(UroToday.com) The 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting held in San Antonio, TX between May 3rd and 6th, 2024 was host to a non-muscle invasive bladder cancer podium session. Dr. Paolo Gontero presented the results of an international multicenter retrospective study evaluating photodynamic diagnosis (PDD)-directed biopsies versus white light bladder mapping in patients with a positive cytology and negative pre-operative work-up.
In patients with a normal cystoscopy and positive cytology, the current European Association of Urology guidelines recommend considering prostatic urethral biopsies and upper tract imaging, as well as enhanced cystoscopic techniques (blue light cystoscopy, when available), or random bladder biopsies (expert opinion). He noted that this recommendation is secondary to the lack of a head-to-head comparison between PDD-guided biopsies and white-light mapping.
The investigators conducted a retrospective analysis of patients with positive urinary cytology and negative flexible cystoscopy and/or negative CT scan at one of six European referral centers between March 2018 and September 2023. Conversely, patients with visible lesions or areas suspicious for CIS at white light cystoscopy were excluded.
Included patients underwent either PDD-directed biopsies or white light mapping, as per international guidelines. The primary study endpoint was the diagnostic accuracy for the detection of CIS. Recurrence-free and progression-free survivals among patients without CIS at biopsy were investigated as secondary endpoints.
With regard to the primary endpoint, CIS was detected in 51 (18%) patients. Of these 51 lesions 38 (74%) were detected using PDD-guided biopsies. On univariable logistic regression analysis, PDD-guided biopsy sampling was significantly associated with increased odds of CIS detection (OR: 2.6, 95% CI: 1.30–5.04, p=0.007).
Among patients without CIS at biopsy, those staged using PDD-guided biopsy had superior recurrence-free, but not progression-free survivals.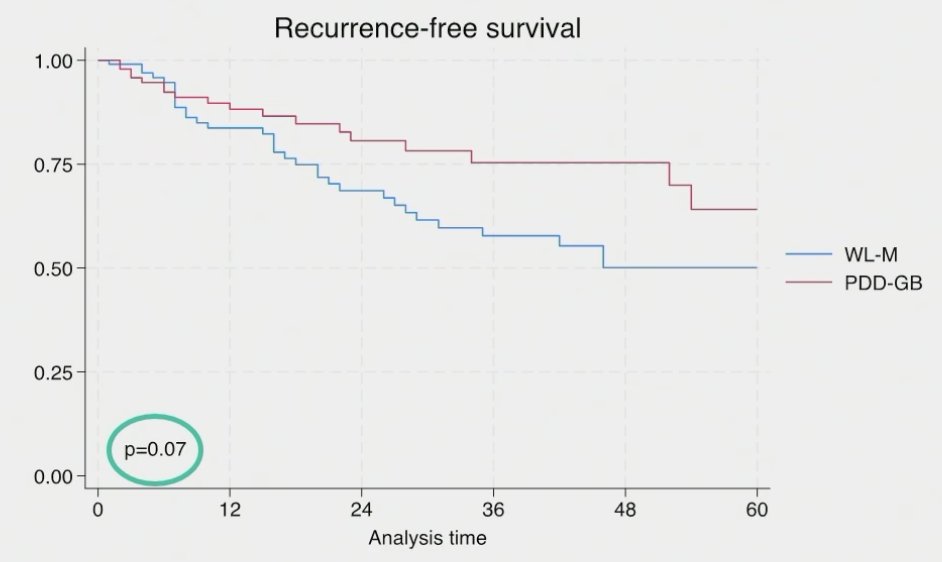

Dr. Gontero concluded that:
- PDD-guided biopsies are superior to white light mapping for the diagnosis of CIS in patients with a positive cytology and negative cystoscopy/imaging
- In patients with sampling negative for CIS, patients staged using PDD had superior recurrence-free survival outcomes
- In patients with suspicion of CIS (e.g., positive cytology and negative cystoscopy), PDD-guided biopsy, when available, should be preferred to white light cystoscopy
Presented by: Paolo Gontero, MD, FEBU, Professor of Urology. Chairman Department of Urology, Molinette Hospital, University School of Medicine, Torino, Italy.
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc - Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, May 3rd - 6th, 2024


