(UroToday.com) The 2024 ESMO annual meeting included a session on kidney cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Eric Jonasch discussing preliminary results of a phase 1/2 study assessing NKT2152, a novel oral HIF-2α inhibitor, in patients with previously treated advanced clear cell RCC. HIF-2α is a clinically validated targeted, given that it is a driver of clear cell RCC with somatic VHL deficiency, a driver of VHL diseases with germline VHL mutations, and has restricted normal tissue expression. NKT2152 is a novel oral HIF-2α inhibitor that inhibitors transcription of HIF-2α-regulated genes important for angiogenesis, glycolysis, and tumorigenesis:
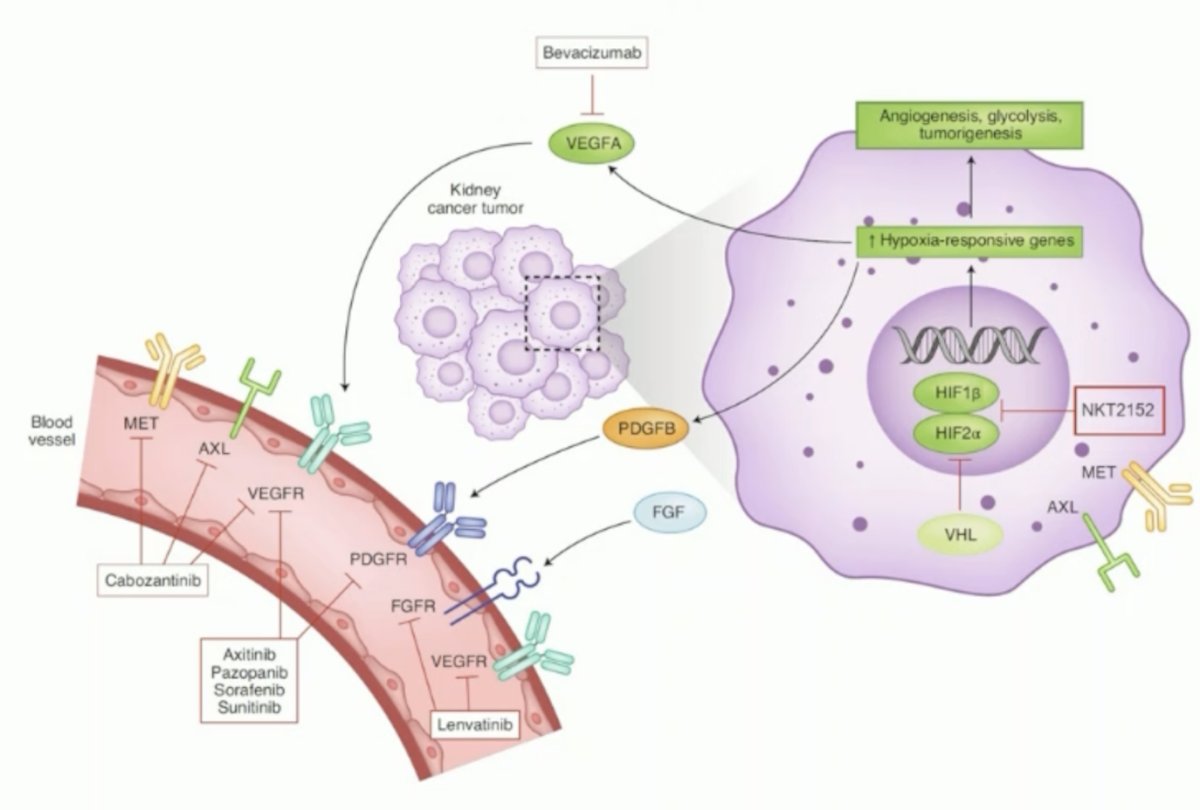
In an ongoing phase 1/2 trial (NCT05119335), Dr. Jonasch and colleagues investigated safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical efficacy in patients with advanced clear cell RCC.
