(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain was host to the session Mini oral session: GU tumours, non-prostate. Dr. Thomas B. Powles presented an exploratory analysis of Nectin-4 Expression and Response to first line Enfortumab Vedotin (EV) + Pembrolizumab (P) in previously Untreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer (UC).
Dr. Powles began his presentation by noting that Nectin-4 is a cell-adhesion molecule involved in various cellular processes associated with oncogenesis and is highly expressed on the surface of most UC cells, as reported in multiple Enfortumab Vedotin (EV) trials. Data on the correlation between Nectin-4 expression and response to EV is limited, mostly deriving from prospective single-arm trials and retrospective real-world analyses.
In the Phase 3 EV-302 study, patients with previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic UC (la/mUC) who were randomized to EV + Pembrolizumab nearly double the median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to those receiving first-line chemotherapy (gemcitabine + cisplatin/carboplatin), establishing EV + Pembrolizumab as the new standard of care in la/mUC. The superior efficacy of EV + Pembrolizumab has been consistently demonstrated across various subgroups, including PD-L1 expression (high/low), cisplatin eligibility, and the presence or absence of liver metastases.1
In this exploratory biomarker analysis of the EV-302 study, the researchers investigated the relationship between Nectin-4 expression and oncological outcomes. They conducted a retrospective assessment of Nectin-4 expression using a CAP/CLIA-validated Nectin-4 immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay on primary or metastatic tumor tissue. Nectin-4 expression and Nectin-4/PD-L1 expression data were available for 800 of the 886 randomized patients (EV + Pembrolizumab: n=394; chemotherapy: n=406). PD-L1 expression status was categorized as high (CPS ≥10) or low (CPS <10) using a validated PD-L1 IHC assay. Oncological outcomes and clinical efficacy (PFS, OS, and ORR) were assessed across Nectin-4 expression subgroups.
Dr. Powles reported that the distribution of Nectin-4 scores was skewed toward high expression. The median H-score was 280 in the EV + Pembrolizumab group and 270 in the chemotherapy group. Only 3 patients (0.8%) in the EV + Pembrolizumab group and 6 patients (1.5%) in the chemotherapy group had an H-score of 0. The graphic below illustrates the distribution of Nectin-4 H-scores:
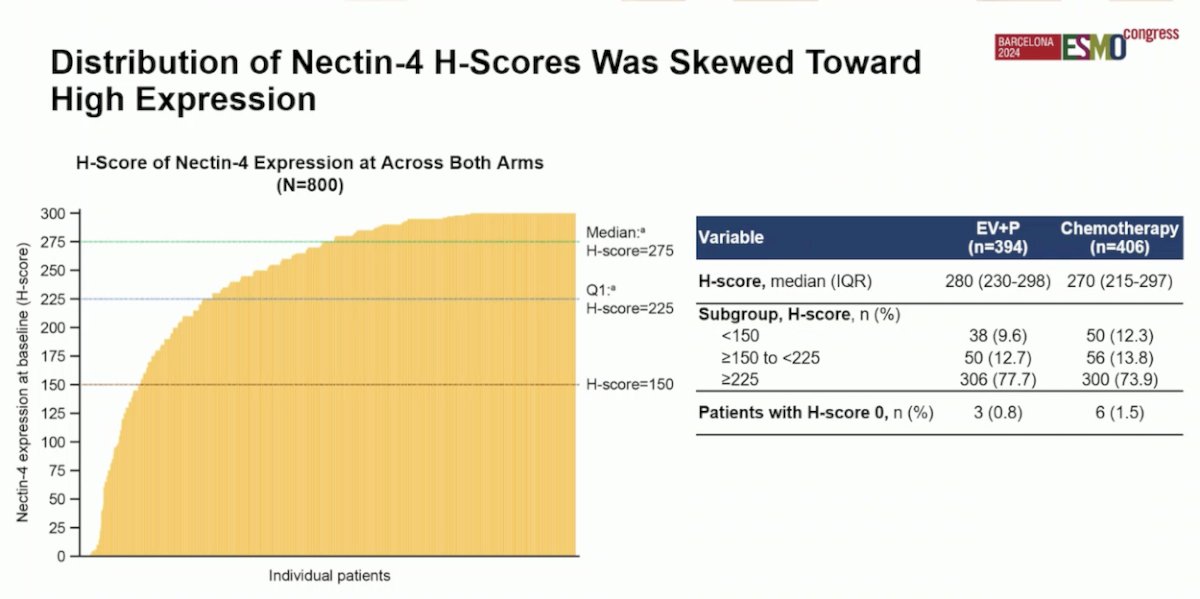
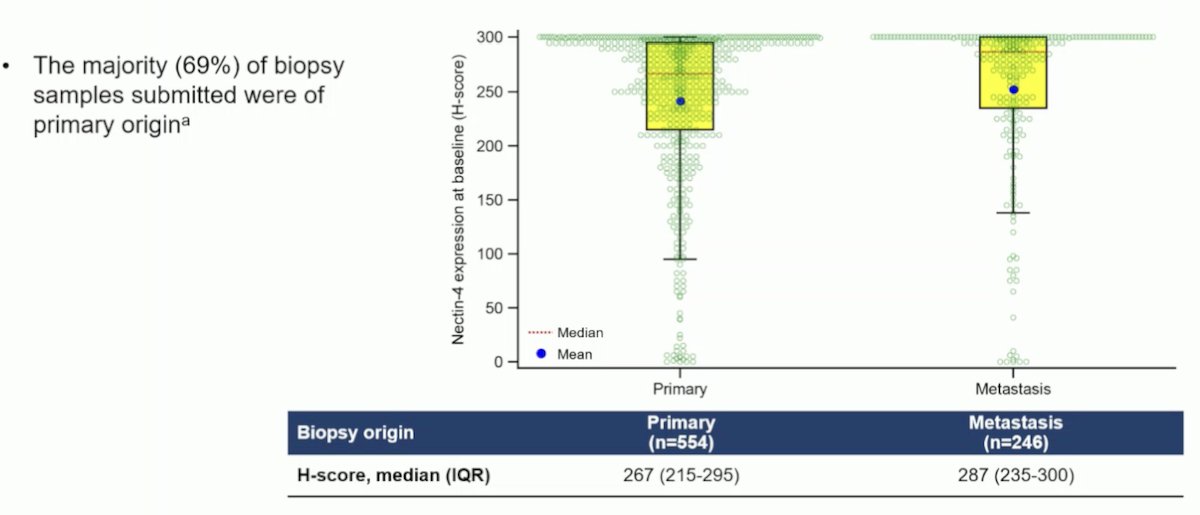
Notably, the high-Nectin H-scores were observed regardless of the biopsy origin (metastatic or primary). However, the majority of biopsy samples (69%) were of primary origin.
The investigators found a consistent PFS benefit with EV + Pembrolizumab in both Nectin-4 H-score subgroups: <275 and ≥275. The hazard ratios for progression were 0.503 (95% CI: 0.385-0.657) and 0.410 (95% CI: 0.313-0.537), respectively, indicating a favorable outcome for EV + Pembrolizumab in both Nectin-4 H-score subgroups.
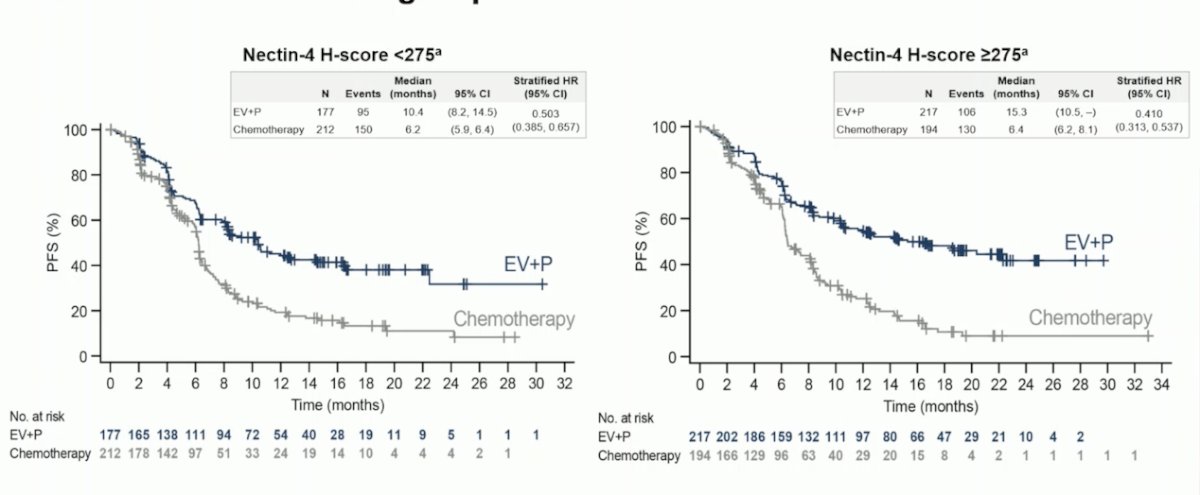
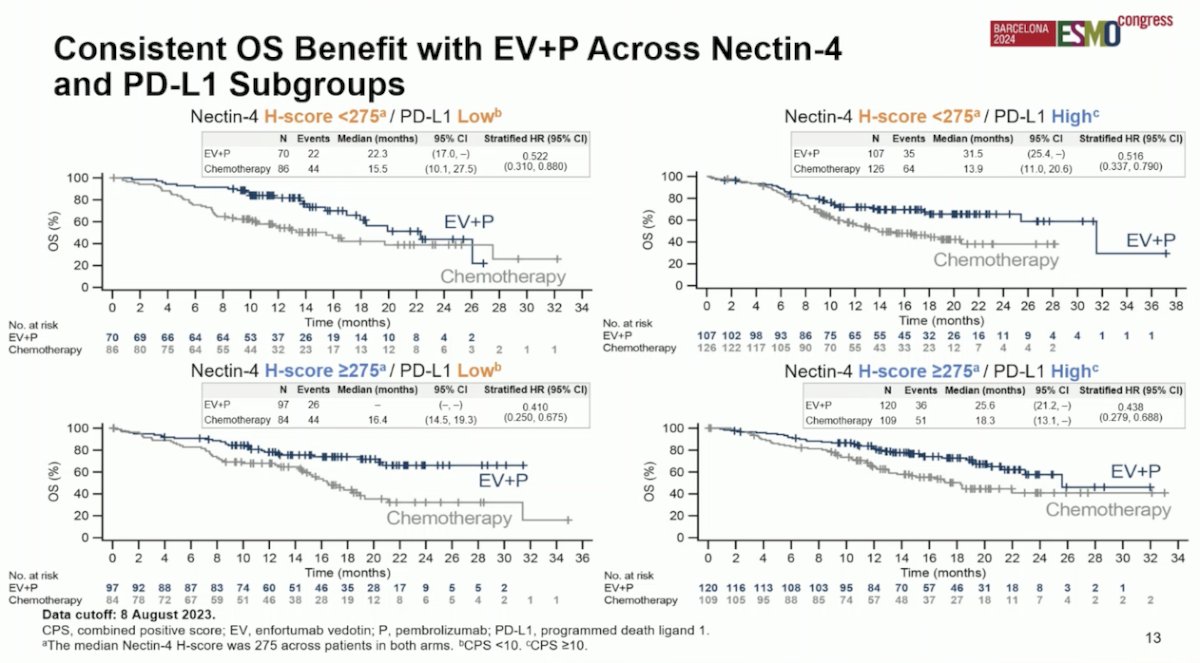
The PFS and OS benefit with EV+P across the Nectin-4 H-score subgroups was consistent in all H-score subgroups with HRs around 0.4 and 0.5 as illustrated below:

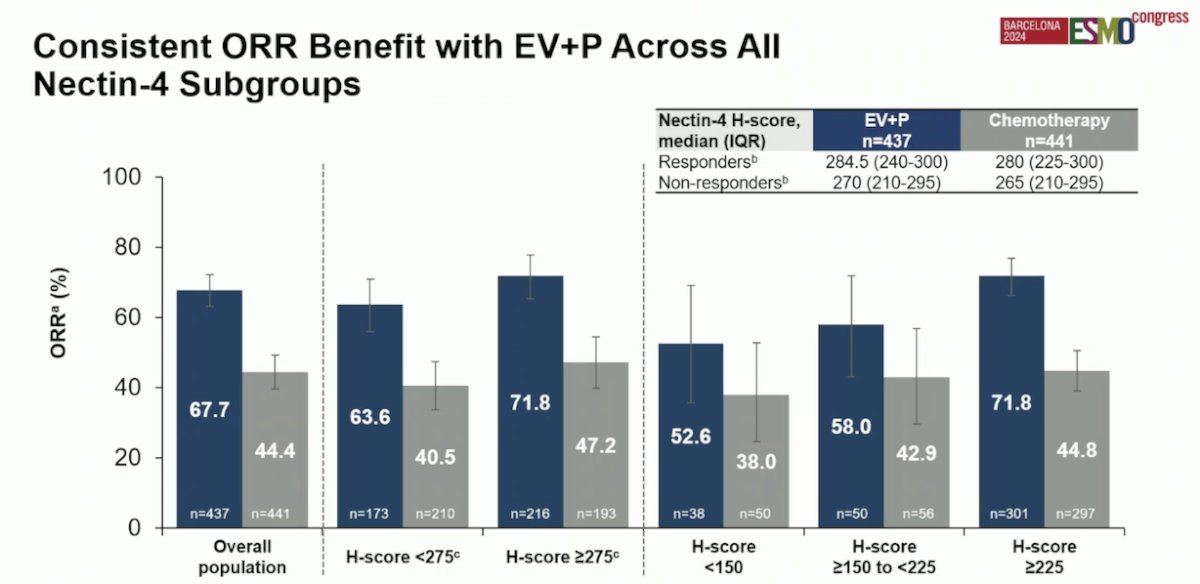
There was also a consistent overall response rate (ORR) benefit with EV + Pembrolizumab across all Nectin-4 H-score subgroups. Specifically, in patients with an H-score <275, the ORR was 63.6%, while in the H-score ≥275 subgroup, the ORR was 71.8%.
An exploratory analysis combined Nectin-4 and PD-L1 expression into four different subgroups (Nectin-4 H-score <275 or ≥275 with PD-L1 low/high). The distribution of Nectin-4 and PD-L1 expression across these subgroups is shown below:
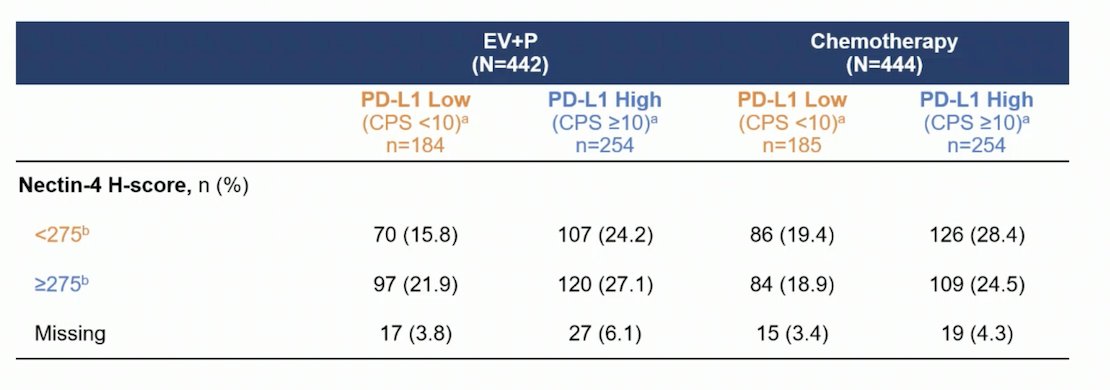
Remarkably there was a consistent PFS and OS benefit with EV+P across all Nectin-4 H-score and PD-L1 subgroups as illustrated in the Kaplan-Meier graphics below.
Dr. Powles concluded the presentation with the following key points:
- Nectin-4 is highly expressed in almost all available EV-302 patient tumor samples and shows consistency between primary and metastatic sites.
- This is the first exploratory Nectin-4 and PD-L1 biomarker analysis to demonstrate a consistent benefit of EV + Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy across all Nectin-4 subgroups and evaluated endpoints (PFS, OS, and ORR).
- The observed benefit of EV + Pembrolizumab remains irrespective of Nectin-4 expression and PD-L1 status.
- These data further support EV + Pembrolizumab as the standard of care in the first line for the la/mUC population and confirm that testing for Nectin-4 expression or PD-L1 status is not required.
Presented by: Thomas B. Powles, MBBS, MRCP, MD, Department of Genitourinary Oncology, Barts Cancer Institute, Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre, Queen Mary University of London, St Bartholomew’s Hospital, London, UK
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD – Urologic Oncologist at Cancer Treatment and Research Center (CTIC) Luis Carlos Sarmiento Angulo Foundation via Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Fellow at The University of Toronto. @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
References:

