(UroToday.com) In this presentation, Dr. Karim Fizazi discussed updated results of PEACE-1, a randomized Phase 3 trial in men with de novo metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC). This update focused on the overall survival (OS) for men treated with or without abiraterone plus prednisone (AAP).
The last decade has seen a rapidly evolving standard of care (SOC) for first-line therapy in men with mCSPC. The PEACE-1 trial employed a 2x2 design to assess, (separately and combined) the impact of the addition of AAP and radiation (RT) to SOC therapy in men with mCSPC.
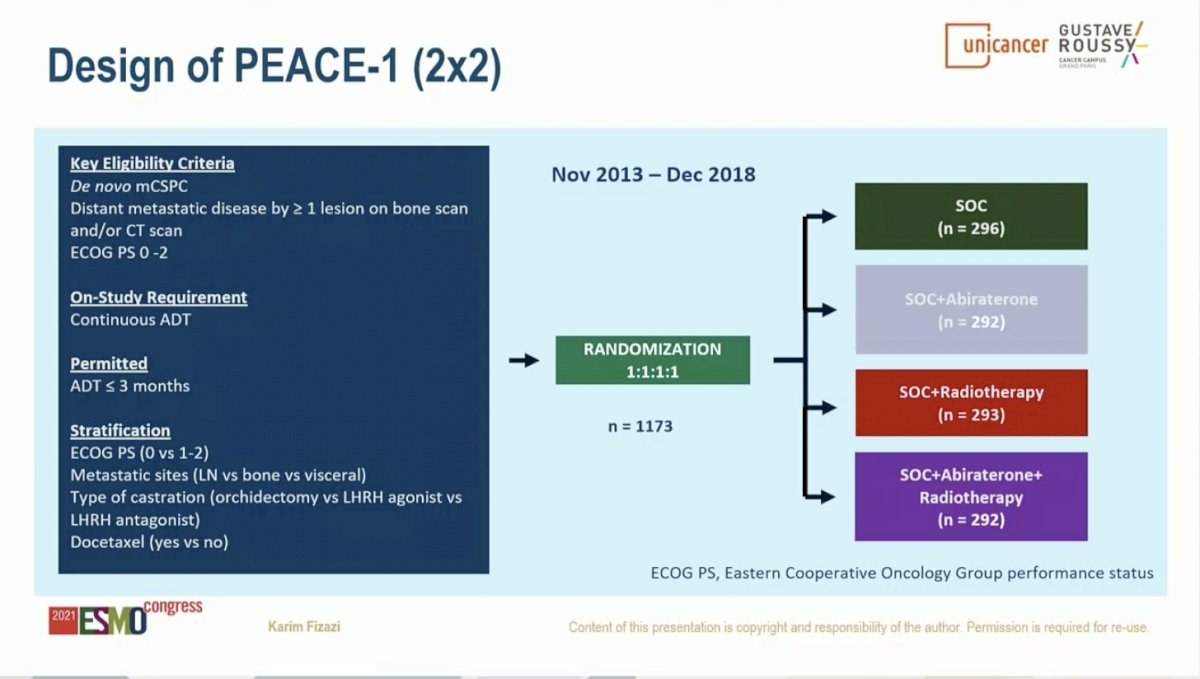
The control arm in this study evolved to reflect the contemporary SOC. When the study began enrolling patients, the SOC for first-line mCSPC was ADT alone. With publication of data from the STAMEDE, LATITUDE, and CHAARTED studies, SOC was updated to include ADT plus Docetaxel 75 mg/m2 every 3 weeks for 6 cycles. The two experimental treatments investigated in this study were: 1) AAP until disease progression or intolerance (concomitant to docetaxel) and 2) RT of the prostate (74 Gy in 37 fractions after completion of docetaxel). Results from the AAP experimental arm are discussed herein.
The PEACE-1 study randomized 1,173 patients with 355 each to the SOC (with or without RT) and the SOC (with or without RT) plus AAP arm. Demographic and baseline characteristics were similar across these two arms. Notably, approximately two-thirds of patients on each arm had high-volume disease.

