(UroToday.com) Dr. Ethan Vargo, minimally invasive endourology fellow at Washington University in St. Louis, presented research on kidney cancer detection. Collaborating with a local laboratory, his team developed a novel urinary cell biomarker capable of detecting and monitoring renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
The study enrolled patients with cT1a-cT2N0M0 renal masses undergoing planned robotic partial (RRN) and radical nephrectomy (RPN) surgeries. Patient demographics, including gender, age, laterality, and the presence of microhematuria, were recorded. Urine samples were collected pre- and post-operation and underwent novel filtration screening and polymerase chain reaction testing to measure urinary tumor cell density (UTC/50 ml) (UTCD), recorded as a log value (log UTCD). Post-operative samples were collected at different time intervals and compared to pre-operative samples. Post-operative variables such as final pathology, histology, tumor grade, presence of lymph vascular invasion, and margin status were assessed and compared. Urine samples from 10 healthy donor nephrectomy patients comprised the control arm for comparison.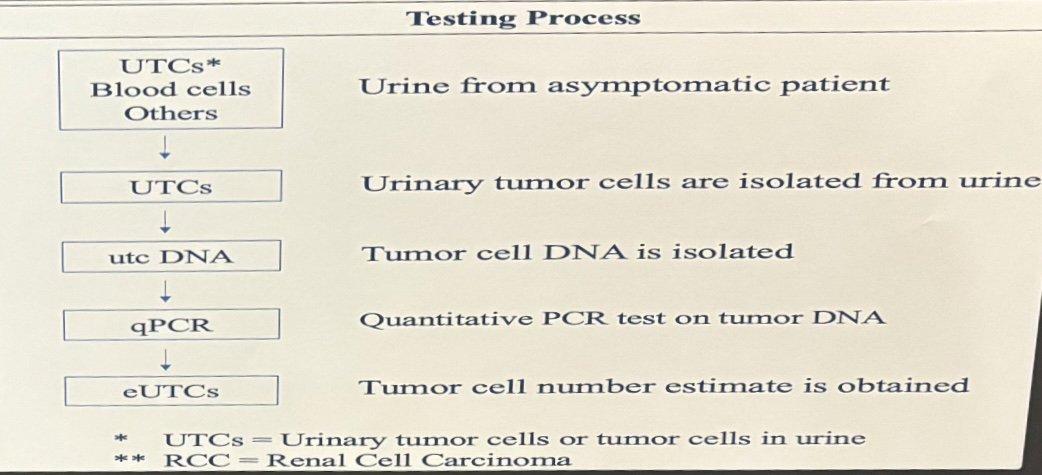
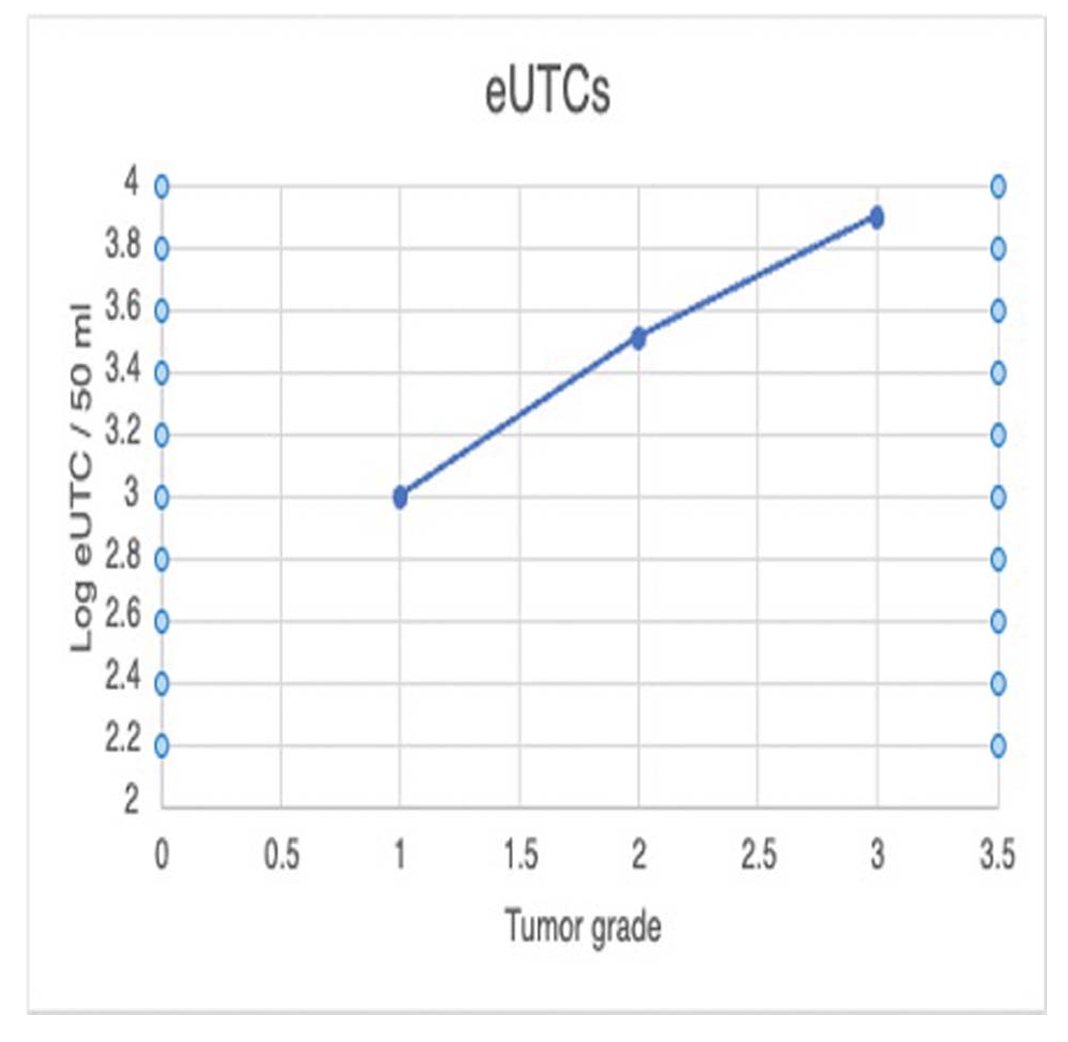
A total of 11 patients, with a fair distribution across genders, provided both pre- and post-operative urine samples. There were no significant differences observed in the ages of the participants. Among RCC patients, the mean log UTCD was 3.68, significantly differing from the control arm with a p-value of 0.00508. Pre-surgical UTC mean values compared to post-surgical values under 24 weeks of surveillance showed no statistical significance. However, after 24 weeks of surveillance, the pre-surgical and post-surgical values were 0.016, indicating the remarkable ability of the biomarker to identify urinary tumor cells. A correlation between tumor grade and UTC was noted, with an increase in tumor grade corresponding to subsequent increases in urinary tumor cell density. Significant differences in pre- and post-operative UTC levels were observed for patients with grade I and grade II tumors but not for those with grade III or IV tumors.
In conclusion, this study underscores the promising potential of a novel urinary biomarker for RCC diagnosis and surveillance. The presenter highlighted the small sample size and emphasized the need for further studies to validate the efficacy of this biomarker in detecting UTC, potentially reducing radiation exposure in actively monitored patients.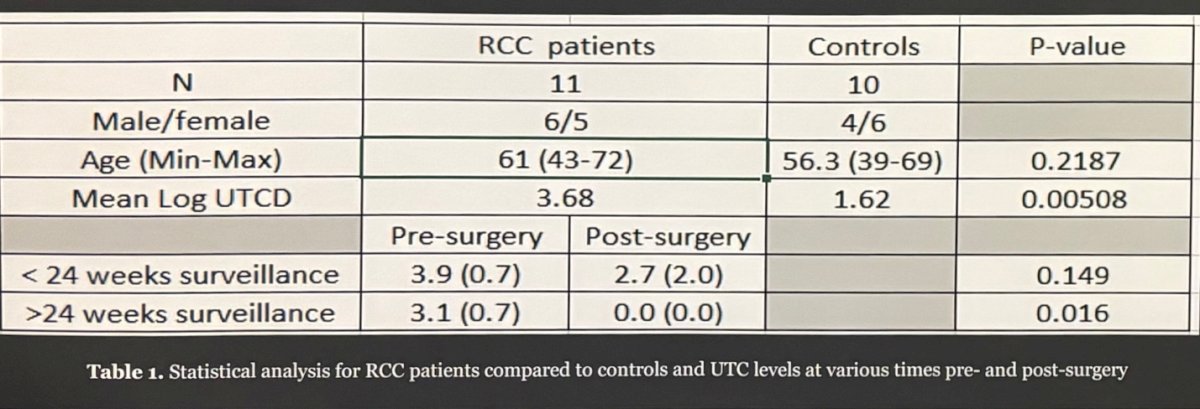
During the Q&A session, a member of the audience inquired about considering patients with locally metastatic disease as positive controls to confirm tumor pathology consistency with UTC levels. The presenter affirmed plans to expand studies in this direction and mentioned efforts to establish thresholds for benign and metastatic diseases.
Presented by: Ethan Vargo, MD, Minimally Invasive Endourology Fellow, Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri.
Written by: Seyedamirvala Saadat, B.S., Assistant Research Specialist, Department of Urology, University of California Irvine, @Val_Saadat on X during the 2024 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting, May 3-6, 2024, San Antonio, Texas.


