(UroToday.com) The 2024 ASTRO annual meeting included a session on novel prognostic tools in prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Kosj Yamoah discussing the VANDAAM Study, assessing the impact of Decipher® testing on treatment recommendations in African American and non-African American men with prostate cancer.
African American men have an increased burden from prostate cancer, with the highest incidence and mortality rates. Notably, prostate cancer-specific outcomes are identical only if there is a timely diagnosis and adequate and equitable treatment delivery. In the era of precision oncology, genomic risk classifiers, such as the Decipher® score, have enhanced the personalization of care for patients with localized prostate cancer. Nonetheless, few prospective studies have prioritized the recruitment of African American men to provide level-I evidence to support the generalizability of these genomic risk classifiers in African American men who endure the disproportionate burden of prostate cancer. At the ASTRO 2024 annual meeting, Dr. Yamoah reported the first prospective validation of the Decipher® genomic risk classifier in predicting biochemical recurrence in African American men.
The final analytical cohort included 207 evaluable cases (104 African American men, 103 non-African American) with both genomic and clinical outcome data. The consort diagram for this study is as follows: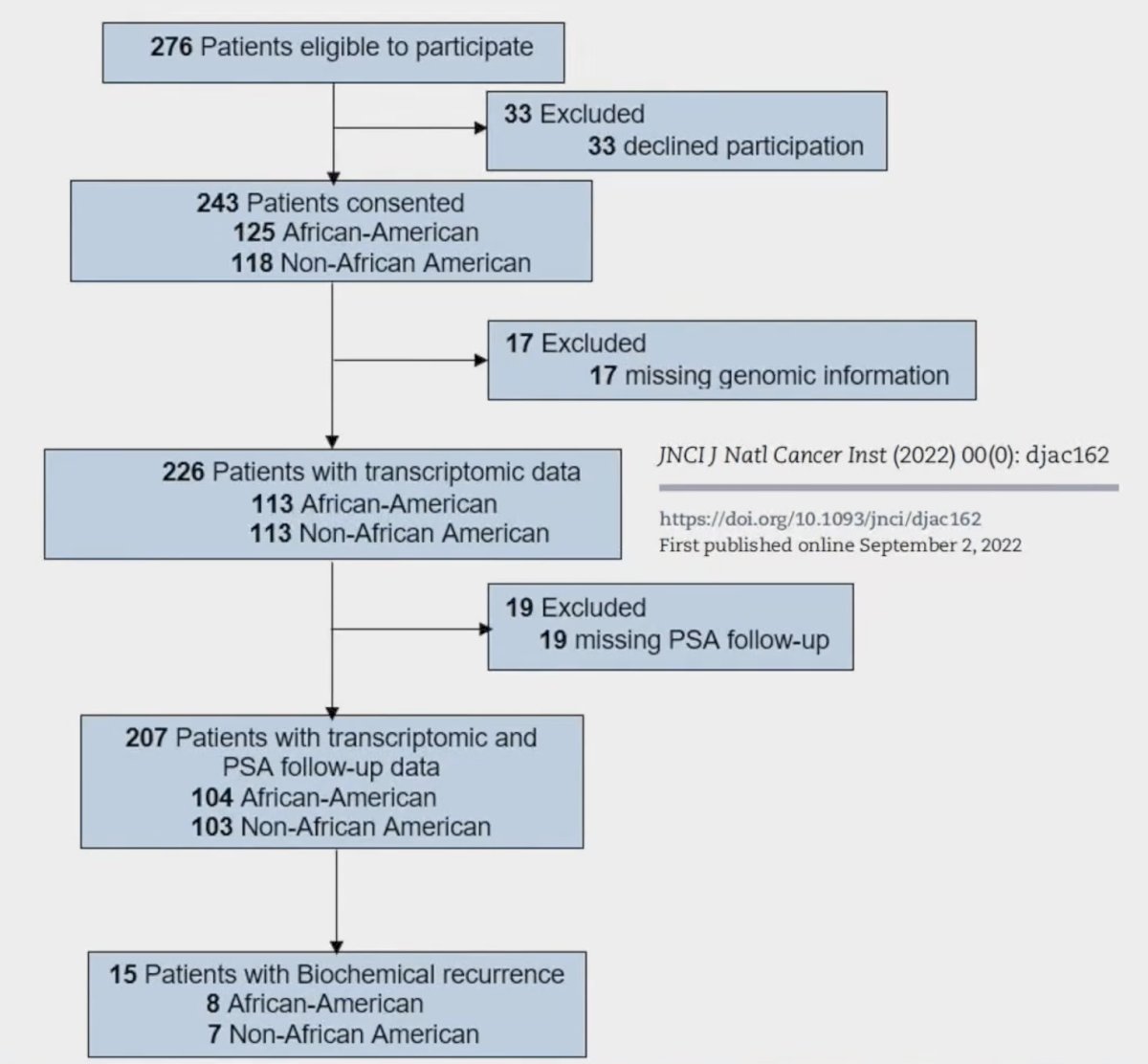
Baseline disease characteristics were as follows, stratified by race: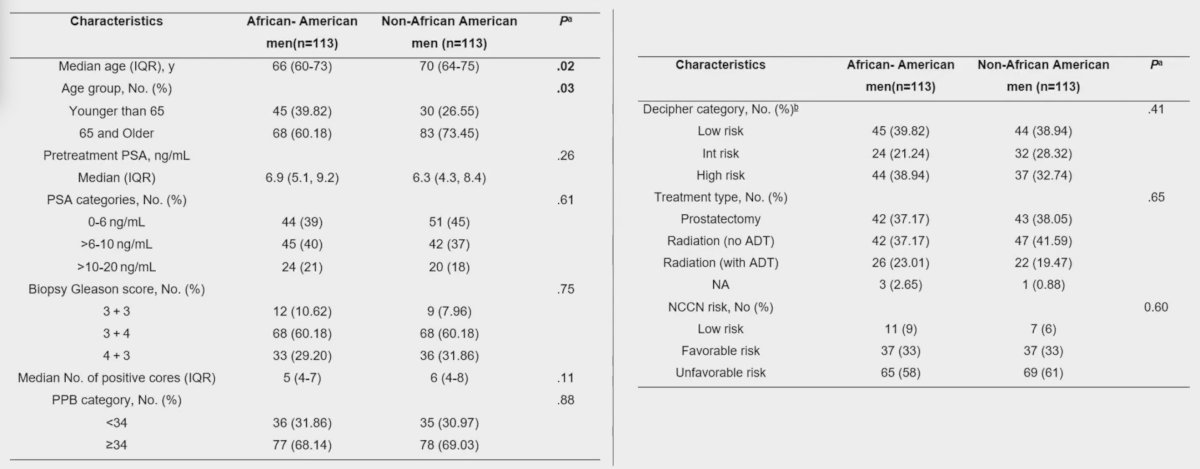
In the surgical cohort (n =74), biopsy and radical prostatectomy-derived genomic risk classifier scores exhibited a 77% concordance rate, defined as no reclassification in genomic risk classifier-based risk categories: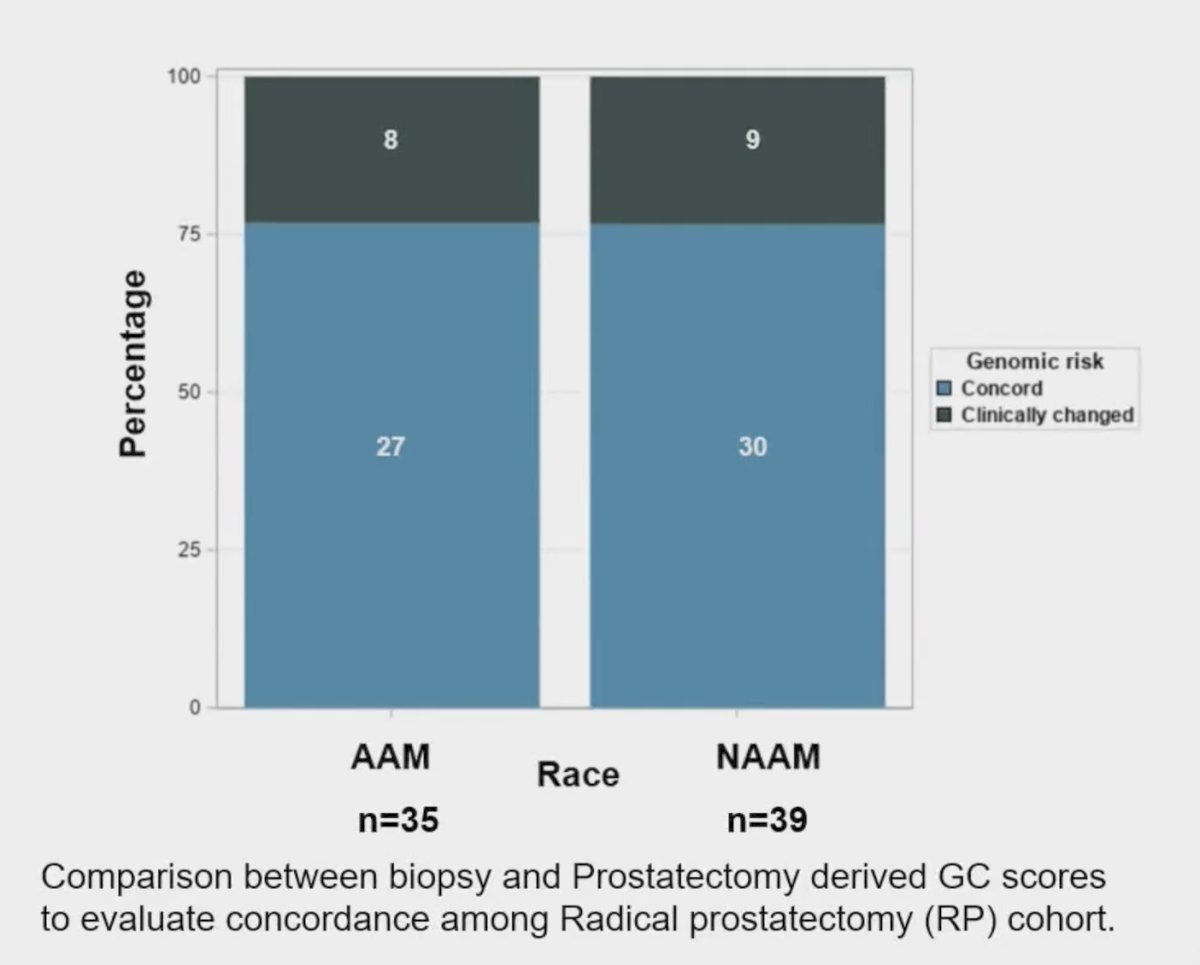
Among cases with discordant genomic risk classifier scores (23%), 80% of patients with low-risk biopsy genomic classifier reclassified as high-risk genomic classifier following radical prostatectomy had anterior located tumors: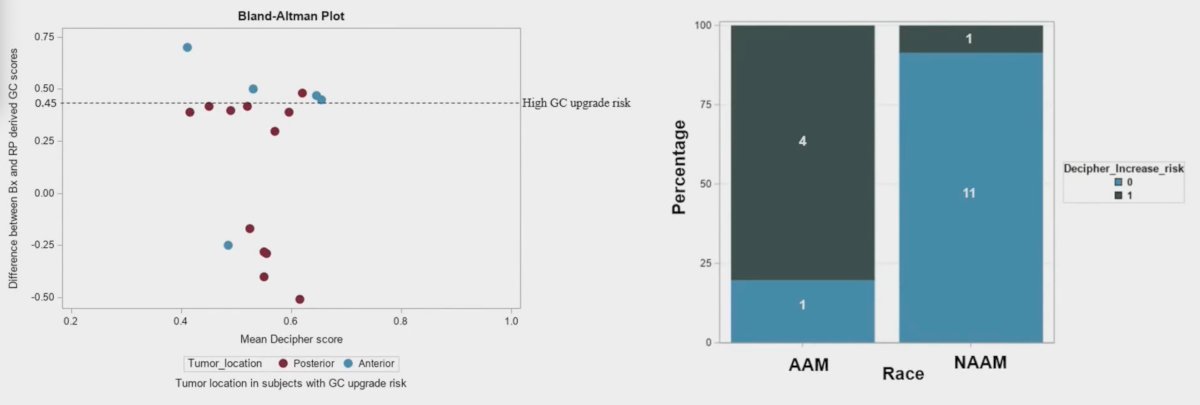
Patients with low genomic classifier scores had a 23-fold likelihood to reclassify as high genomic classifier after radical prostatectomy if they had anteriorly located tumors (OR 23, 95% CI 1.56-338). High-risk genomic risk classifier was associated with an 8-fold increased risk of biochemical recurrence as compared to low-risk counterparts (HR 7.93, 95% CI, 1.71-36.75). When adjusted for other clinicopathological variables, the high risk genomic classifier remained at a significantly higher biochemical recurrence risk (HR 8.97, 95% CI 1.77-45.37):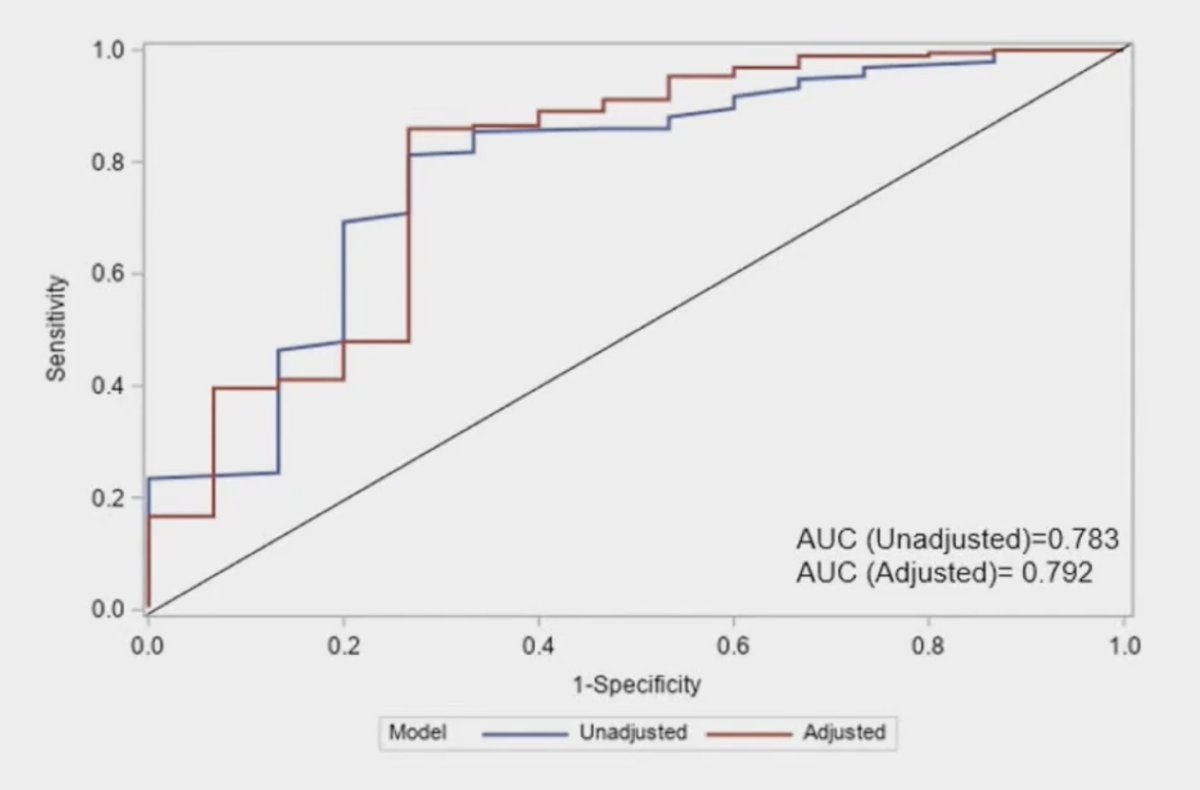
On exploratory analysis, African American patients had improved outcomes with radiotherapy with regards to biochemical recurrence-free survival compared to those undergoing radical prostatectomy (p = 0.004), whereas there was no difference in outcomes for non-African American men: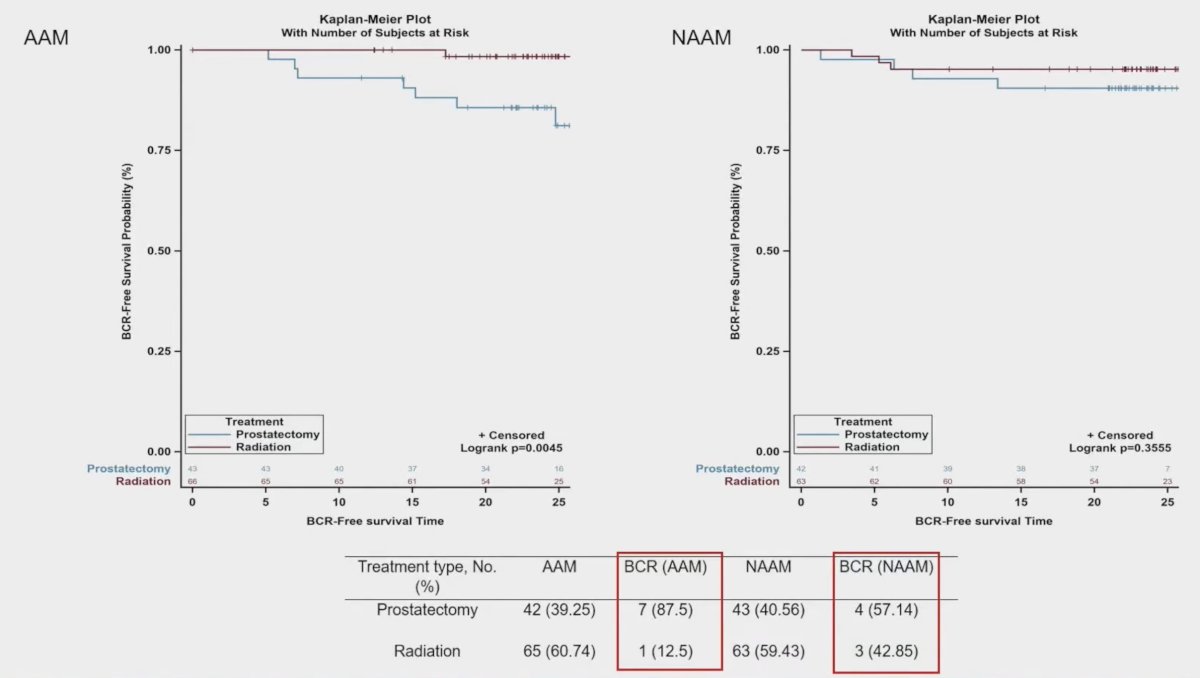
Dr. Yamoah concluded his presentation discussing the VANDAAM Study with the following take-home points:
- The Decipher® genomic classifier is a strong predictor for rapid onset of biochemical recurrence within 2-year in both African American and non-African American men
- There was no significant interaction in predictive performance of genomic classifier across either rate or treatment (radical prostatectomy versus radiotherapy) groups.
- Biochemical recurrence-free survival probability was significantly higher for African American men with radiotherapy compared to those who underwent surgery as their primary treatment.
- African American men with prostatectomy as their primary treatment had a shorter time to biochemical recurrence.
- In non-African American men, there was no significant difference seen among treatment groups regarding time to biochemical recurrence.
- This study provides level-I evidence for integrating genomic classifiers into clinical practice guidelines to improve risk stratification and management for African American patients with early-stage prostate cancer
Presented by: Kosj Yamoah, MD, PhD, Radiologist, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, Tampa, FL
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, Sun, Sept 29 – Wed, Oct 2, 2024.


