The 2023 ASTRO annual meeting included a session on novel prognostication techniques for prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Ryan Phillips discussing validation of a genomic classifier in the NRG Oncology/RTOG 0521 phase III trial of docetaxel with androgen suppression and radiotherapy for localized high-risk prostate cancer.1,2
The Decipher genomic classifier is a 22-gene, microarray-based transcriptomic tool providing superior risk stratification of prostate cancer independent of clinicopathologic risk factors, which has been validated in several prospective NRG Oncology Phase III trials. The genomic classifier contains at least 10 transcripts implicated in the taxane mechanism of action. At the 2023 ASTRO annual meeting, Dr. Phillips and colleagues presented data validating the genomic classifier in pre-treatment biopsy samples for risk stratification in a cohort of high-risk men treated with definitive radiotherapy and androgen suppression with or without docetaxel chemotherapy. The primary objective was to assess prognostic validation, whereby validating the genomic classifier as a prognostic biomarker of metastasis-free survival in the NRG/RTOG 0521 trial. The secondary objective was to assess predictive validation, whereby validating the genomic classifier will identify which men derive greater relative benefit with respect to distant metastasis from the addition of docetaxel to external beam radiotherapy + ADT.
As per a pre-specified and approved NCI analysis plan, Dr. Phillips et al obtained available formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue from biopsy specimens from the NRG biobank from patients enrolled on the NRG/RTOG 0521 randomized phase III trial. After central review, the highest-grade tumors were profiled on clinical-grade whole-transcriptome arrays, and genomic classifier scores were obtained. Pre-specified categorical genomic classifier scores, adjusted for archival tissue analysis, were used to define higher (>0.46) and lower (=0.46) risk groups. Samples were obtained from 283 consented, evaluable patients with tissue (50% of trial) yielding 183 (65%) genomic classifier scores that passed quality metrics, 91 from control and 92 from the interventional arm: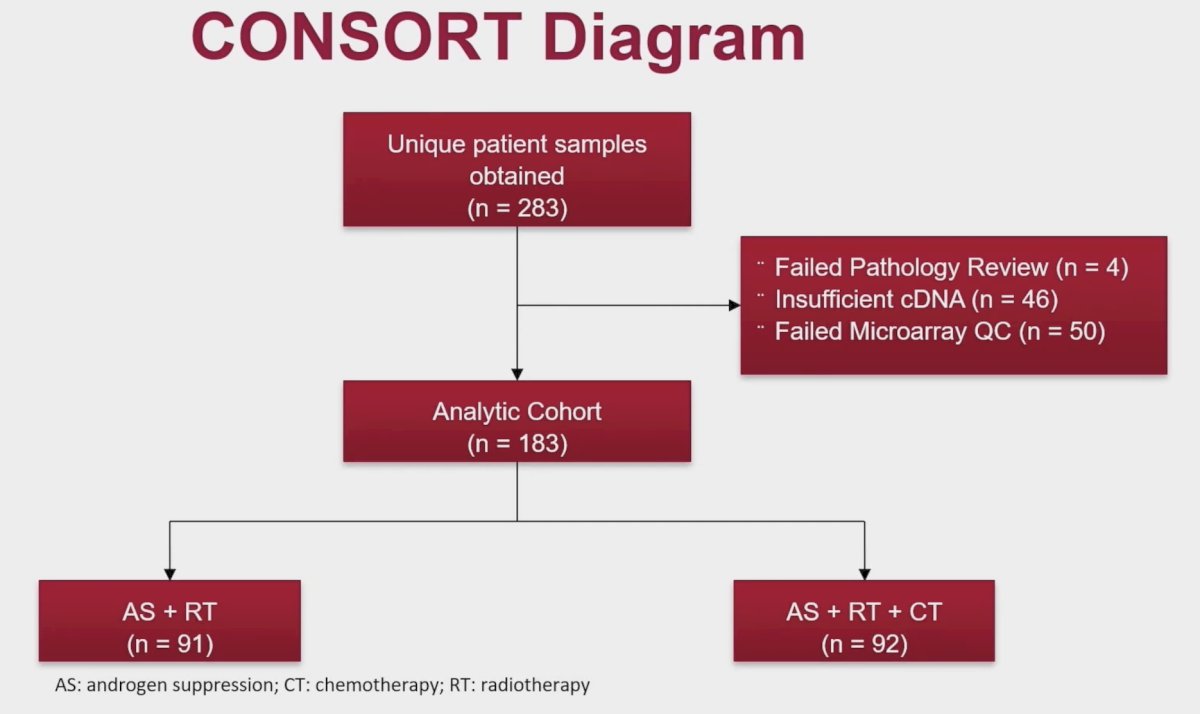
The median age was 66 years, median PSA was 19.3 ng/uL (IQR: 8.1-41.4), 81% had clinical stage >=T2 and 80% had Gleason score =8 (47% =9). The median genomic classifier score was 0.55 (IQR: 0.38-0.78) and overall the arms were balanced for key covariates. With a median follow-up of 9.9 years (IQR: 9.3, 10.7), 67 metastasis-free survival events including 34 distant metastases were observed.
