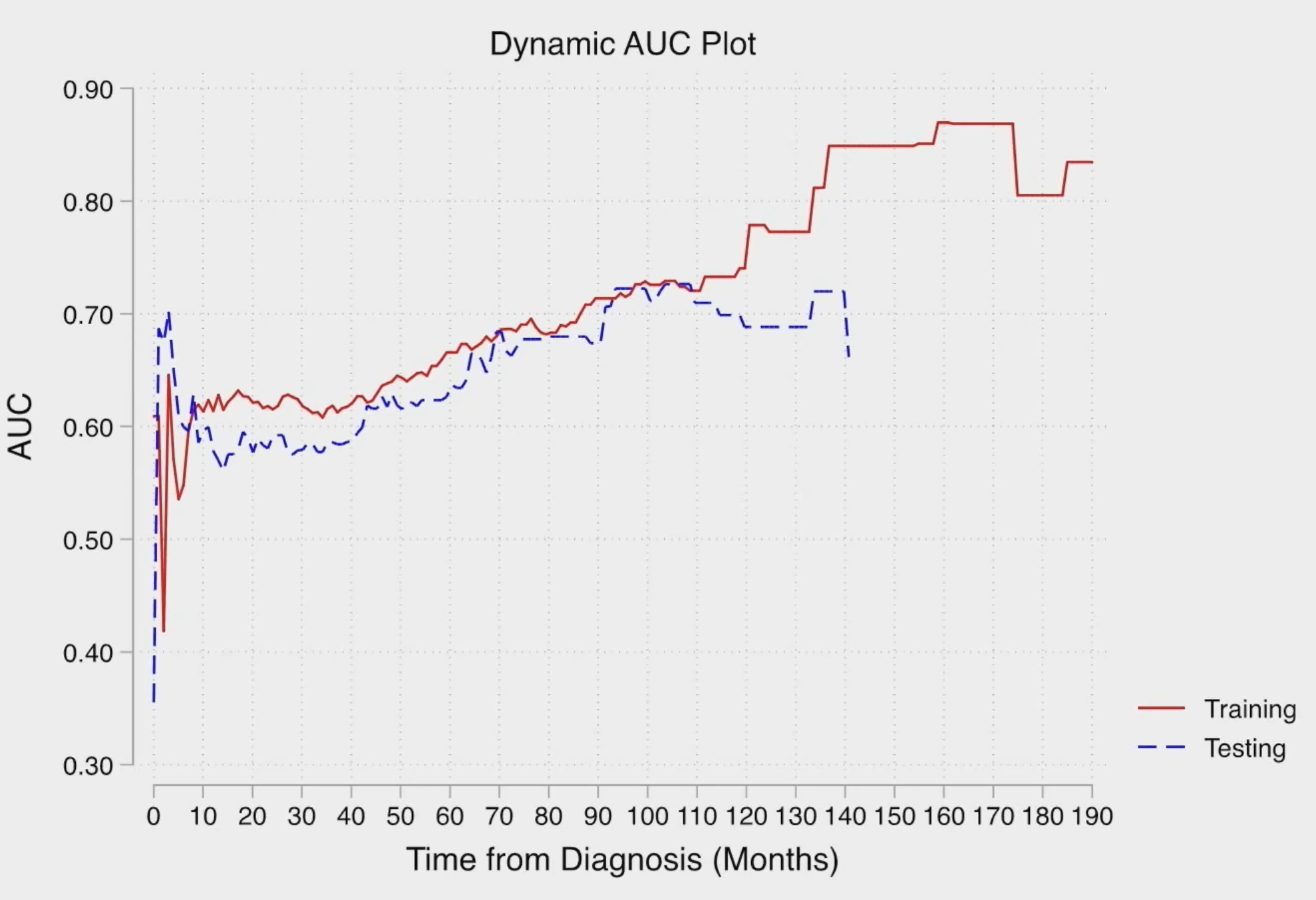
Dr. Harada concluded his presentation with the following take home messages:
- The nomogram risk of ypN+ is prognostic of overall survival for muscle invasive bladder cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy
- High risk patients: Median overall survival 30 - 34 months
- Medium risk patients: 39 - 43 months
- Low risk patients: 73 - 78 months
- Findings consistent when validated in a relatively small institutional cohort
- The survival model suggests the ability to predict those alive versus dead at 6 months and 6.5+ years with ≥70% discrimination
- Pending further validation, these findings can be used to counsel patients on short-and long-term prognosis and could identify candidates for therapy escalation
Presented by: Garrett Harada, MD, Resident Physician, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of California in Irvine, Orange County, CA
Written By: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 American Society for Therapeutic Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 65th Annual Meeting held in San Diego, CA between October 1st and 4th, 2023


