(UroToday.com) The 2023 AUA annual meeting included a session on markers in prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Michael Leapman discussing the development of a longitudinal prostate cancer transcriptomic and real-world clinical data linkage. Genomic classifiers have been shown to be prognostic and impact clinical decision-making in retrospective studies. However, less is known about prognostic performance in the real-world clinical setting. Dr. Leapman and colleagues developed a novel linkage between the Decipher prostate genomic classifier and real-world patient data in the United States across payors and sites of care.
Clinical and transcriptomic data from clinical use of the Decipher prostate genomic classifier between 2013-2022 (Veracyte Inc., San Diego, CA) were linked with real-world data aggregated from insurance claims, pharmacy records, and Clarivate electronic health record data. Patients were anonymously linked between datasets by deterministic methods through a de-identification engine using encrypted tokens. The following is a schematic representation of data sources and the linkage structure:

The objective of this study was to develop algorithms for identifying prostate cancer diagnoses, treatment timing, and clinical outcomes (biochemical recurrence and prostate cancer metastases) in real-world data using diagnosis, CPT codes, pharmacy codes, SNOMED clinical terms, and unstructured text in the electronic health record. They then compared the accuracy of real-world data algorithms using clinical information obtained during Decipher testing as the reference standard.
A total of 92,976 of 95,578 (97.2%) patients with Decipher prostate genomic classifier were successfully linked to real-world data, including 53,871 from biopsy and 39,105 from radical prostatectomy tests. The median age at Decipher testing was 66.4 years [IQR 61.0, 71.0]. The concordance of prostate cancer diagnoses was 85.0%, including 80.8% for biopsy and 90.7% for radical prostatectomy. Year of treatment was concordant in 98.5% of patients undergoing genomic classifier testing at radical prostatectomy, and 87.8% in patients with biopsy genomic classifier tests:

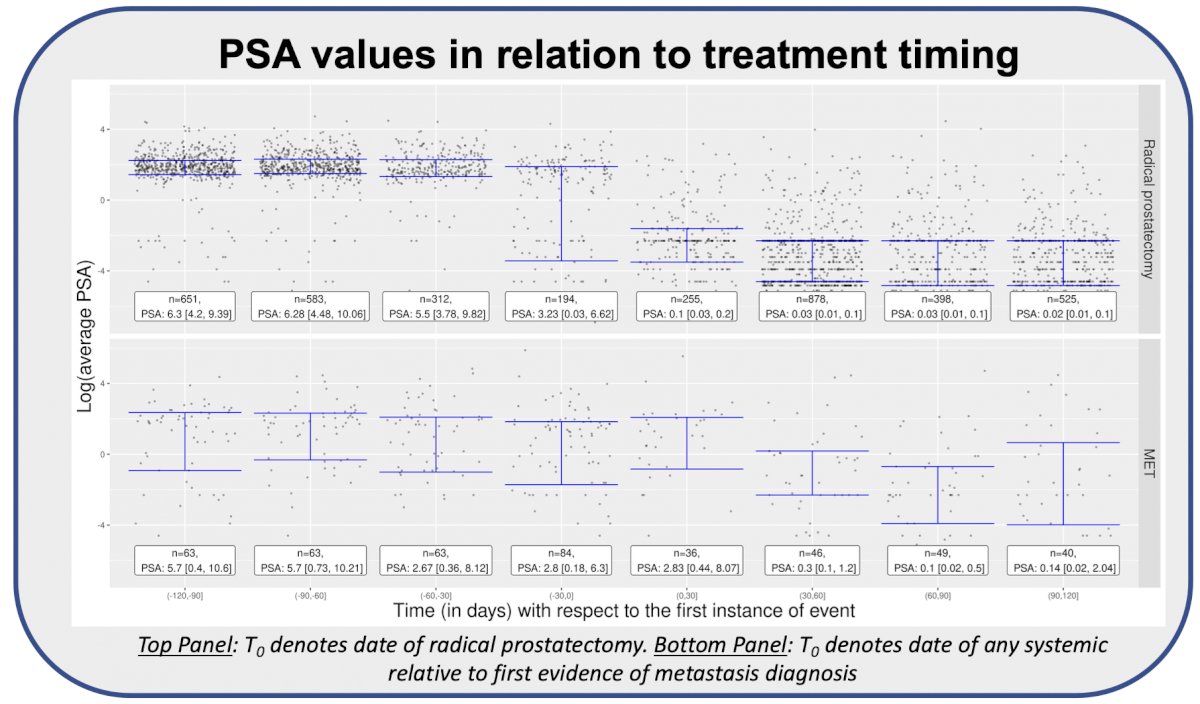
Biochemical recurrence was identified based on diagnosis code (R 97.21 of ICD-10) (96.3%), unstructured text (0.05%), and both in (3.65%). Similarly, metastases were identified based on diagnosis codes (94.9%), unstructured text (1.38%), and both (3.73%). PSA verification was achieved through numerical laboratory data, and declines correlated with timing of radical prostatectomy and systemic therapy:
Dr. Leapman concluded his presentation by discussing the development of a longitudinal prostate cancer transcriptomic and real-world clinical data linkage with the following take-home messages:
- This study establishes the first national-scale linkage of transcriptomic and longitudinal clinical data
- Achieved high accuracy for identifying key clinical junctures including diagnosis, treatment, and early cancer outcome
- This resource can be leveraged to enhance understanding of disease biology, patterns of care, and treatment effectiveness
Presented by: Michael Leapman, MD, MHS, Yale University, New Haven, CT
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2023 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, Chicago, IL, April 27 – May 1, 2023


