(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) annual meeting featured a session on non-invasive bladder cancer, and a presentation by Dr. Yuki Nakamura discussing whether photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsy replaces bladder mapping biopsy. Bladder mapping biopsies are recommended in cases of positive urine cytology or suspected CIS during transurethral resection of bladder tumors.
Although photodynamic diagnosis is acknowledged for its high sensitivity, whether photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsies can replace mapping biopsies has not been adequately evaluated. The aim of this study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of photodynamic diagnosis for flat or normal-looking lesions on white-light cystoscopy in bladder mapping biopsies.
Between 2018 and 2023, a total of 102 patients underwent mapping biopsies using photodynamic diagnosis with oral 5-aminolevulinic acid At Tokyo Medical and Dental University. During the procedures, when a photodynamic diagnosis-positive area was present, a specimen was collected from that area. The diagnostic accuracy of photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsies was assessed in 673 biopsies from flat or normal-looking lesions on white-light cystoscopy, after excluding 98 elevated lesions:
The sensitivity of photodynamic diagnosis was also analyzed by the locations.
The median age was 73 years (range: 44-90), and 89 (87%) patients were male. Overall, 24% of patients had prior BCG therapy, and the rationale for mapping biopsies was positive urine cytology in 70 patients (69%) and suspected CIS in 32 patients (31%). The full patient characteristics are as follows:
Of the total lesions, cancer was identified in 110 (16%) lesions. Photodynamic diagnosis-positive areas were present in 166 (25%) lesions. Comparative analysis of photodynamic diagnosis vs. white-light findings exhibited a sensitivity of 66% vs. 46% (p<0.001), specificity of 83% vs. 89% (p<0.001), and negative predictive value (NPV) of 93% vs. 90% (p<0.001):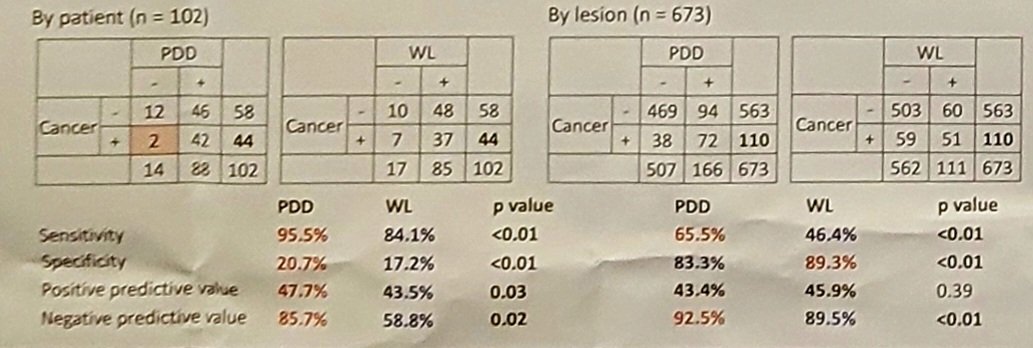
The sensitivity of photodynamic diagnosis findings by the location was as follows: trigone (59%), dome (73%), right (79%), left (71%), anterior (40%), posterior (100%), bladder neck (42%), and prostatic urethra (25%). Introducing mapping biopsies of the anterior wall, bladder neck, and prostatic urethra in addition to the photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsies resulted in a significantly increased sensitivity from 66% to 83% (p < 0.001):
The following shows the sensitivity and NPV of photodynamic diagnosis by anatomical location: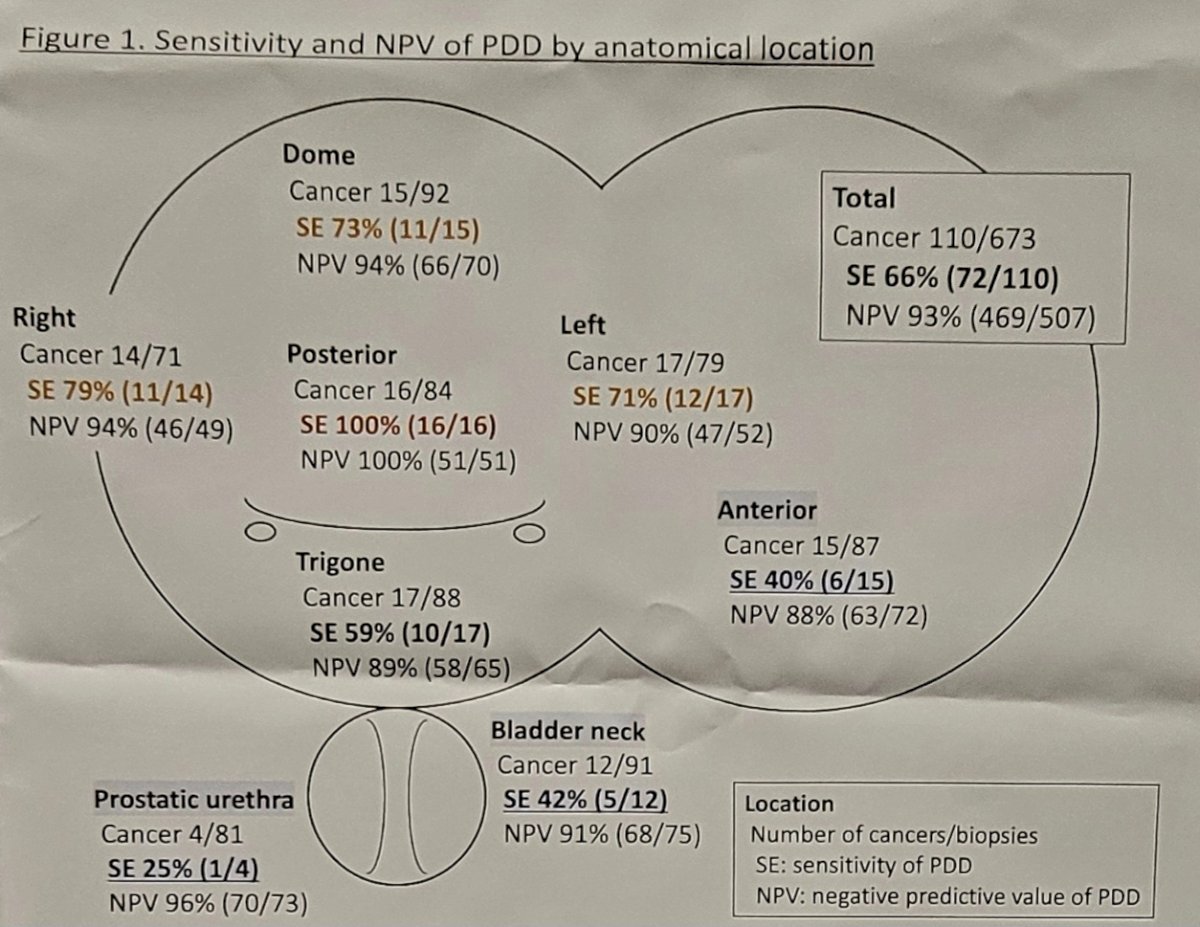
Dr. Nakamura concluded his presentation discussing whether photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsy replaces bladder mapping biopsy with the following take-home messages:
- Photodynamic diagnosis demonstrated superior sensitivity and NPV compared to white light for flat or normal-looking lesions
- Due to the low sensitivity of photodynamic diagnosis in the anterior wall, bladder neck, and prostatic urethra, the integration of mapping biopsies at these locations, regardless of photodynamic diagnosis findings, in addition to photodynamic diagnosis-guided biopsies may lead to a more precise evaluation
Presented by: Yuki Nakamura, MD, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc - Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, Fri, May 3 - Mon, May 6, 2024.