On multivariable analyses, only the genomic classifier (per 0.1 unit) was independently associated with metastasis-free survival (HR 1.12, 95% CI 1.01-1.25):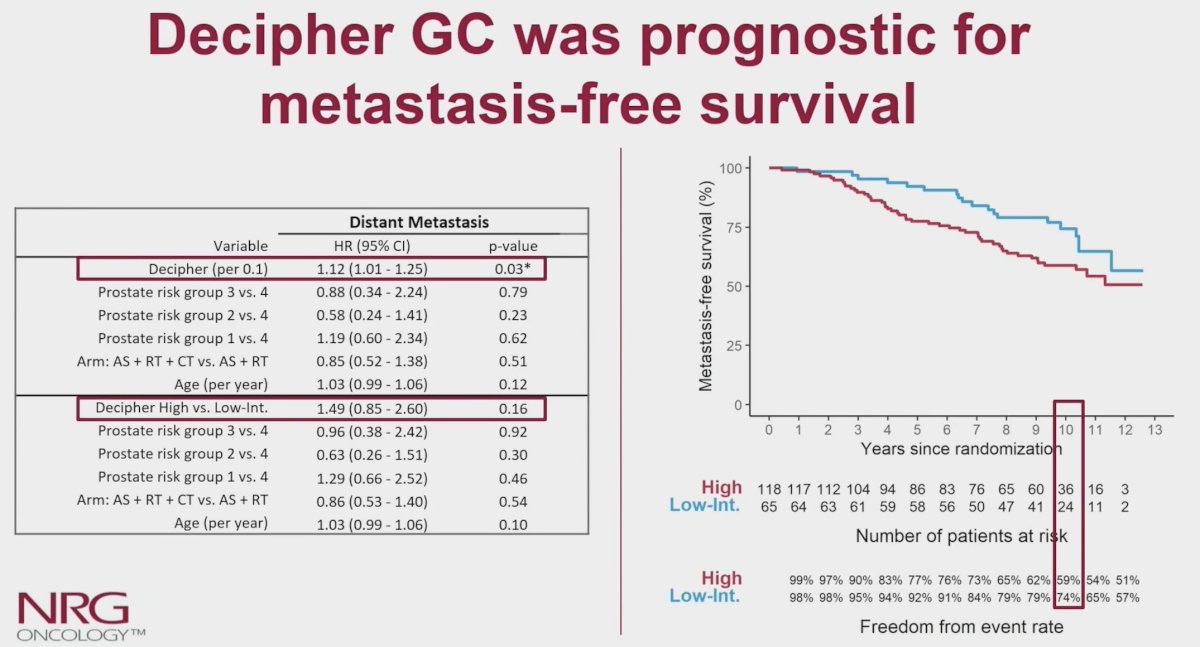
Additionally, the genomic classifier (per 0.1 unit) was independently associated with distant metastases (sHR 1.22, 95% CI 1.06-1.41), whereas the 4 pre-defined trial risk groups used for stratification (based on Gleason score, T-stage, and PSA), randomization and patient age were not. For categorical assessment of the genomic classifier, on multivariable analyses, higher-risk genomic classifier patients (65%) had worse distant metastases (sHR 2.46, 95% CI 1.18-5.13) compared to those with lower genomic classifier. Cumulative incidence of distant metastases at 10-years was 27% for higher genomic classifier vs 9% (95% CI 7-18%) for lower genomic classifier: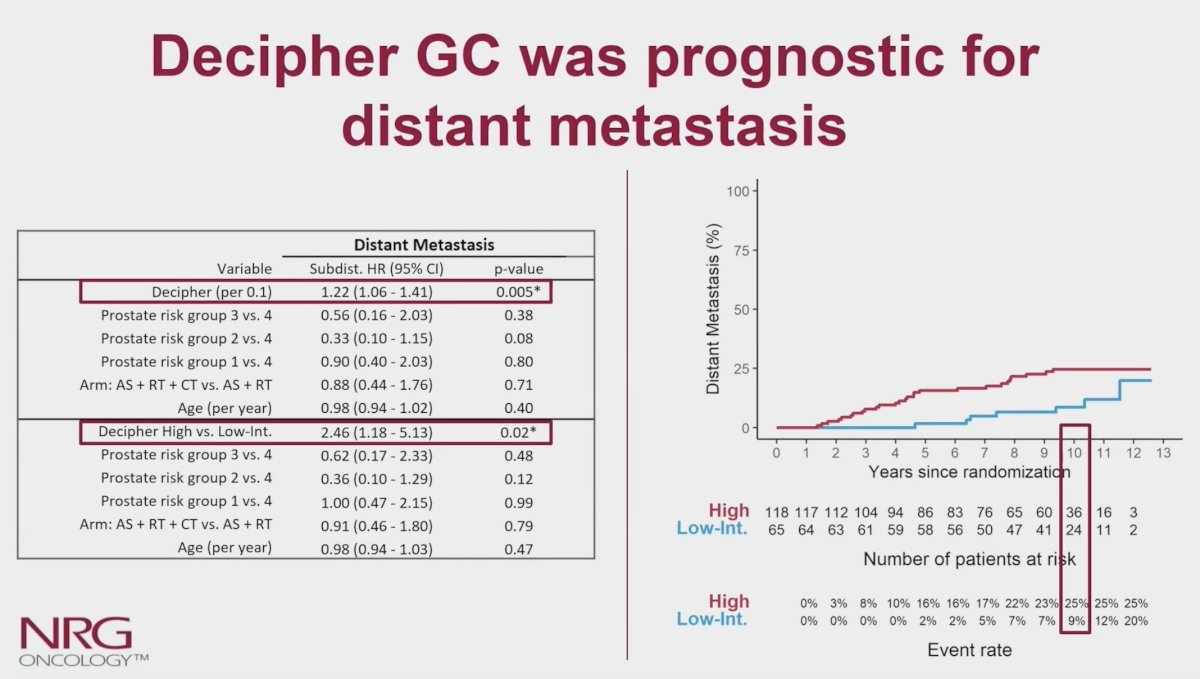
Furthermore, there was no significant genomic classifier interaction with docetaxel, although these were small subgroups and underpowered: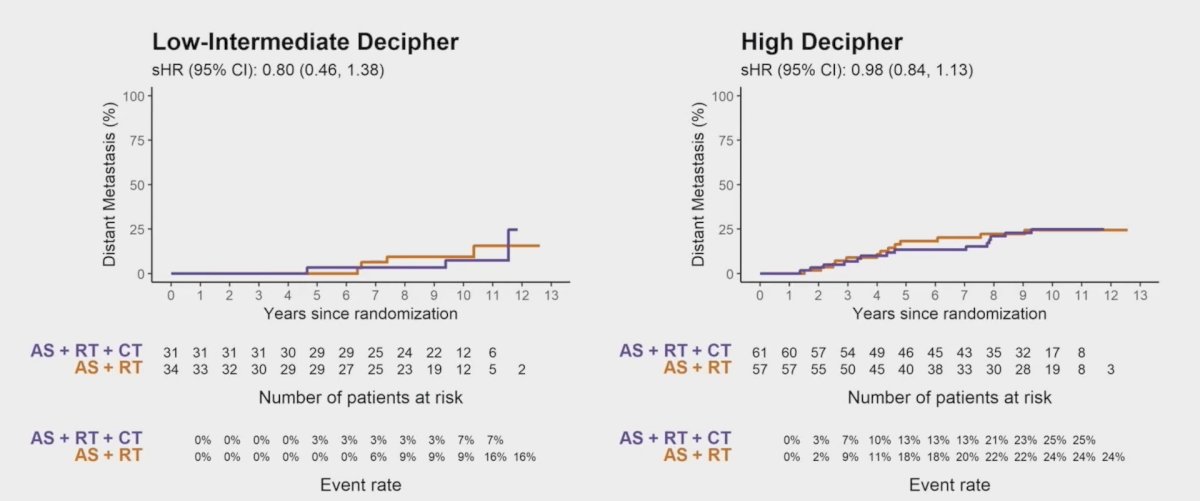
Finally, Dr. Phillips and colleagues generated a prostate subtype classifier (assessing luminal/basal profiling), noting that it predicts OS benefit from docetaxel:
