(UroToday.com) In a podium presentation, Dr. Aideen Madden introduces a novel flexible ureteroscope with an integrated suction developed by Zhuhai Pusen Medical Technology. Advances in laser technologies have allowed for the breakdown of stones into fine particles (defined as < 250µm) during stone laser lithotripsy; however, the issue that emerges is how urologists can efficiently extract all these remnants. The answer comes in various innovative approaches to remove these stone particles such as ureteral access sheath outflow with or without suction as well as direct in-scope suction (DISS). Dr. Madden aims to evaluate the performance of this novel DISS device in vitro by assessing the suction rate, quality, and limitation in a stone size dependent manner.
Calcium oxalate monohydrate phantom stones (Begostone) were used with sizes ranging from 63µm-125µm, 125µm-250µm, 250µm-500µm, 500µm-1mm, and 1mm-2mm. Each stone range was tested with the following conditions (n=3): 5g of stone in 30 mL of 0.9% saline and 1g of stone in 10 mL of 0.9% saline. A heterogeneous mixture made up of 1g from each stone range was also tested (n=3).
Measurements in regard to stone clearance time, rate, and suction durability (time for first blockage) were taken.
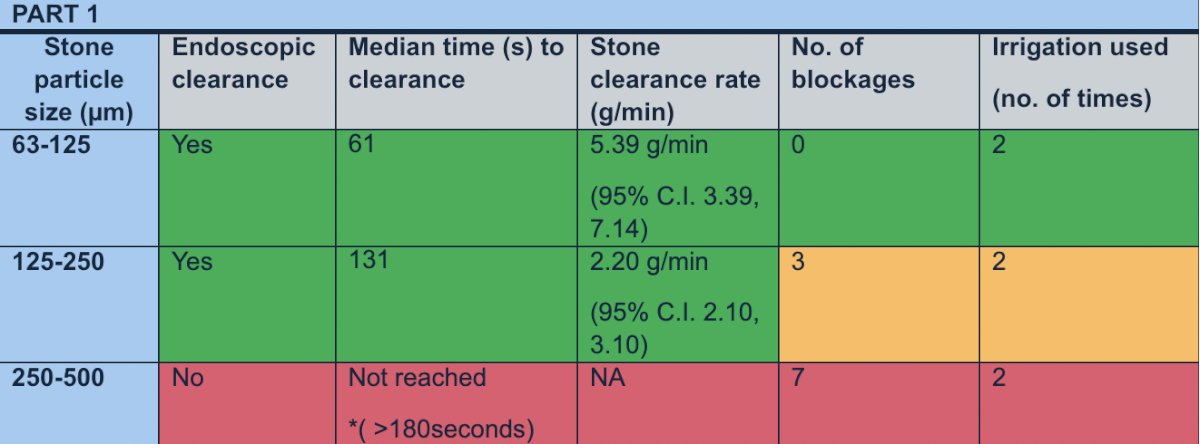
Dr. Madden found that DISS was successful for stone sizes < 250µm as stone clearance failed for sizes above 250µm due to high numbers of blockages. The stone clearance rate was the highest for stones ranging from 63µm-125µm followed by 125µm-250µm with clearance rates of 5.39 g/min and 2.20 g/min, respectively.
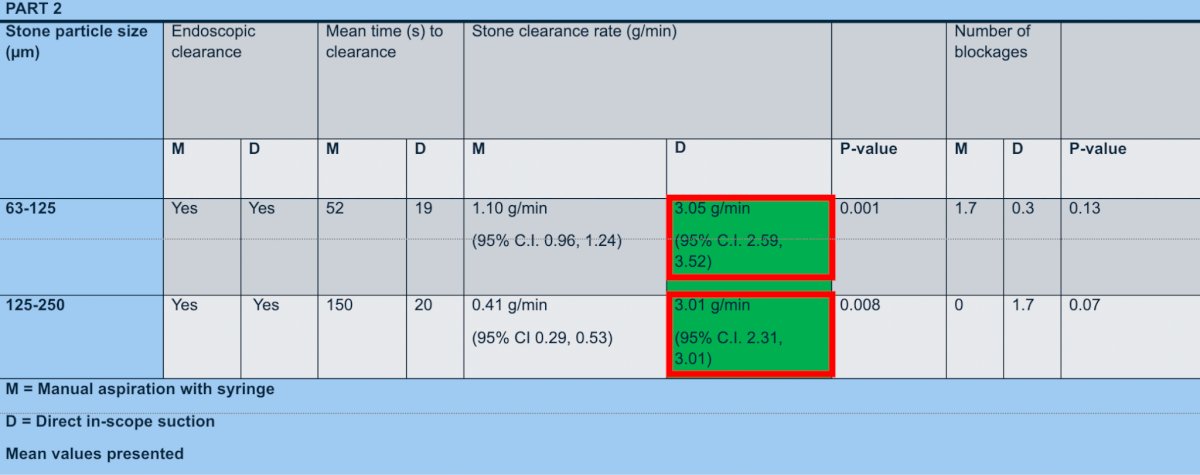
Furthermore, Dr. Madden shows how much more effective the suction is with the integrated suction ureteroscope by comparing this novel method to manual aspiration via syringe. For both ranges (63µm-125µm and 125µm-250µm), DISS had a statistically significant higher stone clearance rate than manual aspiration with a syringe.
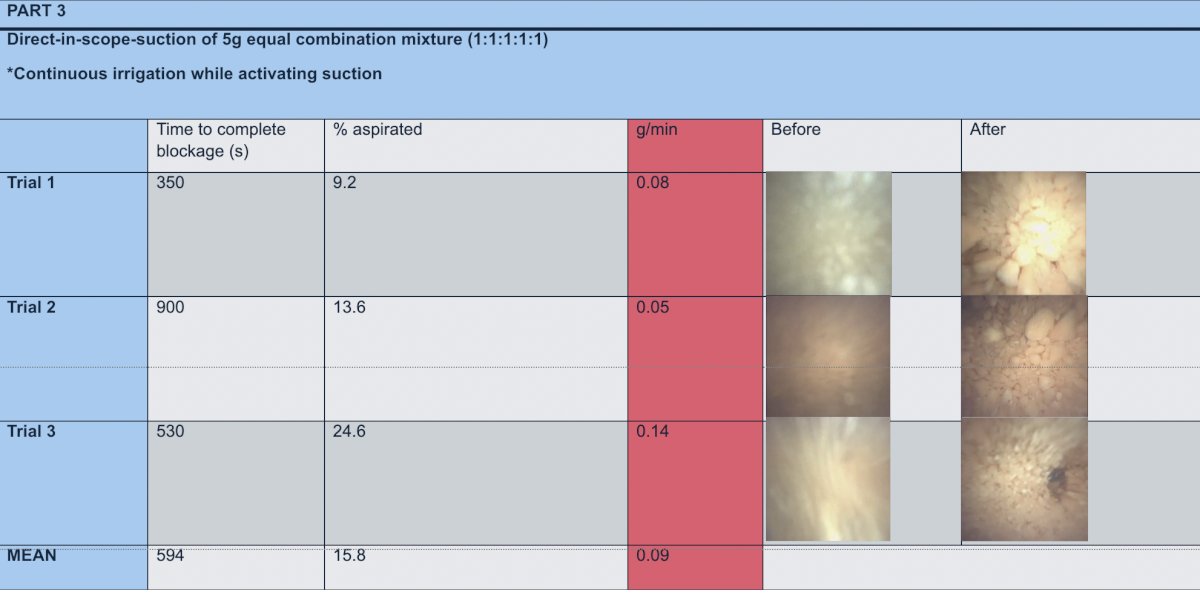
Lastly, a demonstration of DISS with a heterozygous mixture of stone sizes yielded a very low mean clearance rate of 0.09 g/min which can be attributed to larger stone sizes that end up causing a blockage.
Dr. Madden concludes with the following takeaway message:
- An integrated suction performs well in clearing stone particles when compared to other DISS methods and improved visibility.
- An integrated suction is limited to single-use scopes and smaller stone fragments due to ureteroscopic obstruction by large sized fragments.
Before ending the podium presentation, an audience member raised concerns about the Begostones used as, in his prior experience, these stones readily dissolved in water which would affect the stone clearance rates obtained. Dr. Madden defended by stating that endoscopic confirmation ensured stones remained stable in solution and explained how suctioning was activated immediately after dispensing the saline solution onto the stones, effectively minimizing the time for which the stone can be allowed to dissolve.
Presented by: Aideen Madden, MD, Tenon Hospital, AP-HP Sorbonne, Paris, France
Written by: Victor Pham, B.S., University of California Irvine, @victorpham01 on X during the 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, Fri, May 3 - Mon, May 6, 2024.
References:
- Aideen Madden, Carlos Altez, Jordi P. Lueza, Razvan Popescu, Johan Cabrera, Mariela Corralles, and Olivier Traxer. Direct in-scope suction: an in vitro evaluation of a single-use flexible ureteroscope with integrated suction capability [abstract]. In: American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, May 3 – May 6, 2024, San Antonio, Texas


