(UroToday.com) Dr. Clara Cerrato and colleagues held an intriguing presentation regarding the impact of surgical modality on functional outcomes for the treatment of patients with complex renal mass (CRM). Although partial nephrectomy (PN) remains an accepted method of treatment for exophytic renal mass, its oncological efficiency in the utilization for CRM remains highly controversial. Moreover, there exists a paucity in literature regarding a direct comparison of the outcomes and effectiveness between PN and radical nephrectomy (RN) for CRM patients. Provided this, Dr. Cerrato et al. aimed to explore this comparison, with respect to post-operative renal functional outcomes.
Through a retrospective analysis of a multicenter, international registry (ROSULA), the researchers analyzed 969 patients (median FU 24.0 months) undergoing either robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (n=540) or minimally invasive radical nephrectomy (n=429). RENAL Nephrectomy Score 10-12 was used to define CRM. Primary and secondary outcomes included development of de-novo estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <45 ml/min/1.73m2, and de-novo eGFR<60 and DeGFR between diagnosis and last follow-up, respectively. Statistical analysis was completed using Cox proportional hazards for predicting de-novo eGFR decline, linear regression for DeGFR, and a Kaplan-Meier Analysis (KMA) was used to analyze the 5-year freedom from DeGFR <60 and <45.
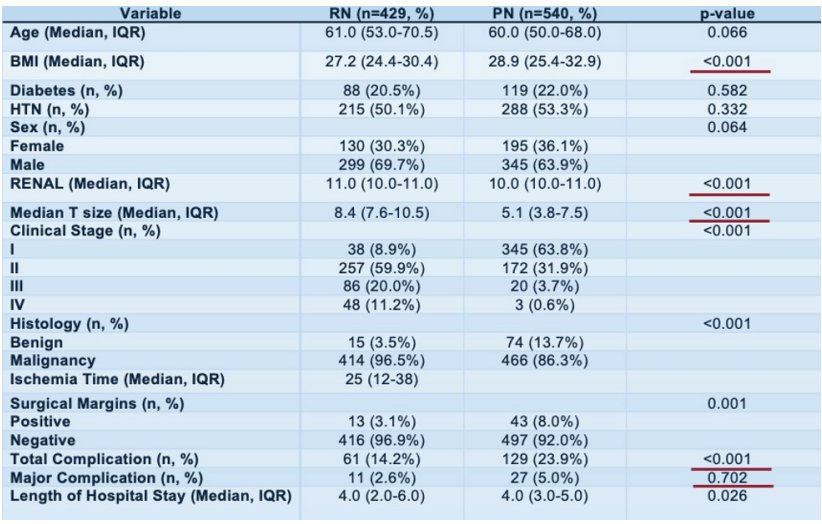
Although an increased post operative complication rate was observed in patients undergoing PN (p<0.001), there was no significant difference in major complications (Clavien III-IV; p=0.702). Risk factors for de novo eGFR <45 ml/min/1.73m2 included age, BMI, baseline eGFR, tumor size, and RN. Additionally, a multivariate analysis found that age, tumor size, RN, and BMI were risk for de novo eGFR<60 ml/min/1.73m2.
Moreover, KMA showed a worsened 5-year freedom from de-novo eGFR<60 (71% vs. 33%, p<0.001) and de-novo eGFR <45 (79% vs. 65%, p<0.001) for RN. Through their analyses, Dr. Cerrato and colleagues found that PN is not associated with an increased risk of complications, and can provide a functional benefit in CRM patients.
Dr. Cerrato concluded her presentation with the following message for this study assessing the impact of surgical modality on post-operative renal functional outcomes for CRM:
- PN provides a functional benefit for in select CRM patients without a significant increase in major complications in comparison to RN, and may be considered when technically feasible and indicated.
Presented by: Clara Cerrato, MD, University Hospital Southampton NHS Trust
Written by: Mariah Hernandez, Department of Urology, University of California, Irvine, @mariahch00 on Twitter during the 2023 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, April 27 – May 1, 2023