Dr. Phillips concluded his presentation discussing validation of a genomic classifier in the NRG Oncology/RTOG 0521 phase III trial of docetaxel with androgen suppression and radiotherapy for localized high-risk prostate cancer with the following take-home points:
- Docetaxel does not improve overall survival for all-comers with high and very high risk prostate cancer
- The Decipher genomic classifier was independently prognostic for distant metastasis and metastasis free survival in patients treated on NRG/RTOG 0521 with large absolute differences in prognosis
- Luminal/basal profiling has shown predictive capabilities in two randomized trials (CHAARTED and NRG/RTOG 0521) testing use of docetaxel and warrants further investigation
Presented by: Ryan Phillips, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2023 American Society of Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, Sun, Oct 1 – Wed, Oct 4, 2023.
References:
- Rosenthal SA, Rodrigues GB, Sartor O, et al. Effect of chemotherapy with docetaxel with androgen suppression and radiotherapy for localized high-risk prostate cancer: The Randomized Phase III NRG Oncology RTOG 0521 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 10;37(14):1159-168.
- Sartor O, Karrison TG, Sandler HM, et al. Androgen deprivation and radiotherapy with or without docetaxel for localized high-risk prostate cancer: Long-term follow-up from the randomized NRG Oncology RTOG 0521 Trial. Eur Urol. 2023 Aug;84(2):156-163.


