(UroToday.com) The 2023 ESMO annual meeting included a session on prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Charles Parker discussing external validation of a digital pathology-based multimodal artificial intelligence-derived model in high-risk M0/M1 prostate cancer starting ADT in the docetaxel or abiraterone phase 3 STAMPEDE trials. Treatment options beyond ADT have improved survival for high risk localized and metastatic prostate cancer, however accurate prognostication is needed for patient selection to avoid over and under treatment of patients. To date, clinical parameters remain the primary decision aid, but can we leverage histopathology for more information? Recently, a multimodal artificial intelligence prognostic test (ArteraAI Prostate) was developed for localized prostate cancer.1 At the 2023 ESMO annual meeting, Dr. Parker and colleagues aimed to validate ArteraAI in advanced prostate cancer using final data from 3 STAMPEDE trials.
The multimodal artificial intelligence model used digitized whole scan images from new H&E core prostate biopsies, local Gleason score, tumor (T) stage, age, and pre-ADT serum PSA. Fine-Gray/Cox regression adjusted for treatment allocation and cumulative incidence analyses were performed to evaluate associations with endpoints, as defined in STAMPEDE, for both continuous score (per standard deviation increase) and categorical (quartile). Prostate cancer-specific mortality (PCSM) was the endpoint of primary interest, and death not from prostate cancer was treated as a competing risk. The ArteraAI STAMPEDE study design is as follows:
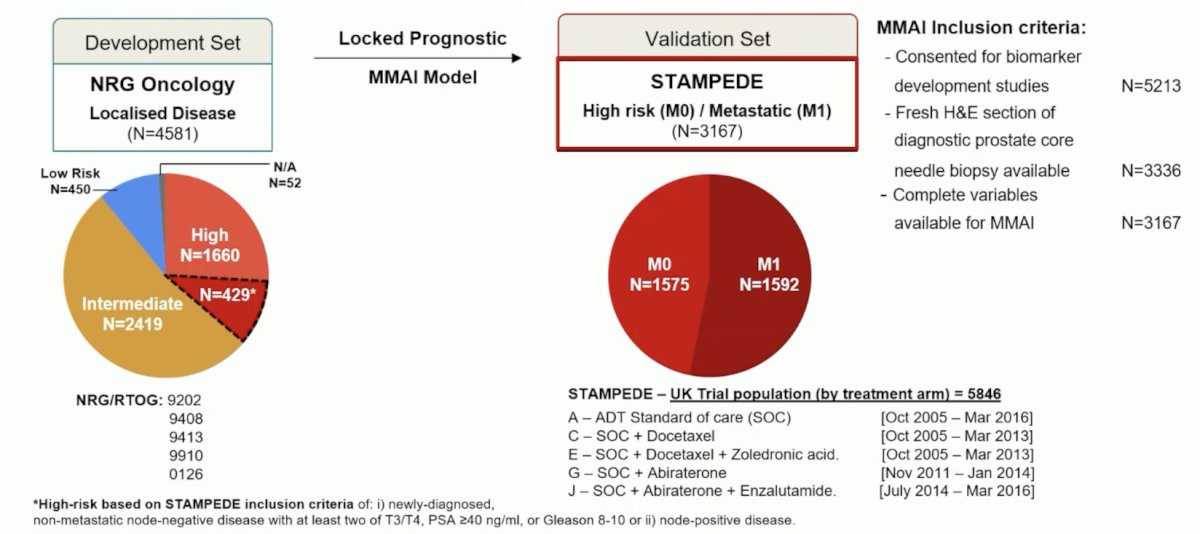
Among patients recruited from October 2005 to January 2014 to ADT +/- radiotherapy alone or + docetaxel +/-zoledronic acid or + abiraterone, 5,213 consented to tissue analysis, 3,336 had H&E with sufficient tumor of which 3,167 had all of Gleason score, T-stage, and pre-ADT PSA (1,575 M0, 1,592 M1). ArteraAI was strongly associated with:
- PCSM (HR 1.67, 95% CI 1.50-1.84)
- Overall survival (HR 1.51, 95% CI 1.40-1.63)
- Failure-free survival (HR 1.48, 95% CI 1.38-1.59)
- Metastatic progression-free survival (HR 1.59, 95% CI 1.46-1.73)
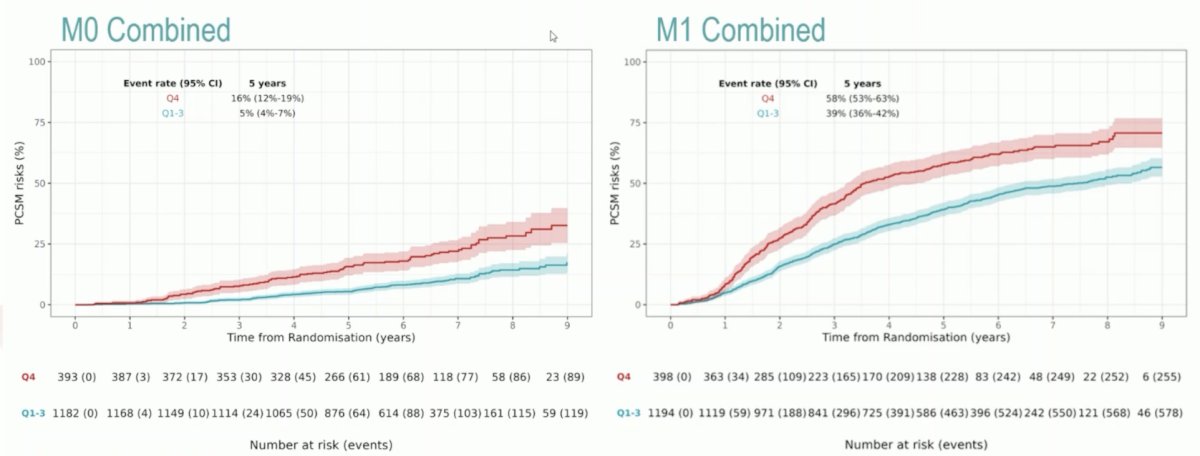
The following figure highlights the strength of association between ArteraAI and PCSM:

Of component clinical variables, p < 0.001 for PCSM were PSA quartile 4 v quartile 1-3 (HR 1.80, 95% CI 1.54-2.11), Gleason 8-10 versus <=7 (HR 1.64, 95% CI 1.36-1.98), and T4 versus T1-2 (HR 1.77, 95% CI 1.36-2.32). Additionally, ArteraAI quartile 4 versus quartile 1-3 had more PCSM events at 5 years: 16% (95% CI 12-19%) versus 5% (95% CI 4-7%) in M0, 58% (95% CI 53-63%) versus 39% (95% CI 36-42%) in M1:
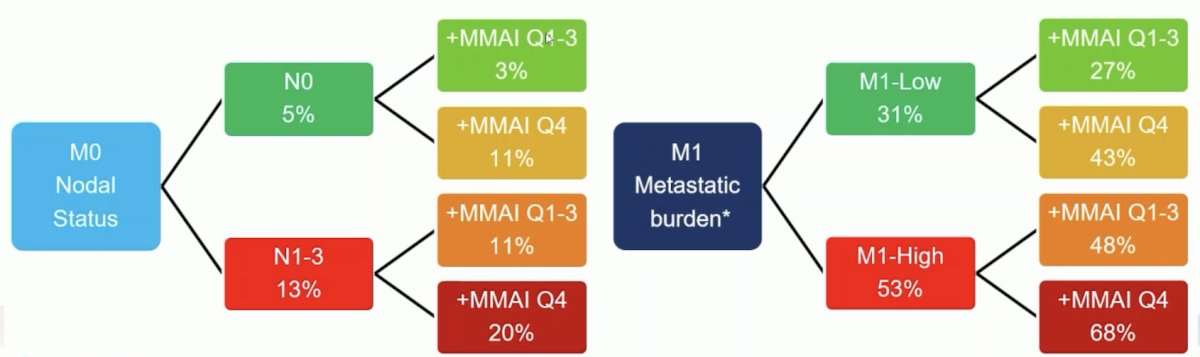
The addition of ArteraAI quartile 4 identifies poor prognosis patients in the high risk/metastatic setting with the following additive impact on event rate estimates for PCSM at 5 years:
Dr. Parker concluded his presentation by discussing external validation of a digital pathology-based multimodal artificial intelligence-derived model in high-risk M0/M1 prostate cancer starting ADT in the docetaxel or abiraterone phase 3 STAMPEDE trials with the following take-home points:
- ArteraAI successfully validated in STAMPEDE with stronger prognostic associations than individual clinical variables
- The multimodal artificial intelligence model identified poor prognostic features in prostate biopsies from high-risk M0 and M1 prostate cancer
Presented by: Charles T. Parker, PhD, University College London Cancer Institute, London, United Kingdom
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2023 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Madrid, Spain, Fri, Oct 20 – Tues, Oct 24, 2023.
References:


