(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain between September 13th and 17th was host to the session Mini oral session: GU tumours, non-prostate. Dr. Vadim S. Koshkin presented the final analysis of efficacy and safety of the phase 2 study of futibatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC).
Dr. Koshkin began his presentation by sharing that despite significant recent changes in the treatment landscape of mUC, patients who are ineligible for platinum-based chemotherapy still need effective and tolerable treatment options. The combination of an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) and FGFR inhibitor has been shown to enhance antitumor immunity in preclinical models in an autochthonous FGFR2K660N/p53mut lung cancer mouse model.1 Additionally, the combination of ICI + FGFR inhibitors has demonstrated clinically meaningful activity in patients with mUC and FGFR alterations in a phase 2 study of Erdafitinib and Cetrelimab.2
Futibatinib is an oral, highly potent, covalently binding inhibitor of FGFR1‒4. This molecule stands out among FGFR inhibitors because of its covalent binding mechanism and low susceptibility to acquired resistance. Futibatinib has shown broad activity in FGFR-altered tumors including urothelial carcinoma.3
Dr. Koshkin shared that this phase 2 trial was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of the first-line combination of futibatinib and pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC), with or without FGFR alterations, who are ineligible for or decline platinum-based chemotherapy.
This global, two-cohort, non-comparative phase 2 study (NCT04601857) enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1 and histologically confirmed mUC. Eligible participants had no prior therapy for advanced/metastatic disease and were either unfit for or declined platinum-based chemotherapy.
Cohort A (n=17) included patients with FGFR3 mutations or FGFR1-4 rearrangements/fusions. Cohort B (n=26) included patients with wild-type or other FGFR/non-FGFR-aberrant tumors not included in Cohort A. The study design is illustrated below.
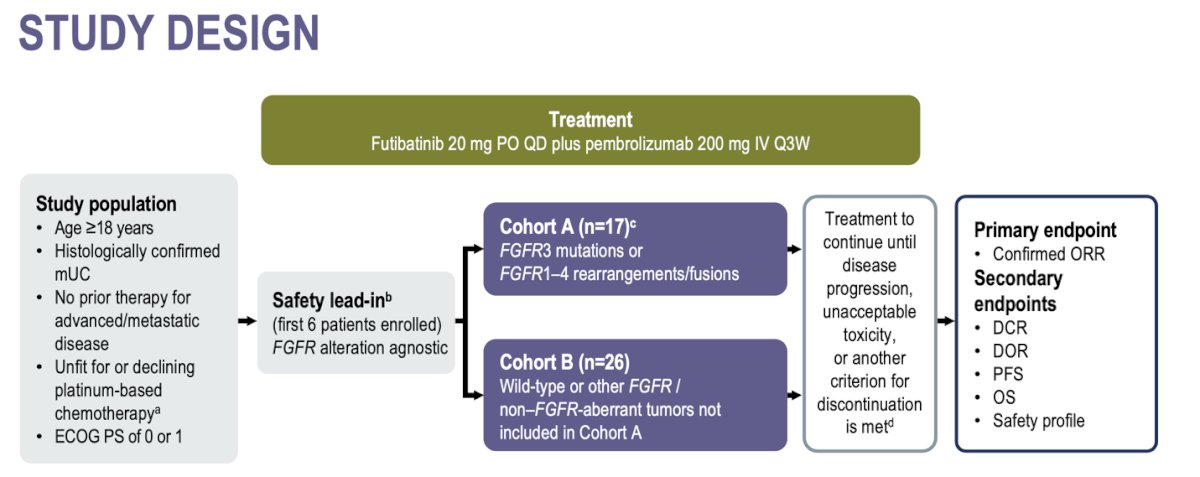
Most patients were male in both cohorts. In Cohort A, 58.8% of patients had an FGFR3 mutation, 35.3% had an FGFR3 fusion, rearrangement, or translocation, and 5.9% had either an FGFR1 or FGFR2 fusion, rearrangement, or translocation. The primary tumor was located in the bladder in 94.1% of patients in Cohort A and in 88.5% of patients in Cohort B.
In Cohort A (patients with FGFR1-4 mutations, fusions, or rearrangements), 14 (82.4%) of evaluable patients had a reduction in target lesions. The overall response rate (ORR) was 47.1%, with 11.8% achieving a complete response, 35.3% a partial response, 35.3% stable disease, and 11.8% progressing. A total of 3 (37.5%) patients had an ongoing response of ≥6 months. The median duration of response was 12.3 months, and the median time to first response was 2.3 months. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 8.3 months and median overall survival (OS) was not reached, after a median follow-up of 17.8 months.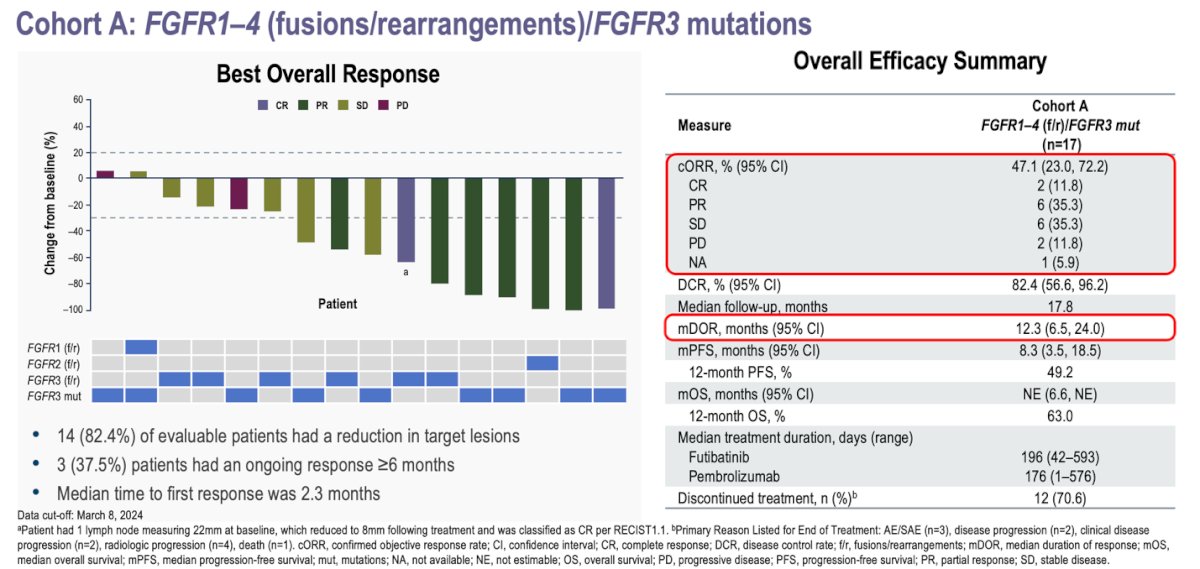
In Cohort B, 17 (65.4%) of evaluable patients had a reduction in target lesions, the ORR was 26.9%, 3 (11.5%) achieving a complete response, 15.4% a partial response, 26.9% stable disease, and 38.5% progressed during treatment. 1 (14.3%) patient in cohort B had an ongoing response ≥6 months. One (14.3%) patient in cohort B had an ongoing response ≥6 months and the median time to first response was 1.9 months as illustrated below:
Overall, there were 16 (94.1%) treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) in Cohort A and 26 (100%) in Cohort B. Grade 3 TRAEs occurred in 41.2% of patients in Cohort A and 42.3% in Cohort B. The most common TRAEs were hyperphosphatemia (64.7%), diarrhea (41.2%), and dry mouth (47.1%).
Dr Koshkin concluded his presentation with the following key takeaway messages:
- Futibatinib plus pembrolizumab demonstrated encouraging antitumor activity with durable responses in patients with mUC, particularly among those with FGFR3 mutations or FGFR1–4 fusions/rearrangements.
- In patients with FGFR3 mutations or FGFR1–4 fusions/rearrangements, the confirmed ORR was 47.1%, with a median duration of response of 12.3 months and a median PFS of 8.3 months after a median follow-up of 17.8 months.
- The combination of futibatinib plus pembrolizumab was well tolerated, with no new safety signals observed.
- These results support further investigation of futibatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with mUC and FGFR3 mutations or FGFR1–4 fusions/rearrangements.
Presented by: Vadim S. Koshkin, MD, Assistant Professor, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Medicine, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD – Urologic Oncologist at Cancer Treatment and Research Center (CTIC) Luis Carlos Sarmiento Angulo Foundation via Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Fellow at The University of Toronto. @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain between September 13th and 17th
References:- Palakurthi S, Kuraguchi M, Zacharek SJ, Zudaire E, Huang W, Bonal DM, Liu J, Dhaneshwar A, DePeaux K, Gowaski MR, Bailey D, Regan SN, Ivanova E, Ferrante C, English JM, Khosla A, Beck AH, Rytlewski JA, Sanders C, Laquerre S, Bittinger MA, Kirschmeier PT, Packman K, Janne PA, Moy C, Wong KK, Verona RI, Lorenzi MV. The Combined Effect of FGFR Inhibition and PD-1 Blockade Promotes Tumor-Intrinsic Induction of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. 2019 Sep;7(9):1457-1471. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0595. Epub 2019 Jul 22. PMID: 31331945.
- Arlene O. Siefker-Radtke et al. Erdafitinib (ERDA) vs ERDA plus cetrelimab (ERDA+CET) for patients (pts) with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC) and fibroblast growth factor receptor alterations (FGFRa): Final results from the phase 2 Norse study. JCO 41, 4504-4504(2023).
- Meric-Bernstam F, Bahleda R, Hierro C, et al.. Futibatinib, an irreversible FGFR1-4 inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors, harboring FGF/FGFR aberrations: a phase I dose-expansion study. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(2):402-415. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0697


