(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain was host to a genitourinary cancers poster session. Dr. Jwa Hoon Kim presented the initial results of RENOIR (KCSG GU22-13), a real-world study of 1st line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations are the standard-of-care 1st line option for the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic RCC. The combination of nivolumab (anti-PD-1) plus ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) was approved based on the results of the CheckMate-214 trial, published in 2018, which demonstrated an improvement in median overall survival (not reached versus 26 months for sunitinib; HR: 0.63, p<0.001), progression-free survival (median, 11.6 versus 8.4 months; HR: 0.82, p=0.03), and objective response rate (42% versus 27%, p<0.001), compared to sunitinib.1
Dr. Kim noted that despite the occurrence of durable responses to dual immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations, there are some lingering concerns about the potential occurrence of initial rapid progression and variable efficacy in various patients in real-world practice. Additionally, there are no clear biomarkers for predicting response, and the decision for which approved systemic regimen to choose in the front-line setting remains challenging in real-world practice. The objective of this study was to investigate the real-world efficacy of first line nivolumab plus ipilimumab and its clinicopathologic predictive biomarkers in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
This study included 455 patients with histologically confirmed advanced RCC who received 1st line nivolumab + ipilimumab between 2018 and 2022 at one of 20 centers in South Korea. The primary study outcome was objective response rate, with secondary outcomes of progression-free and overall survival. Additionally, Dr. Kim and colleagues investigated potential prognostic biomarkers of treatment response, which included the following variables:
- Age
- Sex
- Histology (clear cell versus non-clear cell)
- Presence/absence of sarcomatoid features
- Metastatic sites (number and location)
- IMDC risk group
- Duration of response
- Previous nephrectomy (yes/no)
- Prior history of radiotherapy
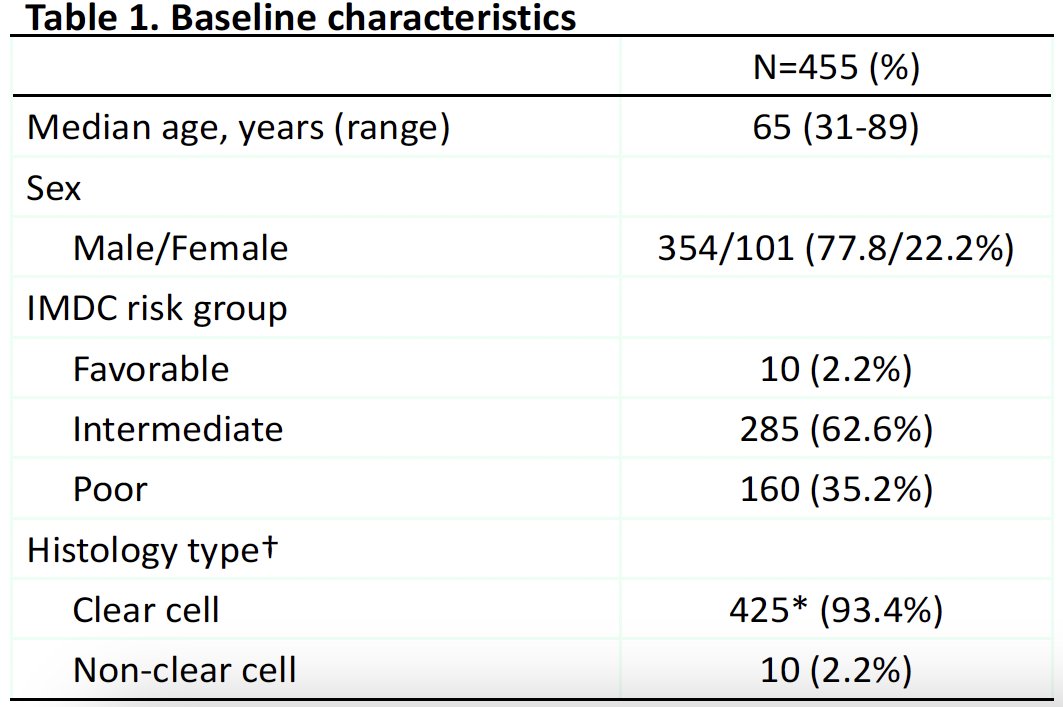
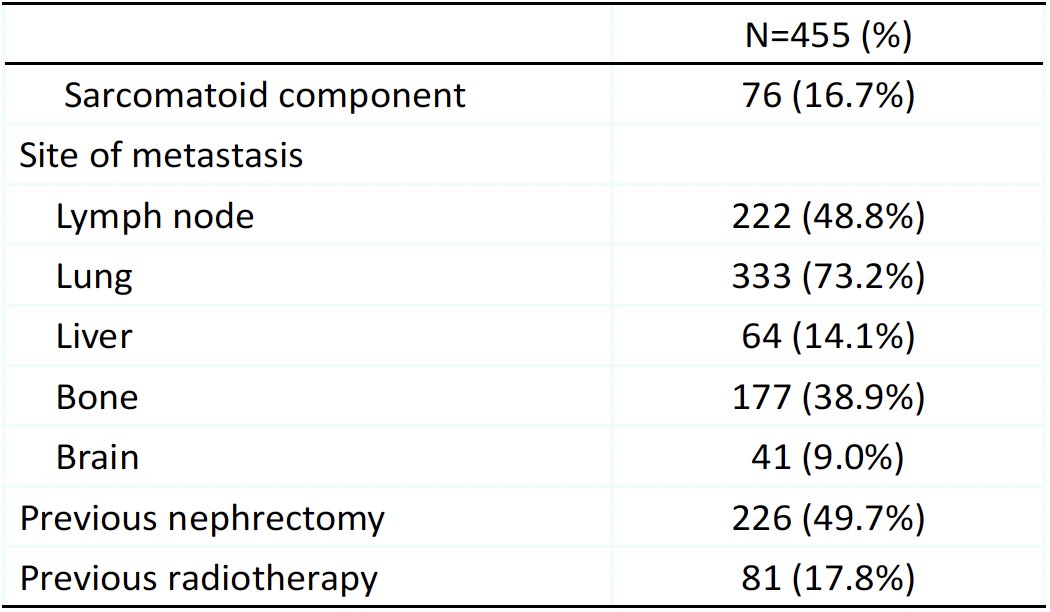
The baseline patient characteristics are summarized below. The median patient age was 65 years. 98% of patients had IMDC intermediate or poor risk disease. 93% of patients had clear cell RCC, and 17% had a sarcomatoid component. The most common sites of metastases were the lungs (73%) and bones (39%). 50% had a previous nephrectomy, and 18% had received prior radiotherapy.
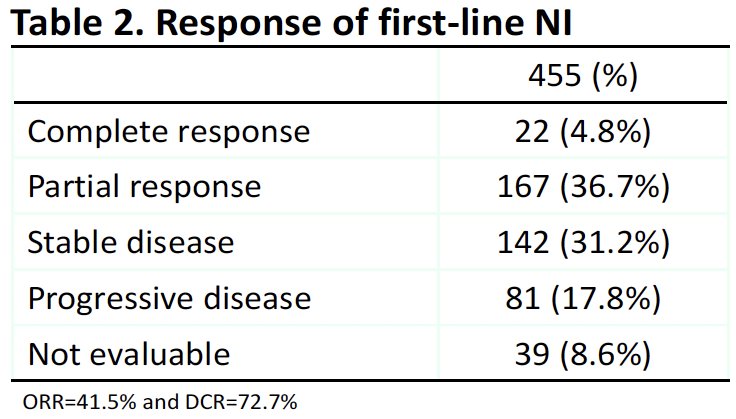
A complete or partial response was observed in 41.5% of patients (complete: 4.8%; partial: 36.7%). The disease control rate was 73%. 18% of patients had progressive disease.
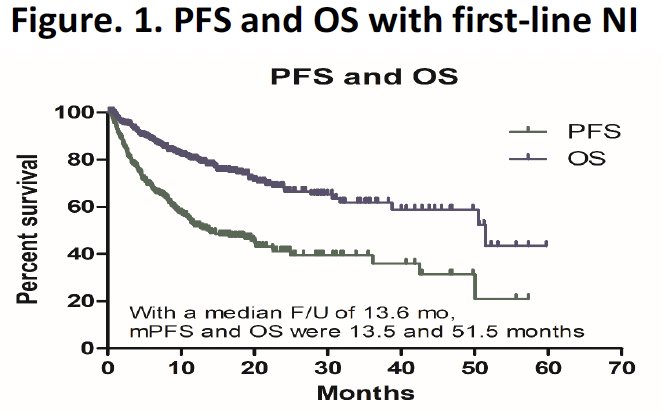
The median progression-free survival was 13.6 months, and the median overall survival was 51.5 months.
