(UroToday.com) The 2023 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Madrid, Spain between October 20th and 24th, 2023 was host to a renal cancer abstracts poster session. Dr. Rana McKay presented the results of a pooled meta-analysis of salvage nivolumab + ipilimumab following nivolumab in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Nivolumab + ipilimumab is approved for the 1st line treatment of patients with metastatic RCC based on the results of CheckMate214, which demonstrated that the use of nivolumab + ipilimumab, compared to sunitinib, for patients intermediate or poor prognostic risk was associated with improved overall survival outcomes at a median follow-up of 25.2 months (18-month survival: 75% versus 60%, p<0.001).1 Since then, a number of phase II trials evaluating the combination of nivolumab + ipilimumab in patients lacking an objective response to nivolumab have been published (OMNIVORE [NCT03203473];2 HCRN GU16-260 [NCT03117309];3 TITAN-RCC [NCT02917772]). The objective of this study was to perform a pooled meta-analysis of these studies to better inform the activity of combination nivolumab plus ipilimumab following nivolumab monotherapy.
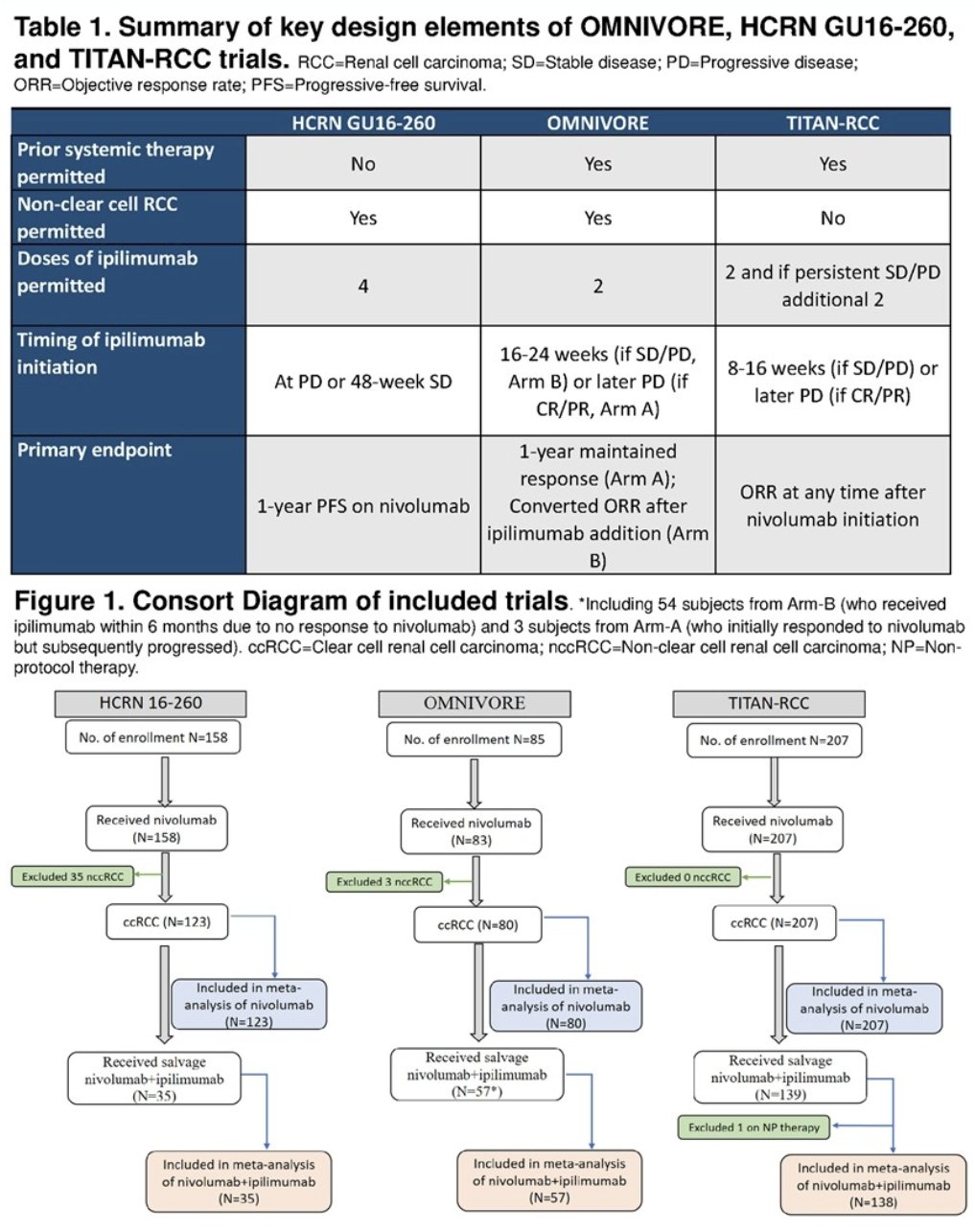
The key baseline characteristics and outcomes were collected and analyzed centrally. The primary study endpoint was confirmed objective response rate (ORR) to nivolumab + ipilimumab, as defined by investigator assessed RECIST v.1. The secondary endpoints included:
- ORR with nivolumab
- Progression-free survival (PFS) rate from the start of nivolumab/ipilimumab (only for OMNIVORE and HCRN GU-16-260)
- Overall survival (OS) rate from nivolumab start.
The analysis included 448 patients of whom 410 (91.5%) had clear cell RCC, 369 (82.3%) had IMDC intermediate/poor risk disease, and 139 (31.0%) had prior treatment.

The 16 to 18-week ORR to nivolumab prior to nivolumab + ipilimumab was 22%, and the best ORR to nivolumab was 24%. 249 (56%) patients treated with nivolumab subsequently received nivolumab + ipilimumab at a median of 16 weeks (IQR: 9 – 21 weeks) following the initiation of nivolumab. Of these 249 patients, 26.1% had stable disease and 64% had progressive disease with nivolumab.
At a median follow-up of 34.2 months, the ORR to nivolumab + ipilimumab was 13% (n=32). The ORR was comparable for patients who were treatment naive (12.4%) or had received prior therapy (13.5%). As expected, ORR was higher in those with IMDC favorable/intermediate-risk disease (14-15% versus 5% for poor-risk). Although there were only 19 patients with non-clear cell pathology, the ORR seemed to be slightly higher compared to those with clear cell pathology (15.8% versus 12.6%). Those with progressive disease with nivolumab had an ORR of 14%, compared to 9% for those with stable disease. The ORR was higher for those with complete or partial response to nivolumab (25%), compared to 12% for non-responders.


6 months PFS with nivolumab + ipilimumab was 39% (95% CI: 30 - 49), and the 3-year overall survival was 57% (95% CI: 52 - 62) from nivolumab initiation.
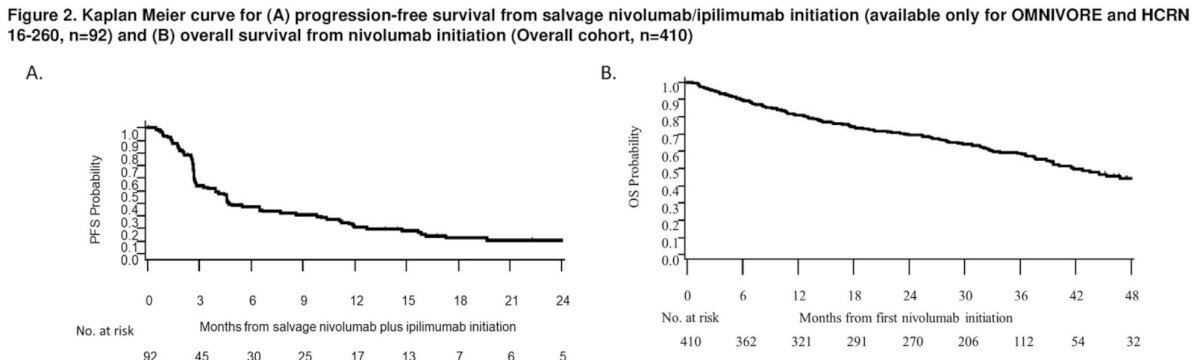
Based on these results, Dr. McKay concluded that a small subset of patients lacking a response to nivolumab monotherapy derive a benefit from salvage combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab. Additional correlative studies are needed to investigate markers associated with benefit of nivolumab plus ipilimumab following nivolumab.
Presented by: Rana McKay, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego, CAWritten by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Madrid, Spain, Fri, Oct 20 – Tues, Oct 24, 2023.
References:
- Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carinoma. N Engl J Med 2018;378(14):1277-1290.
- McKay RR, McGregor BA, Xie W, et al. Optimized Management of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Response-Based Phase II Study (OMNIVORE). J Clin Oncol 2020;38(36):4240-4248/
- Atkins MB, Jegede OA, Haas NB, et al. Phase II Study of Nivolumab and Salvage Nivolumab/Ipilimumab in Treatment-Naive Patients With Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (HCRN GU16-260-Cohort A). J Clin Oncol 2022;40(25):2913-2923.
- Grimm M, Esteban E, Barthelemy P, et al. Efficacy of nivolumab/ipilimumab in patients with initial or late progression with nivolumab: Updated analysis of a tailored approach in advanced renal cell carcinoma (TITAN-RCC). J Clin Oncol 2021;39(Suppl 15):4576-4576.