PEACE-1 was designed with two co-primary endpoints for the AAP analysis: radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) and overall survival (OS). Dr. Fizazi began by evaluating the benefit of adding AAP in the cohort of patients treated with SOC ADT plus Docetaxel (with or without RT). With a median of 3.8 years of follow-up, the addition of AAP to SOC resulted in a 50% improvement in rPFS with median rPFS of 2.0 years on the SOC arm and 4.5 years on the SOC plus AAP arm (HR 0.50, 95% CI 0.40-0.62; P < 0.0001). rPFS benefit was greater in the high volume than low volume subgroups, but both populations benefited. Among patients with high volume disease, the addition of AAP to SOC resulted in a 53% improvement in rPFS with median rPFS of 1.6 years on the SOC arm and 4.1 years on the SOC plus AAP arm (HR 0.47, 95% CI 0.36-0.60; P < 0.0001). The addition of AAP to SOC in patients with low volume disease resulted in a 42% improvement in rPFS with median rPFS of 2.7 years on the SOC arm versus not yet reached on the SOC plus AAP arm (HR 0.58, 95% CI 0.39-0.87; P = 0.006).


Similar results were observed for OS. Starting with the overall study population (SOC of ADT with or without docetaxel), the addition of AAP resulted in an 18% improvement in OS with median OS of 4.7 years on the SOC arm and 5.7 years on the SOC plus AAP arm (HR 0.82, 95% CI 0.69-0.98; P = 0.030). Limiting to the cohort of patients who received ADT plus Docetaxel as SOC, the addition of AAP resulted in a 25% improvement in OS with median OS of 4.4 years on the SOC arm versus not yet reached on the SOC plus AAP arm (HR 0.75, 95% CI 0.59-0.95; P = 0.017). This effect was seen across subgroups, including those with high volume disease (HR 0.72, 95% CI 0.55-0.95) and low volume disease (HR 0.83, 95% CI 0.50-1.38); interaction P-value 0.64. Notably, the OS data is immature for the low volume patients due to a small number of events.



An important consideration is what therapies patients received following progression on study treatment. Notably, 81% of patients on the ADT plus Docetaxel SOC arm subsequently received a next generation hormonal therapy. This suggests that early intensification with the addition of AAP to SOC results in improvement in rPFS and OS compared to sequential therapy.
In the cohort of patients who received ADT plus Docetaxel as SOC, the addition of AAP was well-tolerated. There was no difference in rates of Grade 3-5 neutropenia or febrile neutropenia. As expected, Grade 3-5 liver function abnormalities (6% versus 1%) and hypertension (22% versus 13%) were higher in patients who received SOC plus AAP compared to SOC alone.

Dr. Fizazi put the PEACE-1 results into context with previous randomized Phase 3 studies for first-line therapy in high-volume de novo mCSPC. Median OS ranged from 33 to 35 months for ADT alone, 40 to 48 months for ADT plus Docetaxel, and 50 to 56 months for ADT plus AAP. The median OS for PEACE-1 was an impressive 61 months.

Dr. Fizazi summarized that adding AAP to ADT plus Docetaxel significantly improved median rPFS by 2.5 years in men with de novo mCSPC. OS was also improved with 25% reduction in the risk of death even when 81% of men in the control group subsequently receiving at least one next generation androgen signaling inhibitor. This benefit translates into a median lifetime gain of more than 1.5 years for men with high-volume metastatic disease (3.5 to 5.1 years). OS data for men with low volume disease is immature and updates with be forthcoming. Dr. Fizazi concluded that he believes this data is practice changing and that ADT plus Docetaxel plus AAP should be offered (at least) to men with de novo high-volume mCSPC.
Presented by: Karim Fizazi, MD, PhD, Medical Oncologist at Gustave Roussy and Professor in Oncology at the University of Paris-Saclay in Villejuif, France
Written by: Jacob Berchuck, MD, Genitourinary Medical Oncologist, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (Twitter: @jberchuck) during the 2021 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress 2021, Thursday, Sep 16, 2021 – Tuesday, Sep 21, 2021.