Significant predictors of a treatment response on multivariable logistic regression analysis included male sex (OR: 1.98, p=0.017), presence of lung metastases (OR: 2.45, p=0.001), and a history of a prior nephrectomy (OR: 2.13, p=0.001).
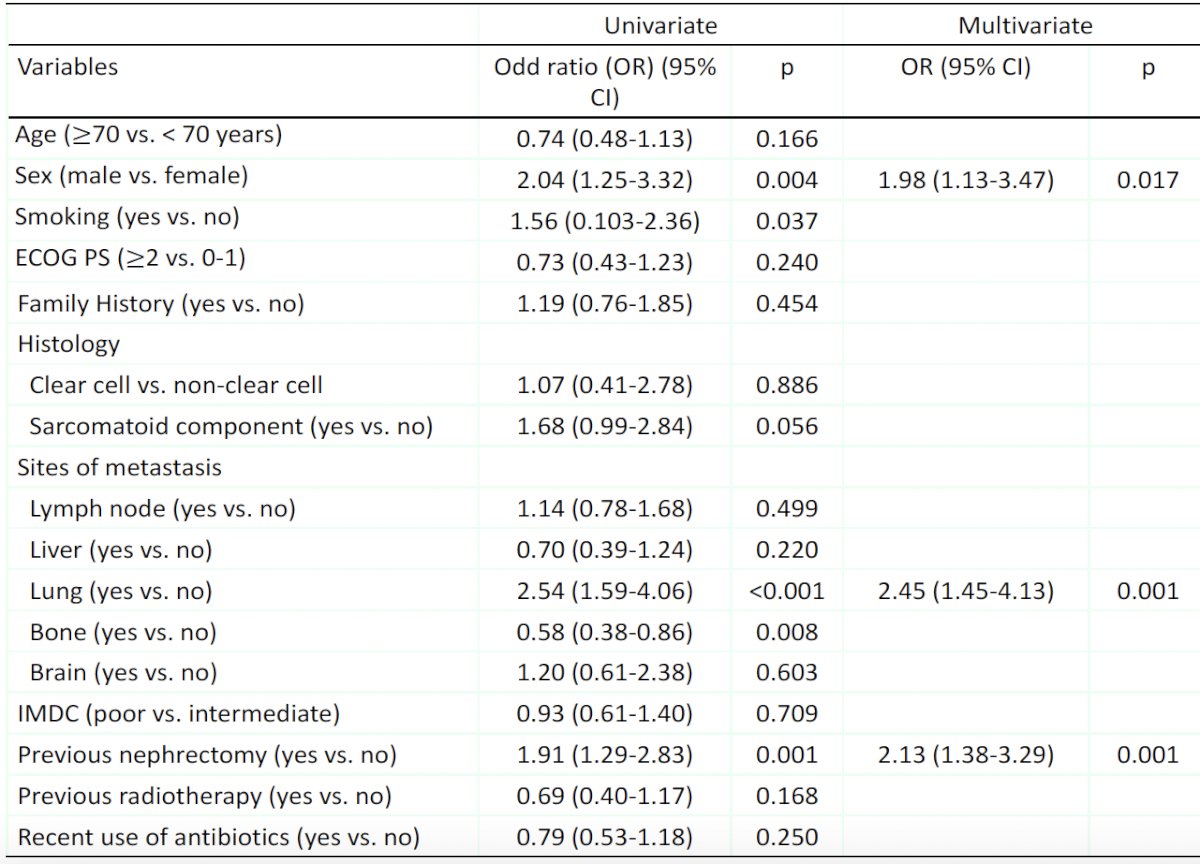
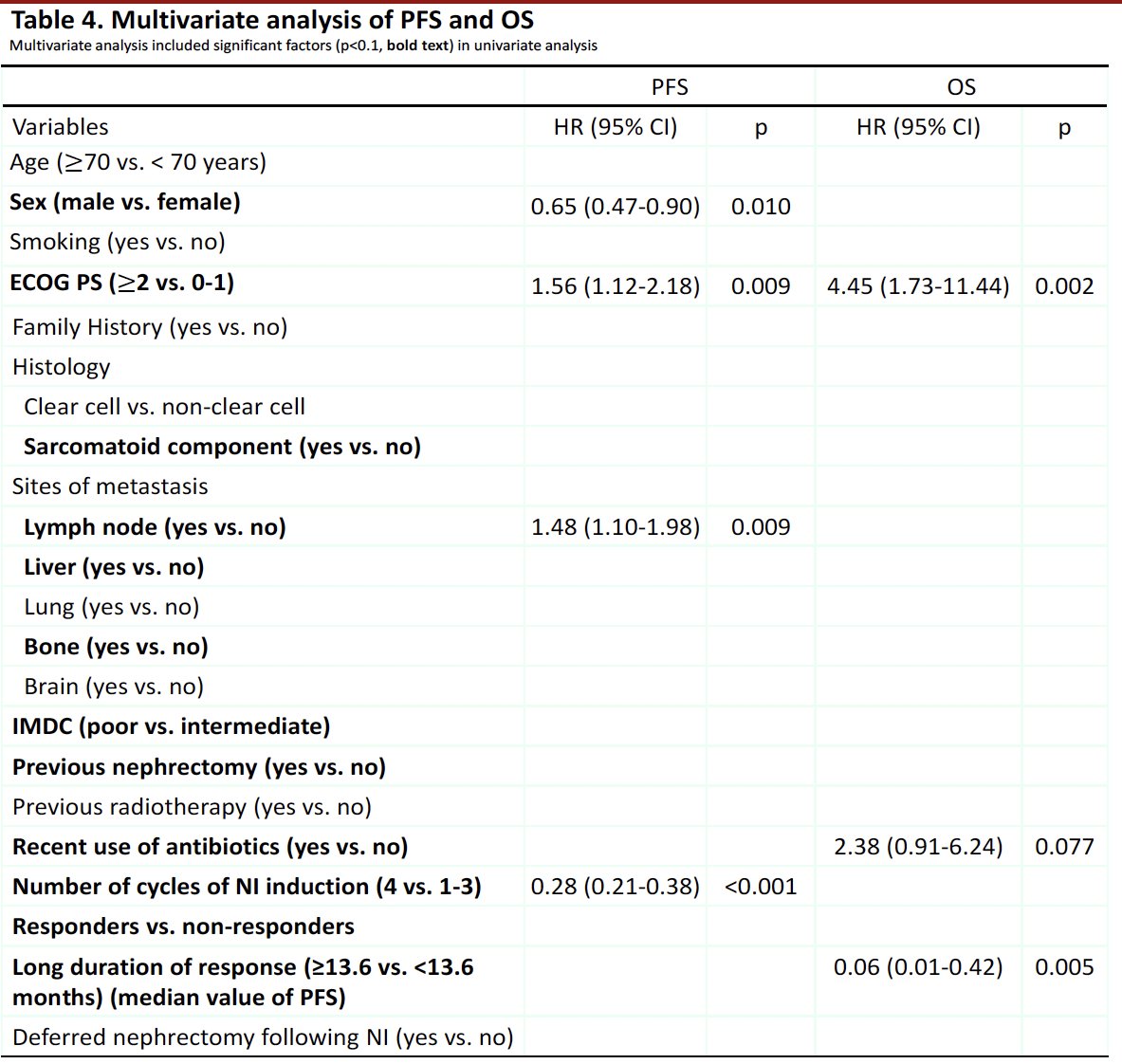
Predictors of worse progression-free survival among advanced RCC patients receiving nivolumab plus ipilimumab were worse ECOG performance status (≥2 versus 0–1) and presence of lymph node metastases. Male patients and those receiving a higher number of induction cycles (4 versus 1–3) had superior progression-free survival. For overall survival, worse ECOG performance status (≥2 versus 0–1) and recent use of antibiotics were associated with worse overall survival outcomes. Patients with a longer median duration of response (≥13.6 versus <13.6 months) had better overall survival outcomes.
Dr. Kim concluded as follows:
- 1st line nivolumab + ipilimumab showed comparable real-world efficacy in Korean patients with advanced RCC.
- Poorer ECOG performance status is associated with worse overall and progression-free survival
- Male sex, presence of lymph node metastases, and completion of four induction cycles of nivolumab + ipilimumab were significantly associated with progression-free survival, whereas recent use of antibiotics and long duration of response were significantly associated with overall survival outcomes.
- Male gender, presence of lung metastasis, and a history of a prior nephrectomy might be ‘practical’ predictors of objective response and, thus, overall survival outcomes
Presented by: Jwa Hoon Kim, Department of Medical Oncology and Hematology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, South Korea
Written by: Rashid Sayyid, MD, MSc – Robotic Urologic Oncology Fellow at The University of Southern California, @rksayyid on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
References:


