(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) annual meeting held in San Antonio, TX between May 3 and May 6, 2024, was host to the muscle-invasive bladder cancer podium session. Dr. Chiara Mercinelli presented the first results of NURE-Combo, a phase 2 study of neoadjuvant nivolumab (NIVO) plus nab-paclitaxel (ABX) followed by postsurgical adjuvant nivolumab in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).
Dr. Mercinelli started her presentation by highlighting that nearly 20% of patients diagnosed with urothelial cancer (UC) present with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), which carries a high risk of recurrence post-radical cystectomy (RC) and an estimated 5-year disease-free survival rate of approximately 50%. Various neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment modalities have been shown to improve overall survival (OS), with cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy increasing OS by nearly 6% at 5 years.1 However, up to 50% of MIBC patients are ineligible for cisplatin-based therapy, posing an unmet clinical need for this specific population.2
She proceeded to discuss data from phase 2 trials investigating neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in MIBC patients, revealing complete response (pCR; ypTONO) rates ranging from 30% to 45%.3 Nivolumab emerged as the first ICI to exhibit efficacy in high-risk MIBC post-RC, demonstrating a significantly prolonged DFS in the CheckMate 274 trial.4
Nab-paclitaxel (ABX), a 130nm particle formulation comprising albumin nanoparticles and paclitaxel with non-covalent bonds, is currently approved for treating various metastatic tumor types. In a phase II study (NCT00683059), ABX demonstrated an objective response rate (ORR) of 27.7% in 48 patients who had progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Moreover, in the PEANUT study (NCT03464734), ABX was evaluated in combination with pembrolizumab in 65 patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma who had progressed on or after cisplatin-based chemotherapy, yielding an ORR of 47.7%.5
Preliminary data suggest that the combination of ABX and NIVO exhibits activity in advanced urothelial carcinoma patients. In her presentation, Dr. Mercinelli presented the findings of an open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial investigating the combination of ABX + NIVO followed by RC and adjuvant NIVO in MIBC patients. The NURE-Combo trial enrolled patients meeting specific eligibility criteria.
- Cisplatin unfit or declined cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
- Previously untreated MIBC (cT2-4a N0, M0, as per CT, MRI, or 18-FDG PET-scan)
- ECOG performance status of 0 or 1
- Predominant (>50%) urothelial carcinoma histology
The treatment schedule was:
- Four cycles of nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks + nab-paclitaxel 125 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 of each 3-week cycle.
- Radical cystectomy
- 13 cycles of adjuvant nivolumab at the same dose/frequency.

The primary endpoint of this trial was:
- Pathologic complete response (pCR; ypT0N0)
The secondary endpoints included:
- Major pathological response (ypT≤1N0)
- Medical and surgical safety (CTCAE v5.0)
- Event-free survival
- Overall survival
- Biomarker analysis (comprehensive genomic profiling, PD-L1 expression, ctDNA monitoring [Signatera])
Dr. Mercinelli summarized the baseline patient characteristics, which are presented in the table below. A total of 31 patients were enrolled between December 2021 and June 2023. Among them, 38.7% had cT3-4 disease, and 6.5% had cN1 disease. Additionally, nearly half of the patients (48.4%) had a variant histology component.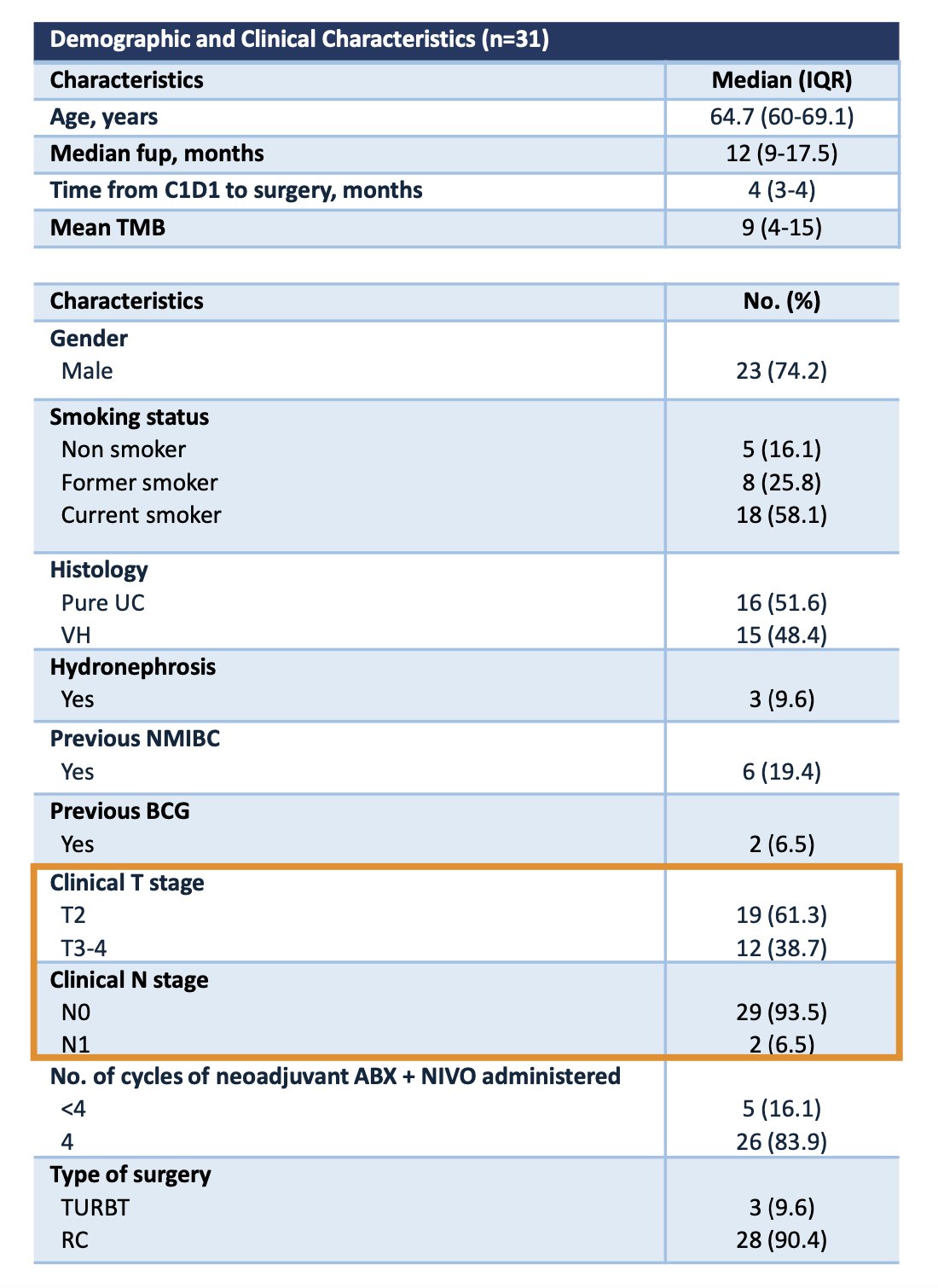
All 31 patients concluded the neoadjuvant therapy and underwent surgery. Three patients refused RC after evidence of clinical complete response (cCR) on MRI (VI-RADS 0) and cystoscopy evaluation. These patients were offered repeat TURBT before adjuvant NIVO, the pathology revealed ypT0 (n=2) and ypT1 (n=1).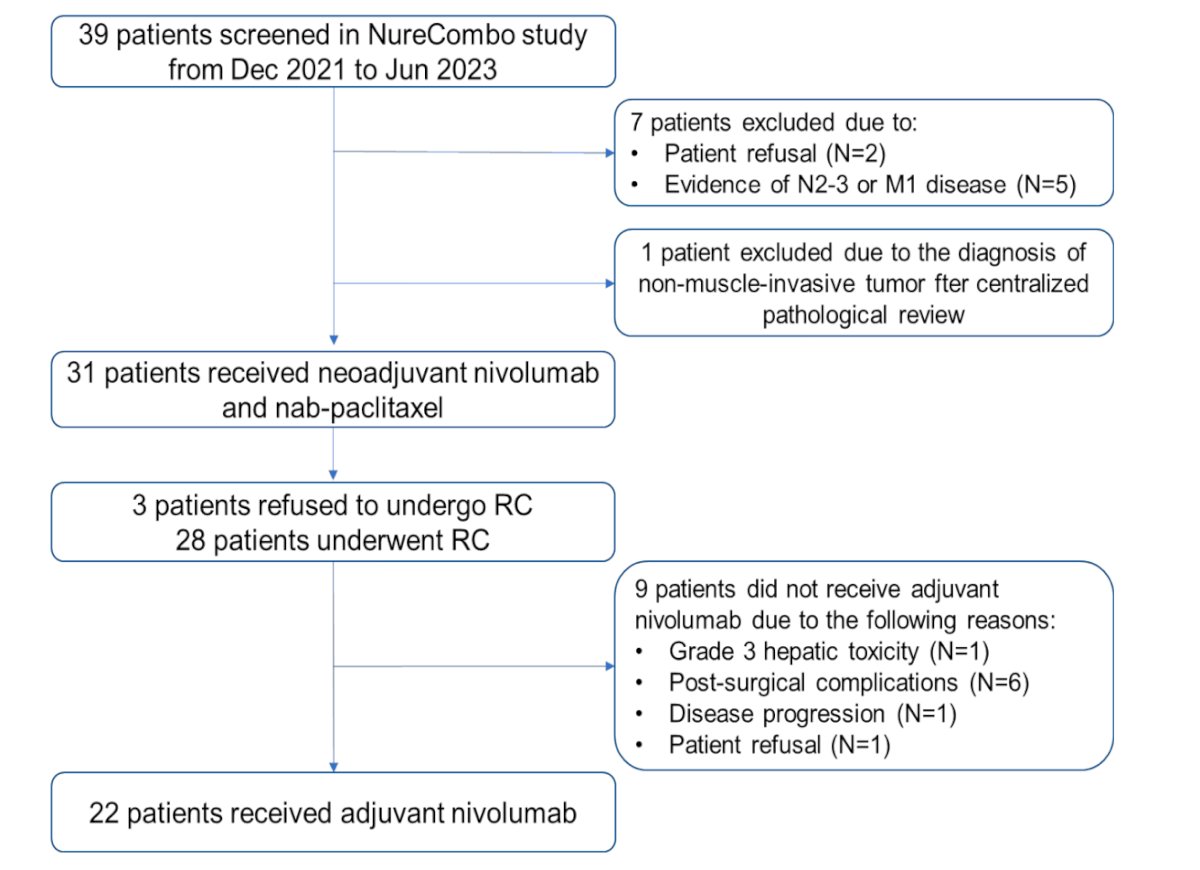
At a median follow-up of 12 months, 12 patients (38.7%) achieved a ypT0N0x response (pCR), and 22 (73%) had a ≤ypT1N0 response (pPR). No disease progression occurred during neoadjuvant ABX +NIVO therapy.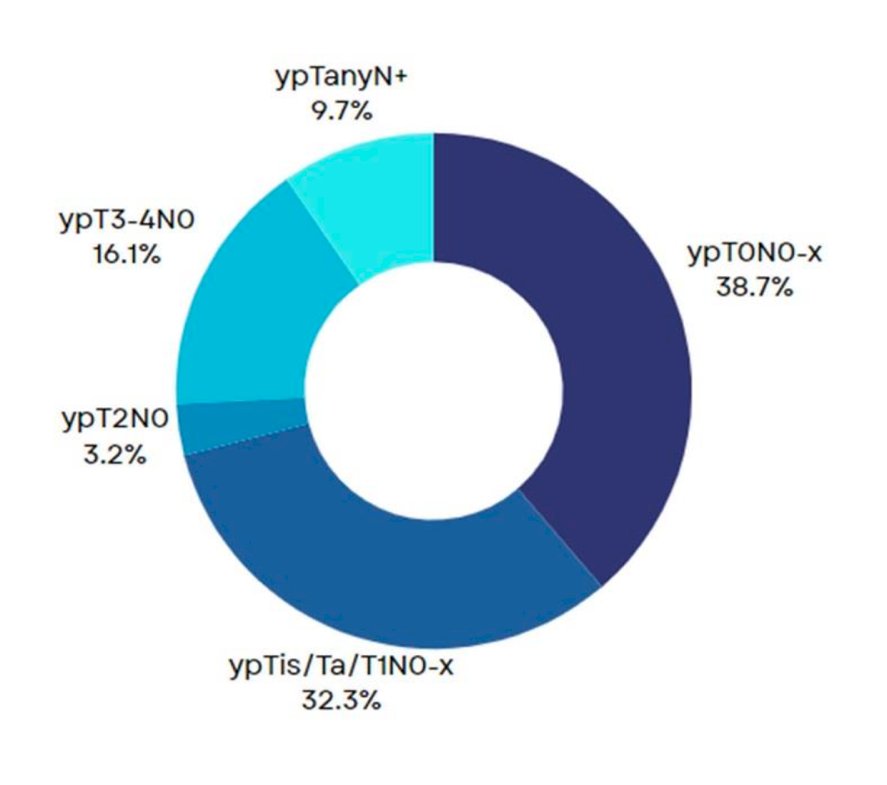
The 12-month event-free survival in the intention-to-treat population was 89.1%. Among the patients who relapsed after radical cystectomy, both failed to achieve a ypT1N0 response.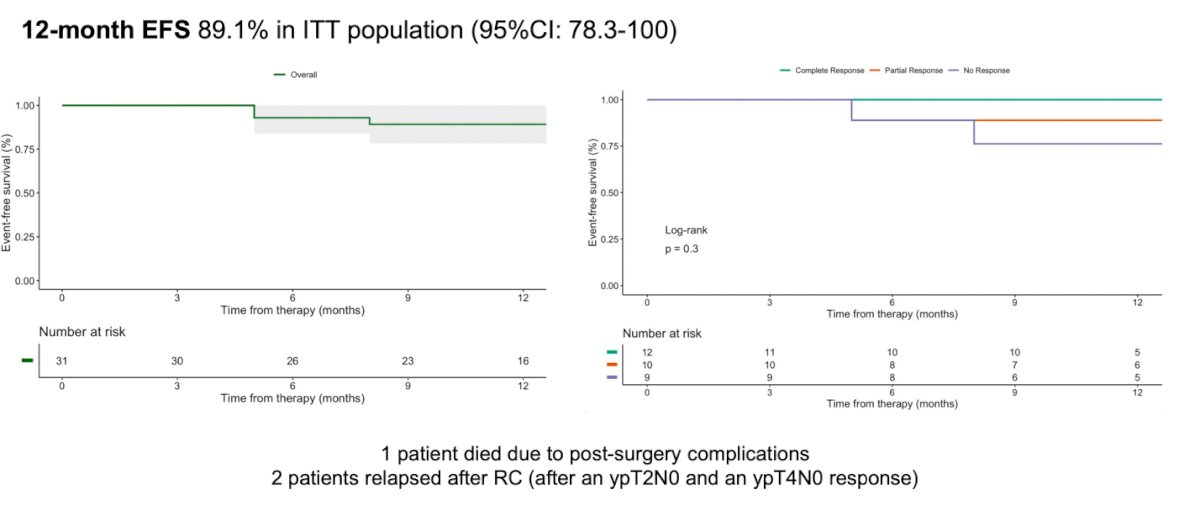
From a safety standpoint, 5 (16.1%) patients discontinued neoadjuvant ABX + NIVO treatment prematurely due to treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), receiving less than 4 cycles. No Grade ≥ 4 TRAEs were reported. Post-surgery, Grade ≥ IIIa complications occurred in 8 patients (28.6%). For a comprehensive list of complications, please refer to the table below.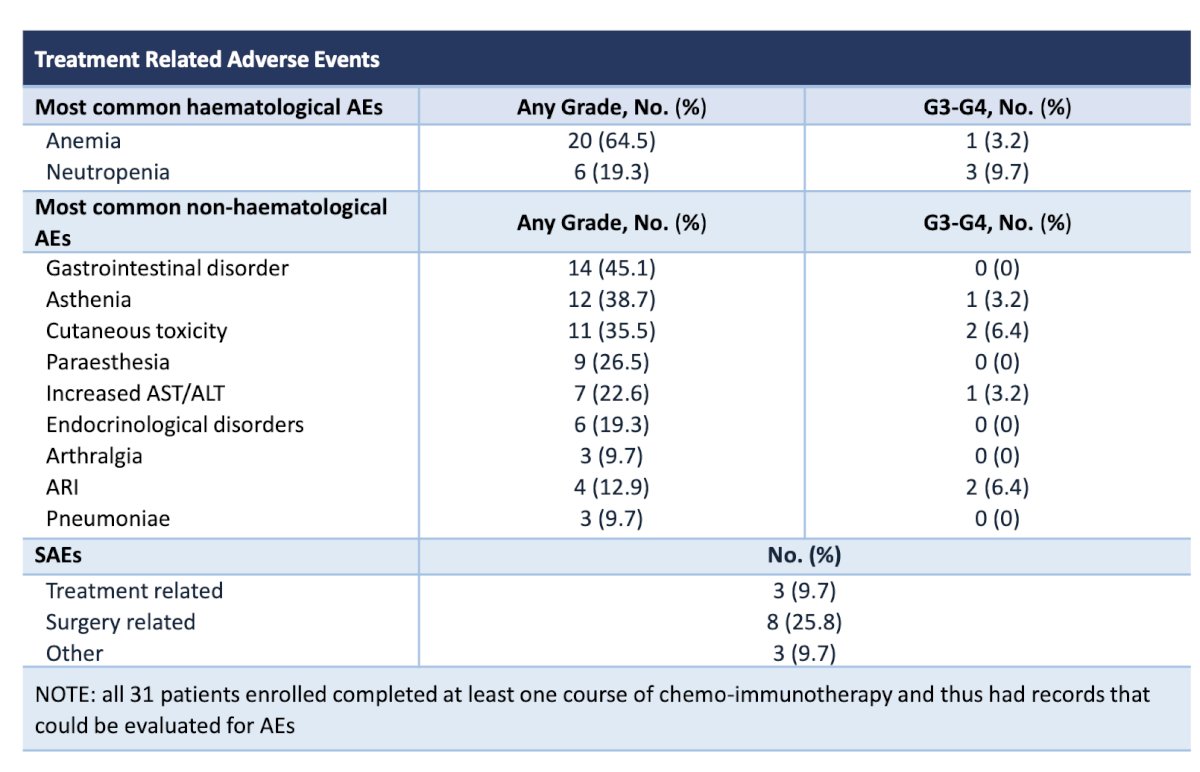
Lastly, they performed comprehensive genomic profiling pre- and -post-therapy. No significant differences in genomic biomarkers were observed. However, it is worth noting that patients with a pCR had a lower fraction of polymorphonuclear cells (CD15+ CD45+) compared to patients with a pPR and those with no response (pNR) (p=0.024).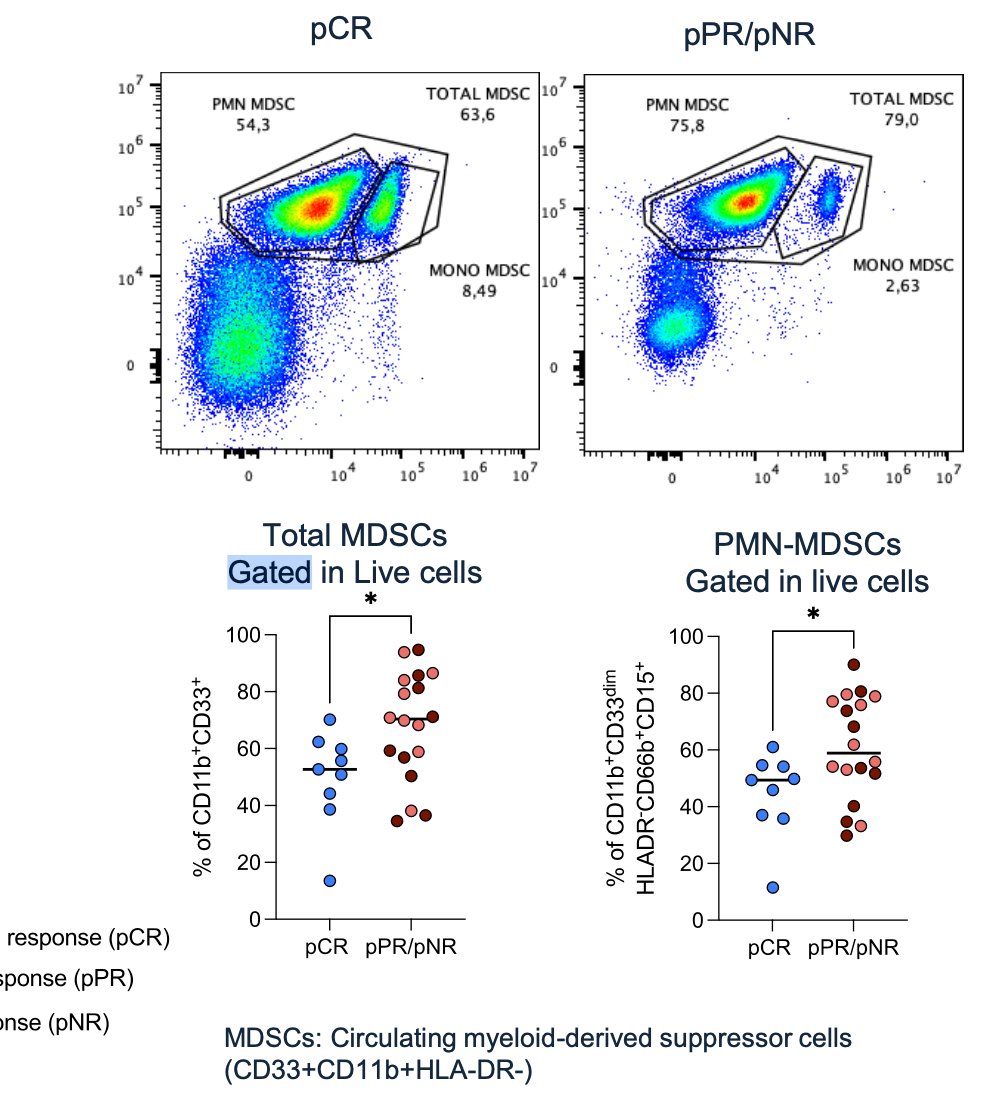
Dr. Mercinelli concluded her presentation by stating that neoadjuvant nivolumab + nab-paclitaxel (ABX) followed by adjuvant NIVO is an effective and safe perioperative strategy for patients with MIBC, showing sustained efficacy post-radical cystectomy. She suggested that these findings indicate ABX+NIVO could potentially replace cisplatin as the backbone therapy for a population with an unmet clinical need (cisplatin-ineligible prior to RC).
Presented by: Chiara Mercinelli, MD, Via-Salute San Raffaele University and IRCCS, Milan, Italy
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD - Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) annual meeting held in San Antonio, TX between May 3rd and May 6th, 2024
References:
- Vale, C. L. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data: advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. European urology 48.2 (2005): 202-206
- Galsky, Matthew D., et al. A consensus definition of patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are unfit for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The Lancet Oncology 12.3 (2011): 211-214.
- Necchi, Andrea, et al. Pembrolizumab as neoadjuvant therapy before radical cystectomy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma (PURE-01): an open-label, single-arm, phase II study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 36.34 (2018): 3353-3360.
- Galsky, Matt D., et al. Extended follow-up results from the CheckMate 274 trial. (2023): LBA443-LBA443.
- Giannatempo, P., et al. Pembrolizumab and nab-paclitaxel as salvage therapy for platinum-treated, locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: interim results of the open-label, single-arm, phase II PEANUT study. Annals of Oncology 31.12 (2020): 1764-1772.