Adult patients with advanced clear cell RCC not amenable to standard therapy, ECOG status of 0-2, and progression after ≥1 prior regimen received NKT2152 in eight dose escalation cohorts: four daily and four loading/maintenance regimens, followed by a randomized expansion at two selected dose levels:
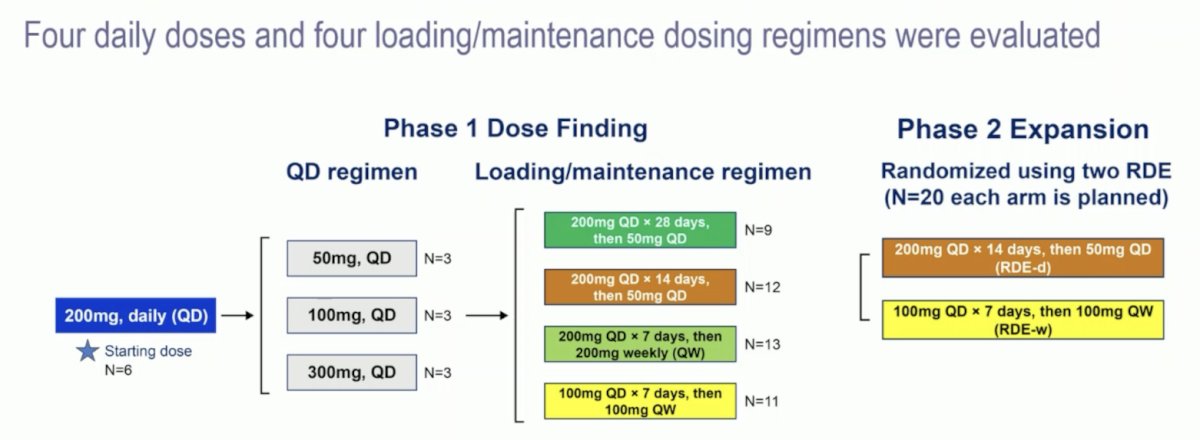
A population pharmacokinetics - erythropoietin model was developed, and an exploratory exposure-response analysis was conducted. At ESMO 2024, Dr. Jonasch reported a preliminary analysis with a data cut-off of June 16, 2024.
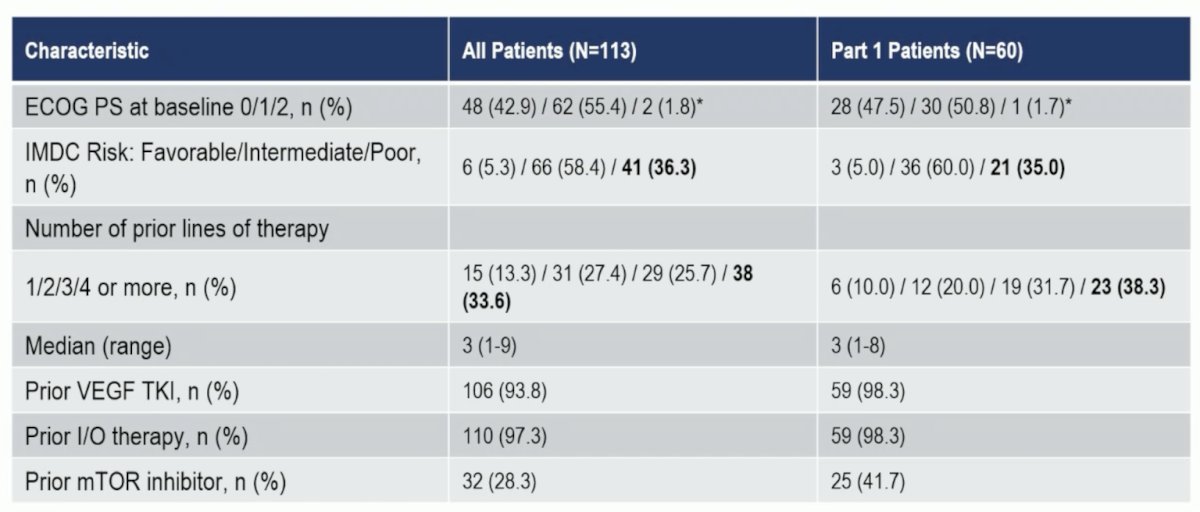
There were 100 patients (60 dose escalation, 40 expansion) enrolled, with the following IMDC risk breakdown: 5.3% favorable, 58.4% intermediate, and 36.3% poor. There were 33.6% of patients that had 4+ prior lines of therapy, 28.3% had prior mTOR inhibitor therapy, 93.8% had prior VEGFR-TKI therapy, and 97.3% had prior anti PD-(L)1 therapy:
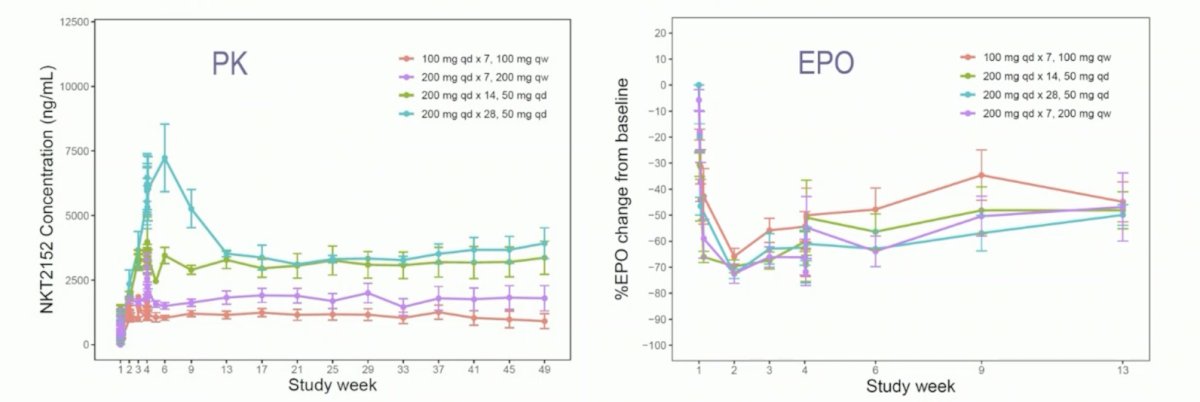
Pharmacokinetics was dose linear and time independent, and erythropoietin suppression was observed at all dose levels (Imax = 0.72, IC50 = 16.4 ng/mL):
