(UroToday.com) The European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2021 annual meeting’s non-prostate cancer session included a presentation by Dr. Rustem Gafanov discussing results of subsequent therapy in KEYNOTE-426 for patients treated with pembrolizumab + axitinib or sunitinib for advanced RCC. First-line combination treatment of an anti-PD-1/PD-L1 with a VEGFR inhibitor is considered standard of care for advanced clear cell RCC. In the phase III KEYNOTE-426 study, pembrolizumab + axitinib showed significant improvement in overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) vs sunitinib in patients with RCC.1 OS results could be impacted by subsequent treatment following study discontinuation and outcomes from second-line treatment could also be affected by the initial immunotherapy used. At the ESMO 2021 congress, Dr. Gafanov and colleagues presented results of subsequent treatment in patients enrolled in KEYNOTE-426.
Treatment-naive patients with clear cell RCC, KPS score ≥70%, and measurable disease (RECIST v1.1) were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive pembrolizumab 200 mg IV every 3 weeks for up to 35 doses + axitinib 5 mg orally twice daily or sunitinib 50 mg once daily (4 weeks on/2 weeks off) until progression, toxicity, or withdrawal. Type of and time to subsequent therapy were assessed. The trial schema for KEYNOTE-426 is as follows:
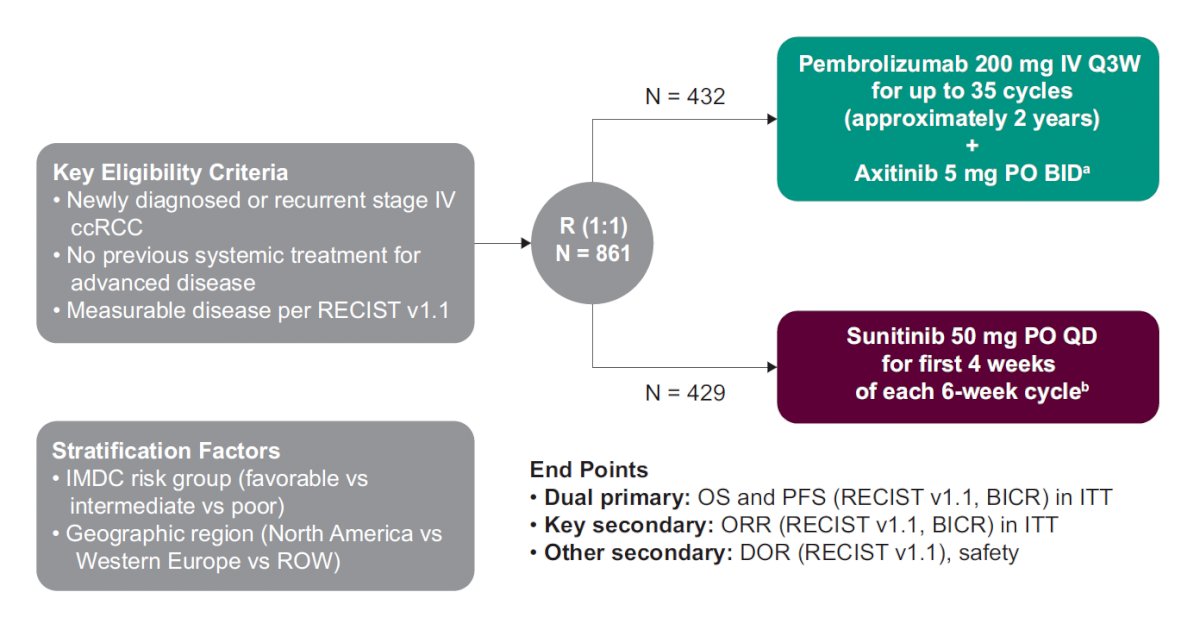
Of patients in the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm and in the sunitinib arm, 81.4% (349/432) and 90.6% of patients (385/429), respectively, discontinued treatment. Radiologic or clinical progressive disease was the most common reason for discontinuation in both treatment arms (pembrolizumab + axitinib: 65.0%; sunitinib: 68.1%). Over a median follow-up of 42.8 months (range: 35.6-50.6), the disposition of the patients in the trial is as follows:

Of patients who discontinued treatment, 58.5% of patients (204/349) in the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm and 73.0% (281/385) in the sunitinib arm received subsequent therapy:

Although a similar proportion of patients in both arms received subsequent therapy with a VEGF/VEGFR inhibitor (pembrolizumab + axitinib: 88.2% [180/204]; sunitinib: 68.7% [193/281]), a greater proportion of patients in the sunitinib arm (74.4% [209/281]) received subsequent PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy than in the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm (21.6% [44/204]). Among patients in the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm and the sunitinib arm, 32.4% (66/204) and 22.8% (64/281), respectively, received other therapies. Time from randomization to first subsequent therapy in all patients who received subsequent therapy generally favored the pembrolizumab + axitinib arm:

Finally, OS of pembrolizumab + axitinib versus sunitinib for patients who received subsequent anticancer therapy favored pembrolizumab + axitinib (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.60-0.88):

Dr. Gafanov concluded his presentation of subsequent therapies in the KEYNOTE-426 trial with the following summary statements:
- Of the patients that received subsequent therapy, baseline characteristics were similar to those in the overall population, subsequent PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy was less frequent after pembrolizumab + axitinib, and subsequent VEGF/VEGFR therapy was more frequent after pembrolizumab + axitinib therapy
- In the ITT population, longer OS with pembrolizumab + axitinib compared with sunitinib was observed despite the increased use of subsequent therapy, particularly the use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, in the sunitinib arm
- These data continue to support the use of first-line pembrolizumab + axitinib compared with sunitinib in patients with advanced clear cell RCC
Presented by: Rustem Gafanov, MD, Urology, Russian Scientific Center of Roentgenoradiology, Moscow, Russian Federation
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2021 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress 2021, Thursday, Sep 16, 2021 – Tuesday, Sep 21, 2021.
References:


