(UroToday.com) The 2023 ASTRO annual meeting included a session on novel prognostication techniques for prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Ashesh Jani discussing the detection rate of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET in patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence at PSA levels <1 ng/mL in the phase 3 SPOTLIGHT study. Novel molecular imaging agents yield potential for localization of disease in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer when PSA levels are still low, and may facilitate early intervention with selective therapy to optimize outcomes. rhPET radiopharmaceutical, 18F-rhPSMA-7.3, is a novel high affinity PSMA-targeting ligand with potential for low bladder activity. The SPOTLIGHT study (NCT04186845) evaluated the diagnostic performance of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence, finding that it offers clinically meaningful verified detection rates for localization of recurrent prostate cancer.1 Based on this data, 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 is FDA approved for diagnostic PET of PSMA-positive lesions in men with prostate cancer with suspected metastasis who are candidates for initial definitive therapy and for those with suspected recurrence based on elevated serum PSA levels. Additionally, 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 was included in the latest NCCN update as a recommended imaging agent for patients with prostate cancer, including to stratify patients for treatment with LuPSMA. At ASTRO 2023, Dr. Jani and colleagues reported findings from a post-hoc analysis of SPOTLIGHT data, which determined the 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 detection rates at low-very low PSA levels.
Patients enrolled in SPOTLIGHT underwent PET 50–70 min after IV administration of 296 MBq 18F-rhPSMA-7.3. Scans were evaluated by 3 blinded central readers, with the majority read representing agreement between >= 2 independent readers. For the present analysis, all patients with an evaluable 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET and who had a baseline PSA <1 ng/mL were selected:

Overall (patient-level) and regional detection rates by majority read were determined, stratifying detection rates according to the patients’ baseline PSA level (<0.2, >=0.2 – <0.3, >=0.3 – <0.5, and >=0.5 – <1 ng/mL). In total, 389 patients (median PSA, 1.10 [range: 0.03–135] ng/mL, 84 with intact prostate) had an evaluable 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scan. The overall detection rate was 83% (322/389) by majority read. Of the 389 patients with an evaluable 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scan, 188 had a baseline PSA <1 ng/mL and were eligible for the present analysis. The baseline characteristics of these patients are as follows:
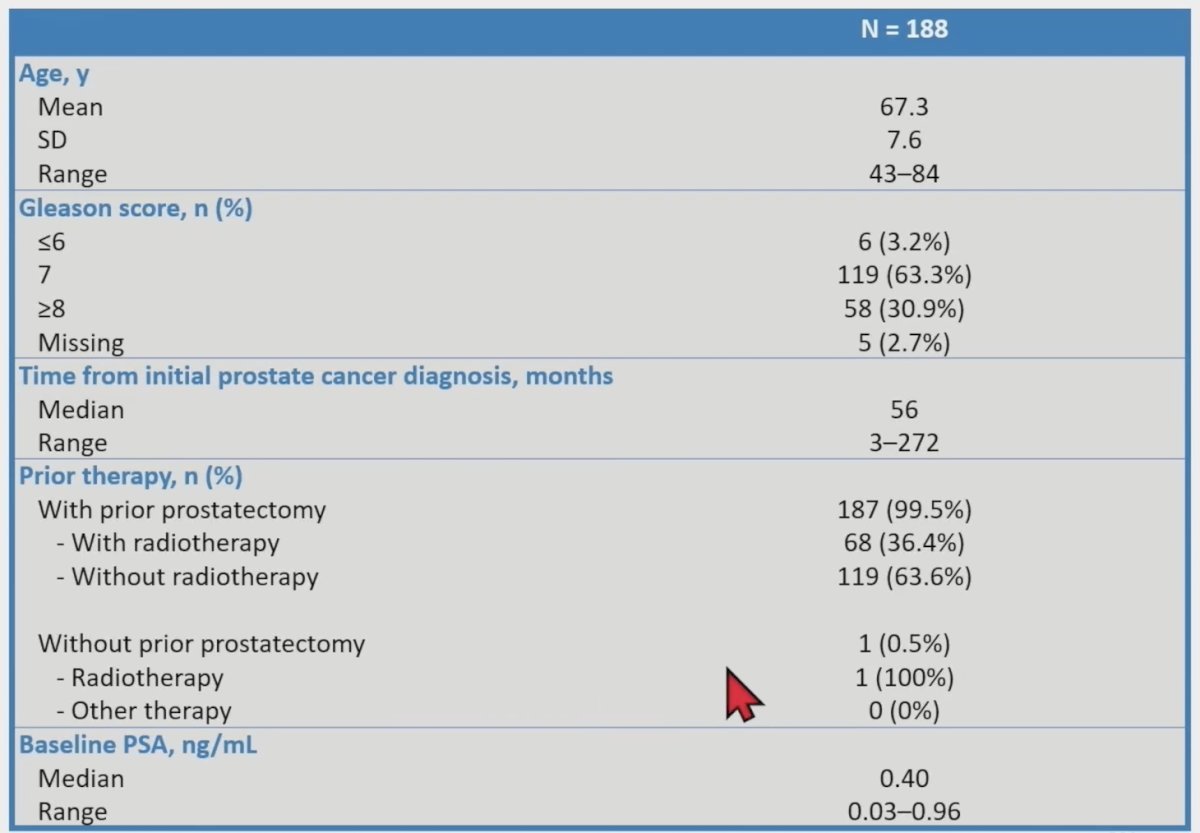
Despite low patient numbers in some PSA categories, moderate to high detection rates were observed, with the patient-level detection rate shown to increase with increasing baseline PSA:
Overall, 68% (128/188) of patients with a PSA <1 ng/mL and 64% (77/121) of patients with a PSA <0.5 ng/mL had a positive 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scan by majority read. Regional detection rates were broadly consistent across all PSA categories. Of note, extrapelvic lesions were observed in 21% (25/121) of patients with a PSA <0.5 ng/mL and 27% (51/188) of all patients with a PSA <1 ng/mL. As follows are detection rates stratified by PSA level for the prostate/prostate bed, pelvic lymph nodes, and other extrapelvic sites:

Dr. Jani concluded his presentation by discussing the detection rate of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET in patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence at PSA levels <1 ng/mL in the phase 3 SPOTLIGHT study with the following take-home messages:
- Among this cohort of 188 patients with low-very low PSA levels, more than two-thirds were found to have positive 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 scans
- Of clinical significance, over a quarter of patients had extrapelvic findings
- 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 PET may be a useful tool for treatment planning in patients with early biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer and may support early intervention with selective therapy to optimize outcomes
Presented by: Ashesh Jani, MD, Emory University, Atlanta, GA
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2023 American Society for Therapeutic Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) 65th Annual Meeting held in San Diego, CA between October 1st and 4th, 2023
References:
- Jani AB, Ravizzini GC, Gartrell BA, et al. Diagnostic performance and safety of 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 positron emission tomography in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence: Results from a phase 3, prospective, multicenter study (SPOTLIGHT). J Urol. 2023 Aug;210(2):299-311.


