The authors retrospectively reviewed the BAUS registry to identify patients from England, who underwent nephrectomy for a non-benign diagnosis between 2016 and 2018.
They identified 18,369 nephrectomies for malignant disease, taking place across 145 centers by 272 surgeons. Using Hospital episode statistics (HES) as the comparator, the BAUS nephrectomy dataset for England (2016-18) was deemed to be 91.3% complete.
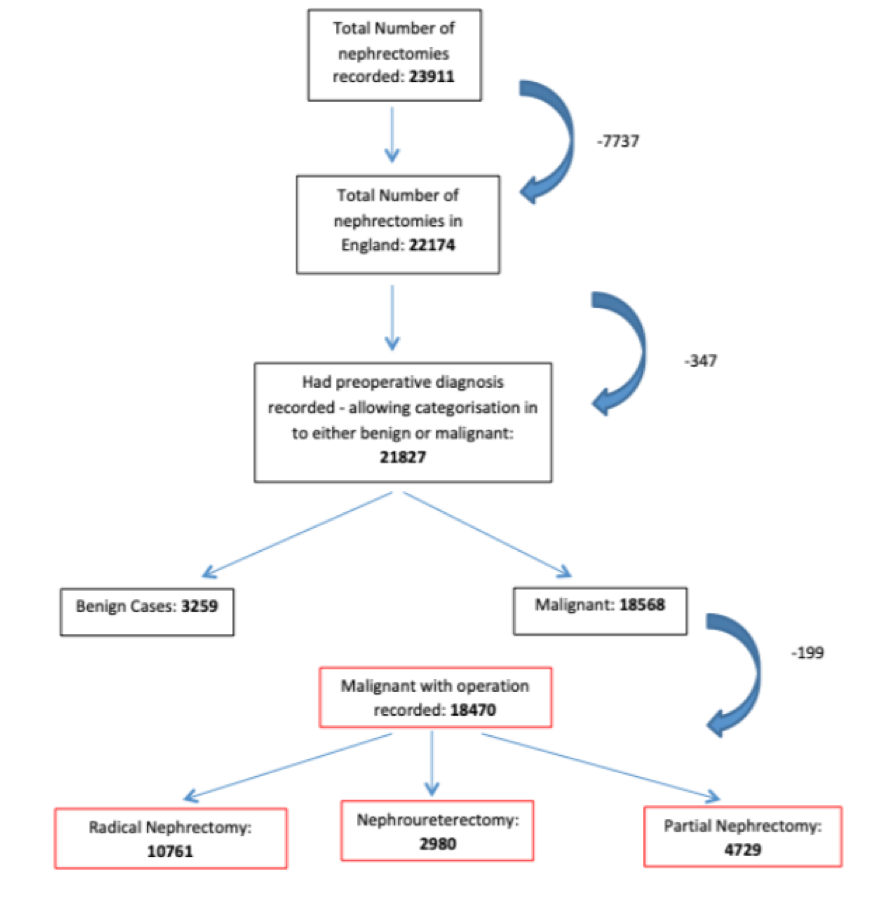
The authors then divided cases into three categories: radical nephrectomy (RN) (58.3%), nephroureterectomy (NU) (16.1%) & partial nephrectomy (PN) (25.6%). Each was individually analyzed focussing on patient demographics, presentation, intraoperative, postoperative, surgical volume & histological variables.
Across all three subgroups, the median patient age was 66 and 64.1% of patients were male. Preoperative diagnosis was recorded as renal mass in 84.5% & upper tract transitional cell carcinoma in 15.5%. Overall, 74.4% of PN and 50.3% RN were performed for incidental findings, while 66.2% of patients undergoing a NU had presented symptomatically with hematuria. Pre-operative biopsies were performed infrequently for renal masses (7.1% of RN and 17.3% of PN), and somewhat more commonly for nephroureterectomy (39.9%).
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) was undertaken in 80.0% of cases with robotically-assisted surgery being the predominant surgical approach in PN (62.2%). Conversion to open remained rare, with rates ranging from 3.1% in RN to 2.1% in NU & 1.79% in PN.
Transfusion was uncommon overall, occurring in 6.3% of patients undergoing RN, 3.4% in patients undergoing NU & 2.1% in patients undergoing PN. Median length of stay was 3 days in patients undergoing RN & PN and 4 in patients undergoing NU.
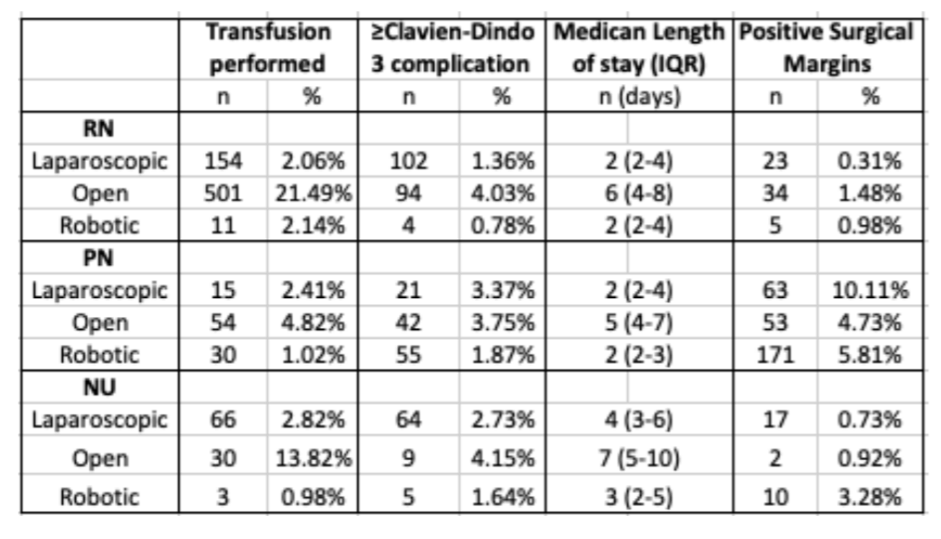
In terms of pathologic characteristics, clear cell renal carcinoma was the most commonly reported final histology in 77% of RN & 65% of PN while upper tract urothelial carcinoma accounted for 84% of NU cases. Benign final histology was present in a relatively small subset of patients: 3.2% (RN), 3.7% (NU) & 13.4% (PN).
These data provide an opportunity for improvement in care both at the individual surgeon level through benchmarking and at a health systems level through the centralization of care. Further, they allow for patients to have an informed expectation pre-operatively.
Presented by: John Pascoe, BMBS, MRCS, PgCert(ClinEd), Clinical Research Fellow in Urology, Royal Devon & Exeter NHS Foundation Trust, Exeter, Devon, UK
Written by: Christopher J.D. Wallis, Urologic Oncology Fellow, Vanderbilt University Medical Center Contact: @WallisCJD on Twitter at the 2020 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Virtual Experience #AUA20, June 27- 28, 2020


