(UroToday.com) The 2023 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Madrid, Spain between October 20th and 24th, 2023 was host to a prostate cancer abstracts poster session. Dr. Zheng Liu presented their newly developed deep learning network, NAFNet, for predicting adverse pathology events and biochemical recurrence using MRI data from prostate cancer patients.
While deep learning algorithms have shown promising results in medical imaging, their application for the prediction of adverse pathology events and biochemical recurrence-free survival in prostate cancer patients remains relatively sparse. In this analysis, Dr. Liu and colleagues aimed to evaluate the performance of a novel deep learning network, NAFNet, for the prediction of adverse pathology and biochemical recurrence-free survival using pre-treatment multiparametric MRI imaging.
This was a multicenter study that included 514 prostate cancer patients from six Chinese tertiary care hospitals between 2017 and 2021 The ‘internal’ set included a total of 367 patients from Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Centre with whole-mount histopathology of radical prostatectomy specimens. The cancer lesions were delineated with whole-mount pathology as the reference. The external test set included 147 patients with biochemical recurrence data from the five other institutions.
The prediction model (NAFNet-classifier) and integrated nomogram (DL-nomogram), which combined the NAFNet-classifier, clinical T stage, and biopsy results, were constructed based on NAFNet. To evaluate the predictive ability of DL-nomogram for adverse pathology, the authors compared DL-nomogram with the PIRADS and CAPRA scores, respectively. Receive operating characteristic (ROC) curves and detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) analyses were performed to assess the prediction ability of various models for adverse pathology, and survival analyses were also conducted to evaluate for biochemical recurrence-free survival.
Following training and validation in the internal set, ROC curves in the external test set showed that the NAFNet-classifier alone outperformed ResNet50 for predicting adverse pathology (AUC= 0.799, 95% CI:0.724 to 0.873 versus AUC=0.703, 95% CI: 0.618 to 0.787, p=0.013). The integrated DL-nomogram showed the highest AUC (0.915, 95% CI: 0.871 to 0.959) and accuracy (0.850) compared with the PIRADS and CAPRA scores. Additionally, the integrated DL-nomogram outperformed the CAPRA score with a higher C-index (0.732, P<0.001) for predicting biochemical recurrence-free survival. 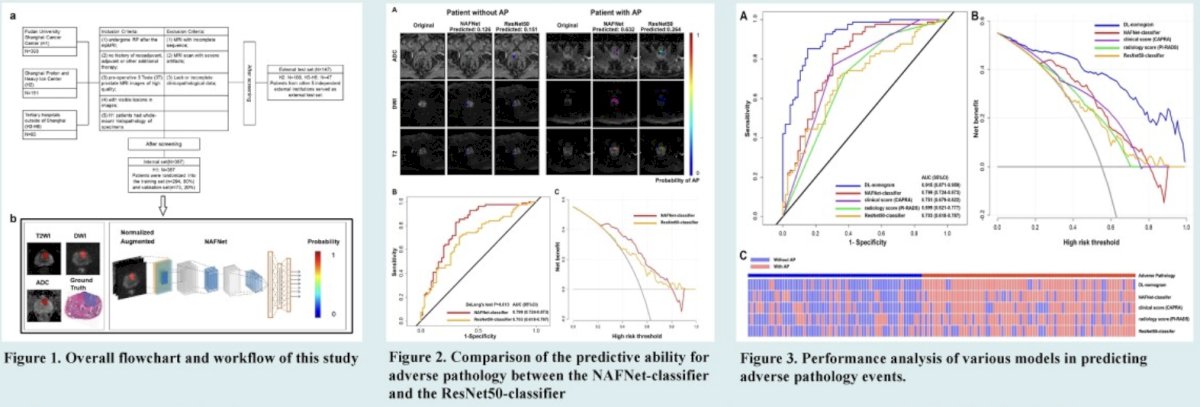
Based on these results, Dr. Liu and colleagues concluded that their newly developed deep learning network, NAFNet, particularly when combined with clinical factors, accurately predicted adverse pathology and biochemical recurrence outcomes in prostate cancer patients using preoperative MRI imaging, providing a potential AI tool for medical imaging-based risk stratification.
Presented by: Zheng Liu, MD, Shanghai, China
Written by: Rashid K. Sayyid, MD, MSc – Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Clinical Fellow at The University of Toronto, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2023 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Madrid, Spain between October 20th and 24th, 2023


