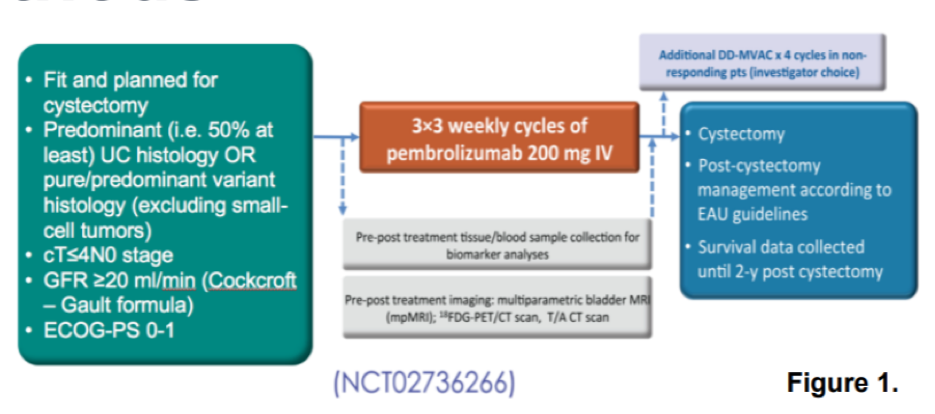
To do so, the authors utilized a secondary analysis of patients enrolled in the PURE-01 study: Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab for Muscle-invasive Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma. To briefly summarize, in PURE-01 (NCT02736266), patients received 3 courses of 200 mg pembrolizumab, every 3 weeks, prior to RC. Imaging assessment was performed using a thorax-abdomen CT scan and with PET/CT scan during screening and after treatment, before RC. Imaging review and analysis was performed by two experienced nuclear medicine physicians blinded to clinical information with semiquantitative and volumetric analysis performed.
For each patient with identified increased activity in abdominopelvic lymph nodes, the SUVmax and the short-axis size of the most intense lymph node were recorded. All patients underwent templated pelvic LN dissection (LND) with packeted node submission at the time of radical cystectomy.
In this analysis, the authors assessed PET/TC diagnostic ability using sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value (NPV), positive predictive value (PPV), and accuracy with surgical pathology considered the gold standard.
Between February 2017 and June 2019, 114 patients were enrolled and treated in PURE-01. 11 of these patients received additional chemotherapy post-pembrolizumab and were excluded from the analyses, resulting in 103 total evaluable patients for whom there were a total of 206 PET/CT scans.
Six pts (5.8%) had positive nodes at baseline PET/CT with a mean SUVmax of 2.75 and a mean short axis length of 6.2 mm. Following neoadjuvant pembrolizumab, eight patients (7.8%) had positive LN at PET/CT with a mean SUVmax of 4.21 and a mean short axis length of 7.2mm.
The rate of pathologic LN positive (pN+) disease was 15.5% (16 patients). The performance of PET/CT in predicting pN+ disease is indicated in the table below:
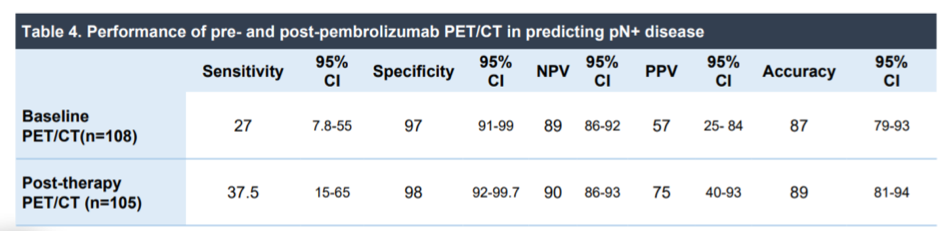
In short, PET/CT has relatively poor sensitivity but quite high specificity. While predictive values are sensitive to disease prevalence, in this study population positive predictive value was 75% while negative predictive value was 89.5%.
4 of 6 patients (66.7%) with baseline FDG uptake were found to have nodal positive disease at the time of LND while 12 of 97 (12.4%) with no baseline FDG uptake had node-positive disease (p=0.005).
A total of 39 pts (37.9%) developed inflammatory FDG-uptakes post-pembrolizumab in several target organs/regions: top 5 sites were thyroid (N=21, 61.8%), stomach and mediastinum (13 pts each, 12.6%), lung (N=10, 9.7%), other lymph nodes (N=4, 3.9%). These changes were clinically evident (signs/symptoms or laboratory changes) in 15 pts (38.5%).
Presented by: Laura Marandino, MD, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, Italy; Andrea Necchi, MD, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan, Italy
Written by: Christopher J.D. Wallis, MD, PhD, Urologic Oncology Fellow, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, USA, Twitter: @WallisCJD, at the 2020 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Virtual Experience #AUA20, June 27- 28, 2020.


