(UroToday.com) During the second Mini Oral session of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress focusing on non-prostate genitourinary cancers, Dr. Andrea Necchi presented results from the CheckMate 274 trial assessing tumor and immune features predictive of disease-free survival. CheckMate 274 randomized patients with high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma (MIUC) after radical resection to receive adjuvant nivolumab or placebo, demonstrating improved disease-free survival (DFS) with adjuvant nivolumab in the intent-to-treat (ITT) and tumor PD-L1 expression ≥ 1% populations.
As previously published, patients in CheckMate 274 were randomized 1:1 to nivolumab 240 mg IV every 2 weeks or PBO for ≤ 1 year of adjuvant treatment. Pre-treatment tumor tissue from the most recently resected site or the transurethral resection yielding MIUC diagnosis was used for biomarker analyses. Tumor mutation burden (TMB; mutations/MB) was measured by whole exome sequencing. CD8+ immune cell infiltration was measured with digital immunohistochemistry (IHC). Gene signature scores were computed from RNA-seq data. The authors performed exploratory analyses to assess the association between DFS and biomarkers (continuous scale) and estimate treatment-effect hazard ratios (HRs) for biomarker tertile subgroups.
Among 709 patients randomized in the trial, 458, 445, and 323 were evaluable for TMB, CD8 IHC, and RNA-seq.

With a minimum follow-up of 11.0 months Among those patients randomized to nivolumab, TMB, and CD8 T cell infiltration and IFN-γ signature scores were positively associated with DFS. When categorized into a three-level variable, IFN-γ signature scores were prognostic for DFS. More notably, there was an interaction where these effects were only seen in the nivolumab arm suggesting that it was predictive of nivolumab efficacy.

A similar effect was seen for CD4 gene expression when operationalized as a three-level variable.
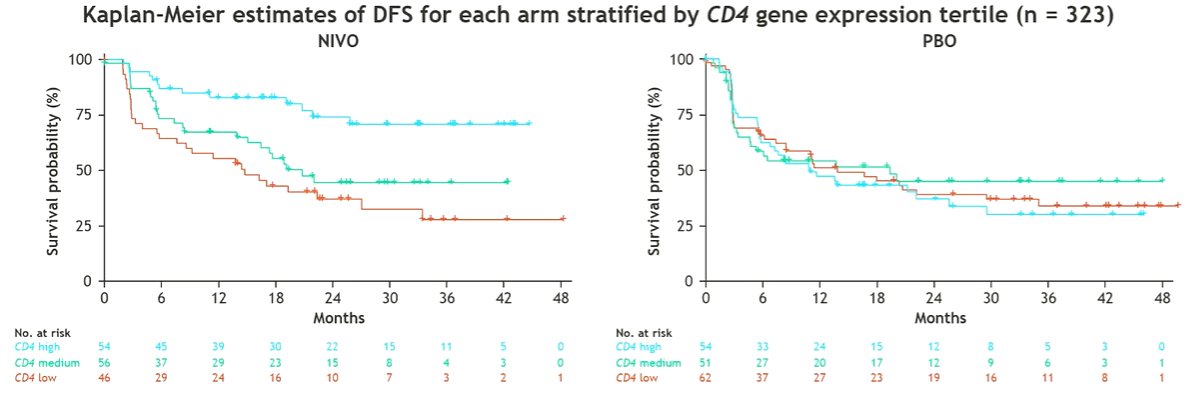
However, for CD8 level, a prognostic effect was seen in both arms, without suggestion of a significant predictive effect.

Interestingly, tumour mutational burden may be predictive of nivolumab efficacy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the associations appeared more pronounced in patients with PD-L1 ≥ 1%. Of these 3 biomarkers, evidence that association with DFS differed between arms was strongest for the IFN-γ signature.
Thus, the authors conclude that biomarkers associated with preexisting antitumor immunity were associated with improved DFS in patients receiving adjuvant nivolumab, reinforcing the mechanism for benefit with immunotherapy and extending prior findings in metastatic UC to the adjuvant setting.
Presented by: Andrea Necchi MD, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University and IRCCS San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, ItalyWritten by: Christopher J.D. Wallis, University of Toronto Twitter: @WallisCJD during the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress, 9-13 September 2022.
Related Content:
The Use Biomarkers in the Adjuvant Setting to Understand the Effect of Nivolumab in the Checkmate 274 Study - Andrea Necchi


