(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Association of Urology (EAU) annual meeting featured a kidney cancer rapid fire debate, and a presentation by Dr. Charles-Karim Bensalah discussing that upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy plays a role in intermediate risk metastatic RCC. Dr. Bensalah started his presentation by suggesting that for the meantime, we need to let CARMENA1 and SURTIME2 go given that these were studies accrued to during the TKI era. He notes that there are two contemporary studies in the immunotherapy era that suggest upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy could impact survival in selected patients.
The first is from Ghatalia et al.3 who assessed 1,910 patients with metastatic RCC in the Flatiron Health database, of which 972 (57%) received systemic therapy, 605 (32%) received upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy, 142 (8%) delayed cytoreductive nephrectomy and 191 (10%) cytoreductive nephrectomy alone. Of note, 433 (23%) patients received immunotherapy-based therapy. The adjusted median overall survival was significantly improved in first-treatment (26.6 vs 14.6 months), landmark (36.3 vs 21.1 months), and time-varying covariate analysis (26.1 vs 12.2 months) in patients undergoing cytoreductive nephrectomy. The adjusted Kaplan Meier among those undergoing systemic therapy first versus cytoreductive nephrectomy first is as follows:

Furthermore, the adjusted Kaplan Meier overall survival curve using a 6-month landmark (ie. so only included patients that survived to 6 months) showed that patients receiving systemic therapy first had worse outcomes than those patients undergoing either a delayed or upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy:

The second study from Bakouny et al.4 assessed the IMDC database to evaluate the relationship between upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy and clinical outcomes in the setting of metastatic RCC treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapy. Among 4,639 eligible patients, 4,202 patients treated with targeted therapy, and 437 patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. There were 2326 (55%) treated with targeted therapy and 234 (54%) treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors that received upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy prior to treatment start. Among those receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, those who underwent upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy had a median overall survival of 54 months vs 22 months for no cytoreductive nephrectomy:

Moreover, cytoreductive nephrectomy was a predictive factor of overall survival in multivariable analysis (HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.41-0.90).
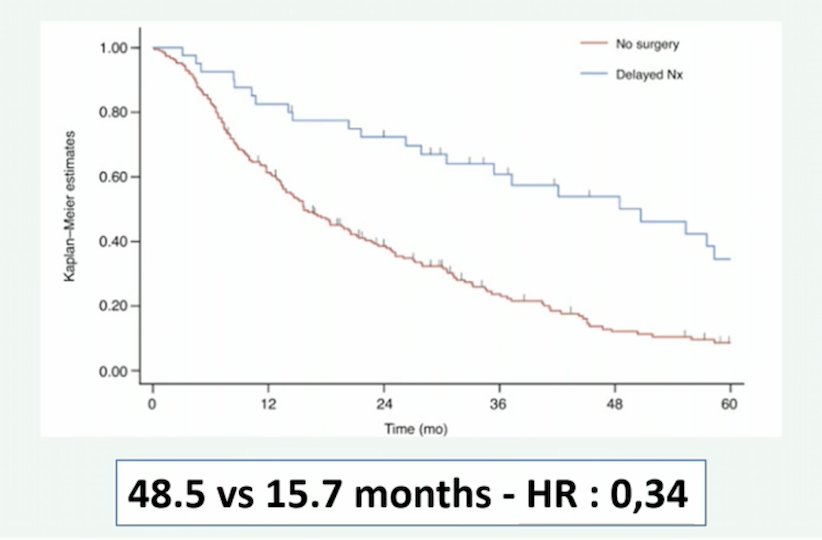
Dr. Bensalah emphasized that based on the aforementioned data, some selected patients can benefit from upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy, but the challenge is patient selection. According to Dr. Bensalah, IMDC risk stratification is not the optimal way for selecting patients. First, IMDC was not designed to select patients for surgery and there are many factors not considered, including tumor burden, location of metastasis, and patient symptoms. Additionally, IMDC is comprised of >55% of patients with metachronous disease, and the IMDC intermediate risk group is a very heterogeneous group. A posthoc analysis of CARMENA, suggests that the best candidates for cytoreductive nephrectomy are those with one IMDC risk factor, one metastatic site, and only lung metastases:
Dr. Bensalah concluded his presentation by discussing the recently published SCREEN score5 which is a prognostic model to improve cytoreductive nephrectomy selection with integration of common radiologic features with known prognostic factors associated with mortality in the first year following surgery. Among 914 patients with metastatic RCC treated with upfront cytoreductive nephrectomy, seven independently predictive variables were used in the SCREEN score:
- Three or more metastatic sites
- Total metastatic tumor burden ≥5 cm
- Bone metastasis
- Systemic symptoms
- Low serum hemoglobin
- Low serum albumin
- Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio ≥4

The predictive accuracy measured as the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves was 0.76 for the SCREEN score and 0.55 for the IMDC model.
Presented by: Charles-Karim Bensalah, Rennes University Hospital, Rennes, France
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 European Association of Urology (EAU) annual congress, Paris, France, April 5th - April 8th, 2024


