(UroToday.com) The 2022 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) annual meeting featured a non-prostate session, including a presentation by Dr. Mohamad Allaf discussing the results of the phase 3 open-label PROSPER trial assessing perioperative nivolumab versus observation in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) undergoing nephrectomy. Specifically, this trial examined the effect of priming the immune system with neoadjuvant nivolumab prior to nephrectomy followed by adjuvant nivolumab in patients with high-risk RCC compared to surgery alone.
For PROSPER, entry criteria included patients with clinical stage ≥T2 or TanyN+ RCC planned for nephrectomy (partial or radical). Select oligometastatic disease was permitted if the patient could be rendered ‘no evidence of disease’ within 12 weeks of surgery. In the investigational arm, nivolumab was administered (480mg IV q4 weeks) with 1 dose prior to surgery followed by 9 adjuvant doses. The control arm was surgery followed by surveillance without a placebo. Baseline tumor biopsy was required only in the nivolumab arm. The trial schema for PROSPER is as follows:

The primary endpoint was recurrence-free survival (RFS) regardless of histology. Secondary endpoints include clear cell RCC RFS, overall survival (OS), and quality of life measures. Key points of this study were that (i) patient advocates aided in this trial design, (ii) no placebo was given, (iii) it was an open-label study, (iv) renal mass biopsy was mandated in the surgery + nivolumab arm (a non-diagnostic biopsy was considered a good faith effort and surgery proceeded thereafter), and (v) bilateral renal masses were allowed if they could be treated at the same time or within 12 weeks. The study had 84.2% power targeting an 11.7% absolute improvement in 5-year recurrence-free survival with an accrual goal of 805 patients.
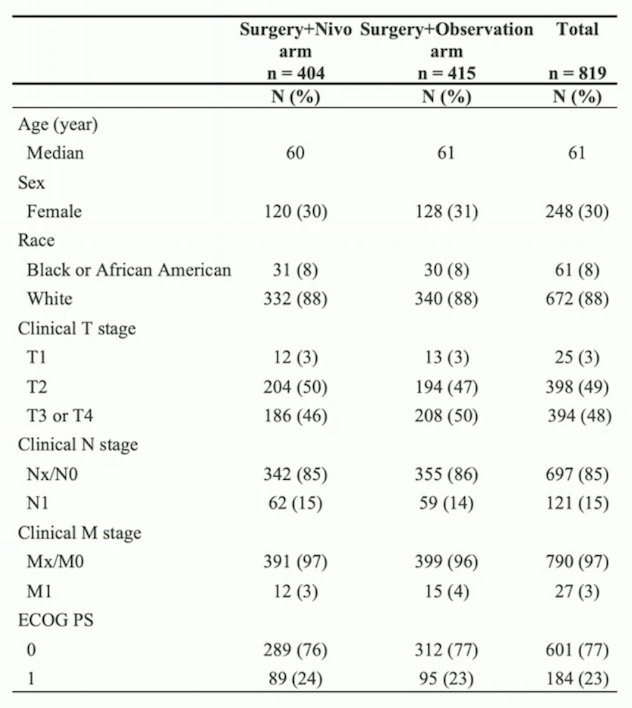
Between February 2017 and June 2021, 819 patients were randomized to perioperative nivolumab (n = 404) or surgery alone (n = 415). Clinical stage at enrollment was 49% cT2, 48% cT3-4, 15% cN1, and 3% cM1. Overall, 83% of patients had clear cell RCC. The baseline characteristics are as follows:
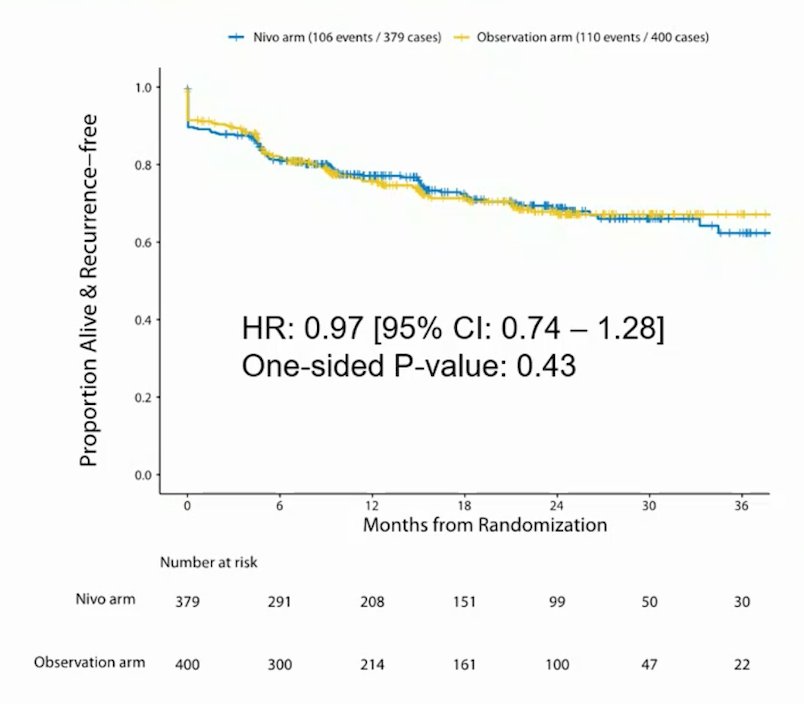
The post-surgery characteristics include >60% of patients having pT3/T4 tumors, >60% having high-grade tumors, ~80% being clear cell RCC, with ~5% undergoing partial nephrectomy, ~3% of RCC patients that had surgery not being disease-free post-surgery, and ~5% of patients being non-RCC cases (that were excluded from the primary analysis). Full information was available on 209 follow-up events, and at 71.8% information time inefficacy analysis results were presented to the data safety monitoring committee and the trial was stopped early due to futility (stratified hazard ratio for RFS exceeded a threshold of 0.96). The conditional power for primary and sensitivity analyses was <30% and the trial was quickly approaching full information when this decision was made. At a median follow-up of 16 months, RFS was similar between the arms (HR 0.97, 95% CI 0.74 – 1.28; p 1-sided = 0.43), and the median RFS was not reached:
The forest plot of RFS according to subgroups demonstrates no clinically meaningful benefit among these groups:

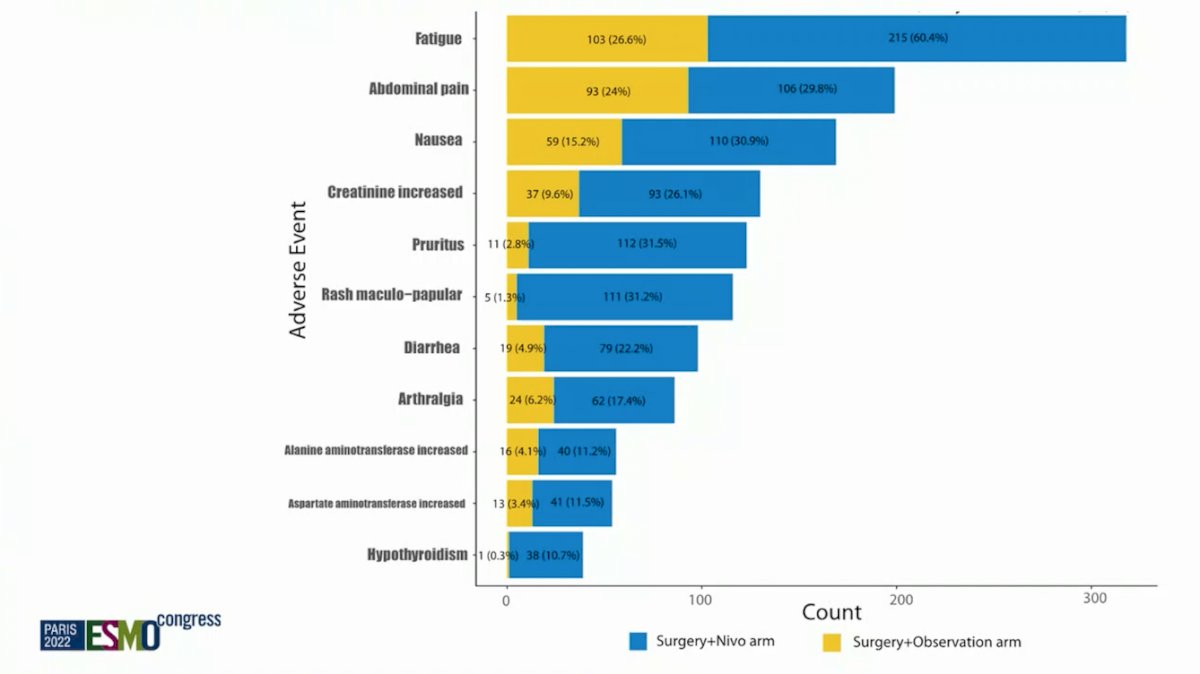
OS was not mature at the time of analysis but was not statistically different between study arms (HR 1.48, 95% CI 0.89 – 2.48; p 1-sided = 0.93). Similar withdrawal rates occurred in both arms, which was approximately 12% (48/404 patients in nivolumab arm versus 50/415 in surgery alone arm). Overall, 20% of patients treated with nivolumab experienced at least one Grade 3-4 adverse event that could be attributable to nivolumab, compared with 6% in the control arm. The most common treatment-related grade 3-4 adverse events were kidney injury (1% vs. 2%), rash (2% vs. 0%), and elevated lipase (4% vs. <1%). Treatment-related adverse events with an incidence of >10% are as follows:
There were 15 (4%) deaths from RCC in the nivolumab arm and 18 (4%) deaths from RCC in the surgery-alone arm.
Dr. Allaf concluded his presentation by discussing the results of the phase 3 open-label PROSPER trial assessing perioperative nivolumab versus observation in patients with RCC undergoing nephrectomy with the following take-home messages:
- This is the first phase III neoadjuvant IO trail in RCC
- Perioperative nivolumab did not improve RFS in RCC patients at high risk for recurrence
- OS data remains immature but is not statistically different between arms
- Adverse events in the surgery + nivolumab arm were consistent with the toxicity profile of other nivolumab trials
- Ongoing radiomic, pathomic, and other biomarker analyses within this trial may inform the design of future neoadjuvant RCC trials
- Further analyses of patient subsets within this unique trial design should help inform future research
Presented by: Mohamad Allaf, MD, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Co-Authors: S.E. Kim2, L.C. Harshman3, D.F. McDermott4, V.A. Master5, S. Signoretti6, S. Cole7, H. Moon8, N. Adra9, E.A. Singer10, J. Gills11, T.K. Choueiri12, B. Leibovich13, M.D. Michaelson14, B. shuch15, P.N. Lara16, D.Y.C. Heng17, A. Kapoor18, M.A. Carducci19, N.B. Haas20
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Assistant Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Augusta University/Medical College of Georgia, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2022 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Hybrid Meeting, Paris, FR, Fri, Sept 9 – Tues, Sept 13, 2022.