Overall, median follow-up was 13.5 months (range: 0.23-31.2), 41% of patients had ongoing treatment, and 12% discontinued the study for an adverse event. In 100 efficacy evaluable patients, the confirmed objective response rate by RECIST 1.1 was 20.0%, with the following objective response rate subgroup analysis:
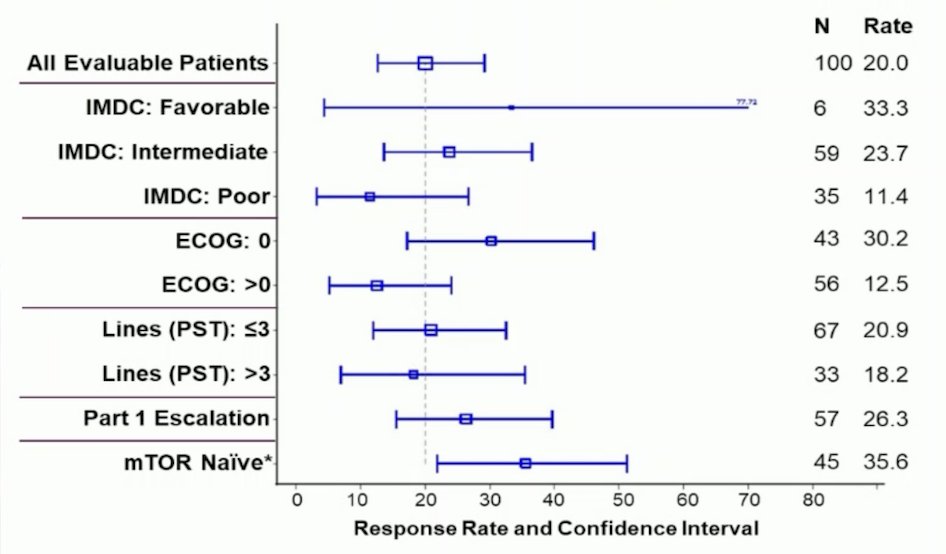
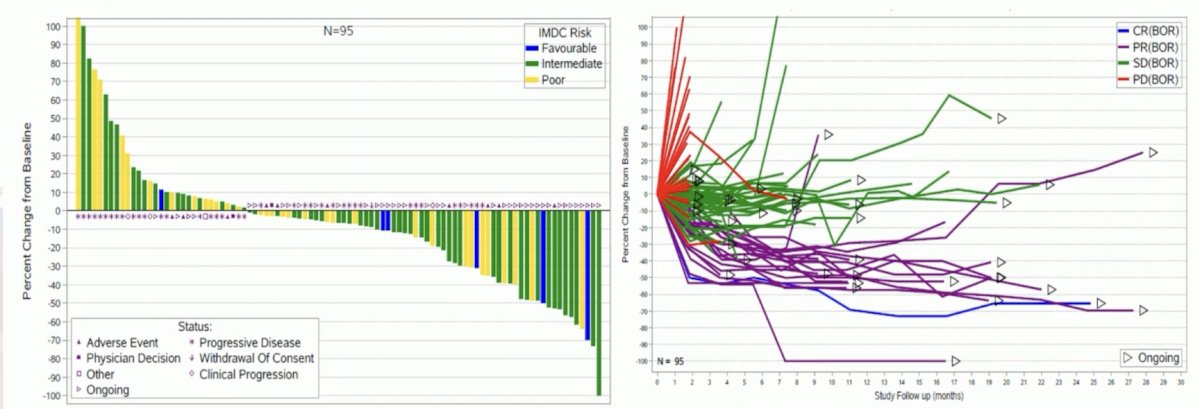
The complete response rate was 1.0%, partial response rate was 19.0%, stable disease rate was 52.0%, and progressive disease rate was 28.0%. The median time to tumor reduction was 3.7 months (95% CI 1.6-9.1), median duration of response was not reached, and disease control rate was 60% (95% CI 50% - 70%):
The median progression-free survival was 7.4 months and 12 month PFS rate was 42%:
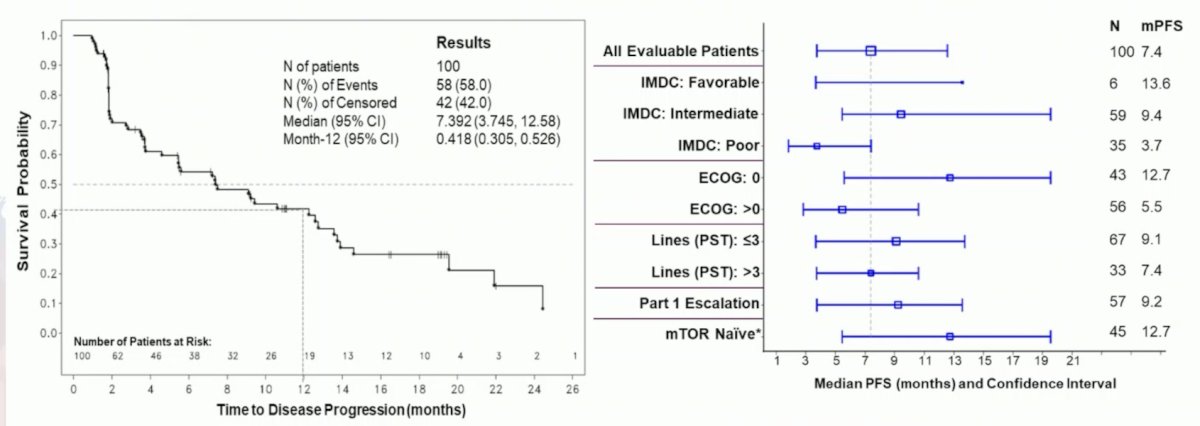
In a subset of 45 evaluable patients with no prior mTOR inhibitor (median prior lines: 3) enrolled at least 9 months prior to the cut-off, median progression-free survival was 12.7 months. The pattern of related adverse events was similar across all dose levels. Dose limiting toxicity was fatigue and hypoxia in 1/12 subjects at 200 mg QD x 14, then 50 mg QD, and was also observed in 1/9 subjects at 200 mg QD x 28, then 50 mg QD. The most common adverse events were anemia (9.7% grade 1, 44.2% grade 2, 35.4% grade 3) and fatigue (8.8% grade 1, 44.2% grade 2, 17.7% grade 3).
Dr. Jonash concluded his presentation by discussing the preliminary results of a phase 1/2 study assessing NKT2152 in patients with previously treated advanced clear cell RCC with the following take-home points:
- NKT2152 demonstrated robust anti-tumor activity in heavily pretreated, high risk advanced clear cell RCC patients
- Overall, in 100 efficacy evaluable patients, the objective response rate was 20% and median progression free survival was 7.4 months
- In patients with no prior mTOR and at least 9 months of follow-up, objective response rate was 35.6% and median progression free survival was 12.7 months
- NKT2152 showed linear PK and significant and prolonged EPO suppression at all tested dosage levels
- The safety profile was consistent with this class of agent
- Two dose regimens with loading/maintenance dosing have been selected and are under evaluation in the dose expansion of this study
Presented by: Eric Jonasch, MD, University of Texas MD Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Related content: NKT2152: Promising New HIF-2 Alpha Inhibitor for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma - Eric Jonasch
New Dual-Target Drug Shows Promise Against Bladder Cancer - Jonathan Rosenberg
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.


