(UroToday.com) The 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Congress held in Barcelona, Spain was host to the presentation of the trial in progress 1717. Dr. Laurence Albiges presented CARE1 which is a first line randomised study platform to optimize treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC).
Systemic therapy for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) relies on two classes of agents: vascular endothelial growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (VEGFR-TKI) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) targeting either the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) or the programmed death 1 (PD-1) immune checkpoints.
ICI-based combination therapy is the standard-of-care for clear cell RCC, utilizing either ICI+ICI or ICI+TKI regimens. (1-4) To date, there has been no head-to-head comparison between the ICI+ICI and ICI+TKI approaches. As a result, patients are treated based on physician preference and decision, without biomarkers to guide treatment selection.
Dr. Albiges and colleagues hypothesized that PD-L1 staining may help select patients who would derive benefit from an upfront ICI-ICI strategy.
The CARE1 study (NCT0636463) is an academic phase III international multicenter randomized clinical trial funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation program. Patients will be randomized 1:1 to receive ICI+ICI or ICI+TKI and PD-L1 positivity will be defined locally as ≥1% of stained tumor cells.
The inclusion criteria are:
- Histologically confirmed metastatic ccRCC patients with intermediate/poor-risk by IMDC classification
- ≥ 18 years of age at inclusion
- Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) ≥70%.
The exclusion criteria would be:
- Prior systemic anticancer therapy for mRCC
- Uncontrolled brain metastases
The CARE 1 study design is outlined below:

The primary endpoint of the CARE1 study is to demonstrate that ICI+ICI combination therapy improves overall survival compared to ICI+TKI in PD-L1 positive patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma in the first-line setting. Conversely, the study aims to show that ICI+TKI improves overall survival compared to ICI+ICI in PD-L1 negative patients.
They key secondary endpoints are:
- Progression-free survival (PFS) - however, PFS will be a co-primary endpoint specifically in the PD-L1 negative population
- Objective response rate (ORR) according to RECIST 1.1
- Duration of treatment
- Time-to-treatment discontinuation
- Treatment-free survival
- Time to subsequent systemic anticancer therapy
- Quality of life, safety
- Cost-effectiveness.
Patients randomized in this trial will receive either:
- Nivolumab + Ipilimumab or
- ICI + VEGFR-TKI (investigator choice between Axitinib+Pembolizumab, Cabozantinib+Nivolumab or Lenvatinib+Pembrolizumab).
CARE1 Pragmatic design aims at demonstrating statistical differences in overall survival (OS), in the 2 distinct populations:
- PDL1+: HR OS 0.70
- PDL1-: HR OS 0.75, HR PFS 0.78
The Final analysis is planned when 135 patients from the control arm have died in the PDL1+ population and at least 288 patients from the control arm have progressed or died in the PDL1- group.
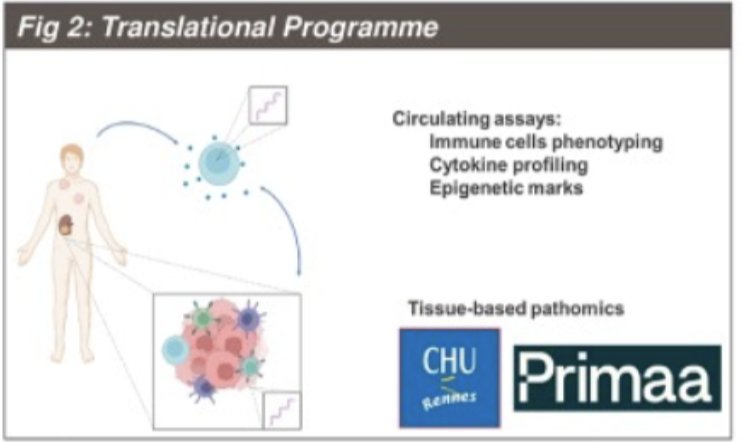
Additionally, a comprehensive translational program, including tissue and circulating biomarkers, AI tools, remote patient monitoring (Resilience), and radiomic tools, has been integrated into the CARE1 study.
The trial has already activated 25 open sites across 2 countries, with plans to open at least 100 sites. Patients will be randomized across 8 European countries. The graphic below shows the countries where the CARE1 study has been authorized and those where it is still under submission.

Presented by: Laurence Albiges, MD, PhD, Medical Oncologist at Gustave Roussy, Université Paris Saclay, Villejuif, France.
Written by: Julian Chavarriaga, MD – Urologic Oncologist at Cancer Treatment and Research Center (CTIC) Luis Carlos Sarmiento Angulo Foundation via Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO) Fellow at The University of Toronto. @chavarriagaj on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
References:- Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Hammers HJ, Carducci MA, Salman P, Escudier B, Beuselinck B, Amin A, Porta C, George S, Neiman V, Bracarda S, Tykodi SS, Barthélémy P, Leibowitz-Amit R, Plimack ER, Oosting SF, Redman B, Melichar B, Powles T, Nathan P, Oudard S, Pook D, Choueiri TK, Donskov F, Grimm MO, Gurney H, Heng DYC, Kollmannsberger CK, Harrison MR, Tomita Y, Duran I, Grünwald V, McHenry MB, Mekan S, Tannir NM; CheckMate 214 investigators. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):1370-1385.
- Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Zurawski B, Oyervides Juárez VM, Hsieh JJ, Basso U, Shah AY, Suárez C, Hamzaj A, Goh JC, Barrios C, Richardet M, Porta C, Kowalyszyn R, Feregrino JP, Żołnierek J, Pook D, Kessler ER, Tomita Y, Mizuno R, Bedke J, Zhang J, Maurer MA, Simsek B, Ejzykowicz F, Schwab GM, Apolo AB, Motzer RJ; CheckMate 9ER Investigators. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 4;384(9):829-841.
- Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T, Grünwald V, Hutson TE, Kopyltsov E, Méndez-Vidal MJ, Kozlov V, Alyasova A, Hong SH, Kapoor A, Alonso Gordoa T, Merchan JR, Winquist E, Maroto P, Goh JC, Kim M, Gurney H, Patel V, Peer A, Procopio G, Takagi T, Melichar B, Rolland F, De Giorgi U, Wong S, Bedke J, Schmidinger M, Dutcus CE, Smith AD, Dutta L, Mody K, Perini RF, Xing D, Choueiri TK; CLEAR Trial Investigators. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021 Apr 8;384(14):1289-1300.
- Motzer RJ, Robbins PB, Powles T, Albiges L, Haanen JB, Larkin J, Mu XJ, Ching KA, Uemura M, Pal SK, Alekseev B, Gravis G, Campbell MT, Penkov K, Lee JL, Hariharan S, Wang X, Zhang W, Wang J, Chudnovsky A, di Pietro A, Donahue AC, Choueiri TK. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial. Nat Med. 2020 Nov;26(11):1733-1741.


