(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) annual meeting held in Washington D.C., between September 29 and October 2 was host to the session EDU 16 - Management of Unfavorable Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer: Role of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT), Brachytherapy and Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Dr. Yash Soni presented a Bi-Institutional Safety Analysis of Combining Radiotherapy and Enfortumab Vedotin in Advanced Urothelial Cancer.
The landscape of advanced urothelial carcinoma is rapidly evolving with the introduction of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), which combine a cytotoxic payload with tumor-specific antibodies. Enfortumab vedotin (EV) has demonstrated improved overall survival (OS) both as a monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab.1 However, the role of EV in conjunction with radiation therapy (RT) requires further analysis, particularly due to the lack of safety data regarding this combination. In breast cancer, ADCs paired with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) have shown a risk of symptomatic radionecrosis, reported in 7.1% of patients with brain metastases.2 This highlights significant challenges for palliation and the development of clinical trials in the context of advanced urothelial carcinoma.
This study was a retrospective analysis conducted between 2020 and 2024, focusing on patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) who received palliative radiation therapy either one month prior to, concurrently with, or one month after enfortumab vedotin administration. In this analysis, RT was categorized as either higher or lower intensity, and RT locations were classified as pelvic (with or without bladder involvement) or extrapelvic with or without the central nervous system (CNS). The primary outcomes of interest included the discontinuation of EV therapy due to disease progression or toxicity, as well as the attribution of any toxicity either to RT or EV. An overview of the study is presented below:
The overall cohort comprised 60 patients treated with EV and RT, encompassing a total of 118 RT courses. The investigators conducted a sub-analysis focusing on RT administered within six months prior to the completion of EV treatment. In this analysis, the RT target was identified as follows: 55% of cases involved extrapelvic non-CNS regions, 22% targeted the pelvis without including the bladder, 19% involved the pelvis with the bladder, and 4% focused on the CNS.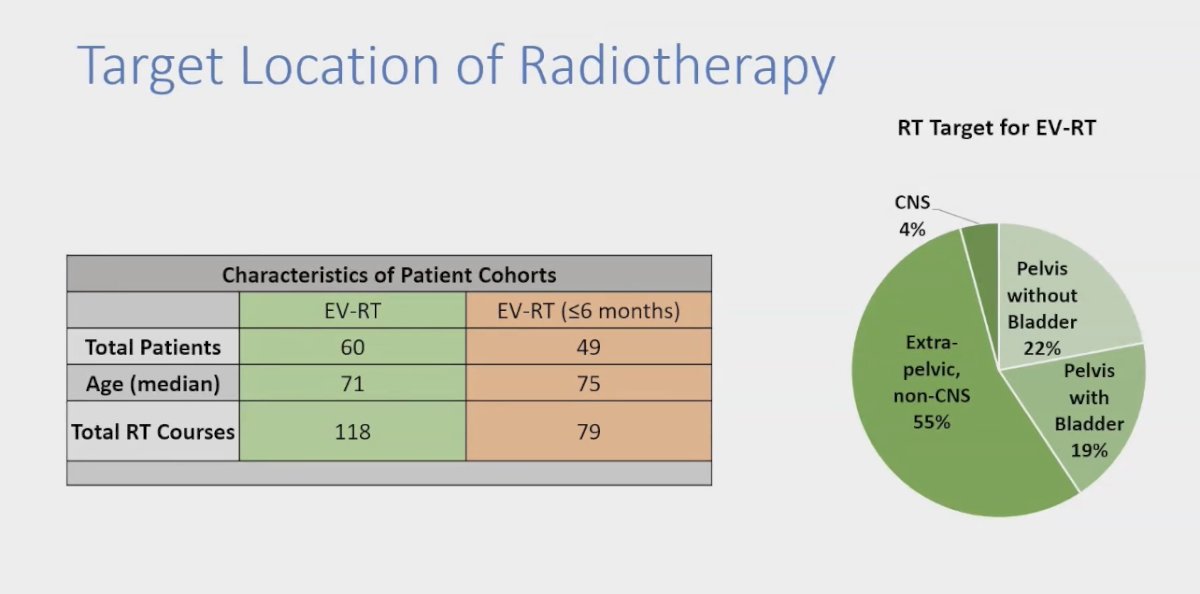
When examining the timing of RT in relation to EV infusion, a total of 79 RT courses were administered within six months of EV treatment. Specifically, 22 RT courses were given prior to EV, 40 courses were administered concurrently with EV, and 17 courses were provided after the EV infusion.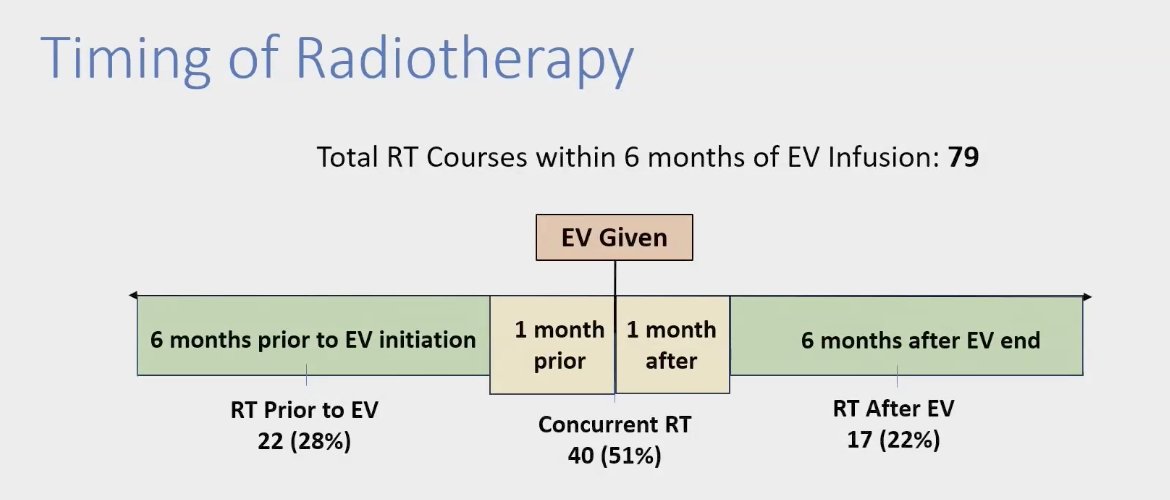
EV had to be stopped in 7/30 (23%) patients due to toxicity. The most common treatment-limiting toxicities were
- Neuropathy (57%)
- Skin (29%)
- Pneumonitis (14%)
However, none of these toxicities were deemed likely attributable to RT based on location or timing. Each patient and RT course were analyzed regarding their location and timing; for example, if a patient experienced skin toxicity, the rash was evaluated to determine if it was within the RT field.
The investigators analyzed if higher vs. lower intensity of the RT were associated with toxicity. In this study 42.3% received high-intensity RT (i.e. 30Gy in 5fx, 20Gy in 1fx, 60Gy in 5fx) and 76.6% low-intensity RT. They noted that 1/10 courses delivered concurrently and discontinued due to toxicity were in the higher intensity group. However, no treatment-limiting toxicities could be attributed the higher intensity RT in these patients. The biological effective dose (BED): (a/b=10) range: between 48 - 151.2Gy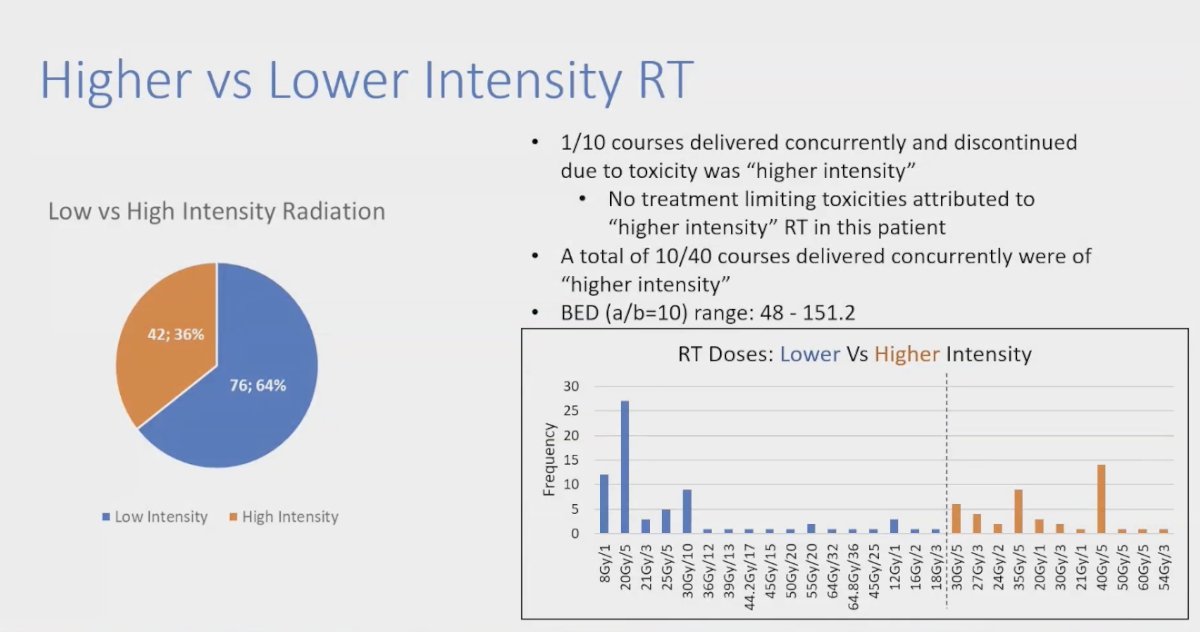
Dr. Soni concluded his presentation by saying that
- The EV discontinuation rate was 23%, consistent with prior studies (16.9% in the EV-301 trial).
- No evidence of increased toxicity was observed within RT fields, regardless of sequence or intensity.
- Data suggests that palliative RT can safely be administered to patients currently on EV.
- This could lead to early-phase studies of EV + RT in localized muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC)
- The STAR EV trial is investigating SBRT combined with 3 cycles of EV in cisplatin-ineligible patients planned for radical cystectomy.
- Results from the STAR EV trial will shed light on the combination of ADCs and RT in a randomized clinical trial setting.
Presented by: Yash Soni, MD, BS, PGY3 Department of Radiation Oncology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) annual meeting held in Washington D.C., between the 29th of September and the 2nd of October.
References:- Powles T, Valderrama BP, Gupta S, Bedke J, Kikuchi E, Hoffman-Censits J, Iyer G, Vulsteke C, Park SH, Shin SJ, Castellano D, Fornarini G, Li JR, Gümüş M, Mar N, Loriot Y, Fléchon A, Duran I, Drakaki A, Narayanan S, Yu X, Gorla S, Homet Moreno B, van der Heijden MS; EV-302 Trial Investigators. Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab in Untreated Advanced Urothelial Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 7;390(10):875-888. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2312117. PMID: 38446675.
- Lebow ES, Pike LRG, Seidman AD, Moss N, Beal K, Yu Y. Symptomatic Necrosis With Antibody-Drug Conjugates and Concurrent Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases. JAMA Oncol. 2023 Dec 1;9(12):1729-1733. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4492. PMID: 37883079; PMCID: PMC10603573.


