(UroToday.com) The 2024 ESMO annual meeting included a session on prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Dana Rathkopf discussing the clinical activity of BMS-986365 (CC-94676) in heavily pretreated patients with mCRPC. The majority of mCRPC remains AR-dependent even if resistant to AR pathway inhibitors such as enzalutamide and abiraterone. BMS-986365 is a heterobifunctional, oral therapy designed to inhibit AR activity via a first-in-class dual mechanism of AR degradation and antagonism:
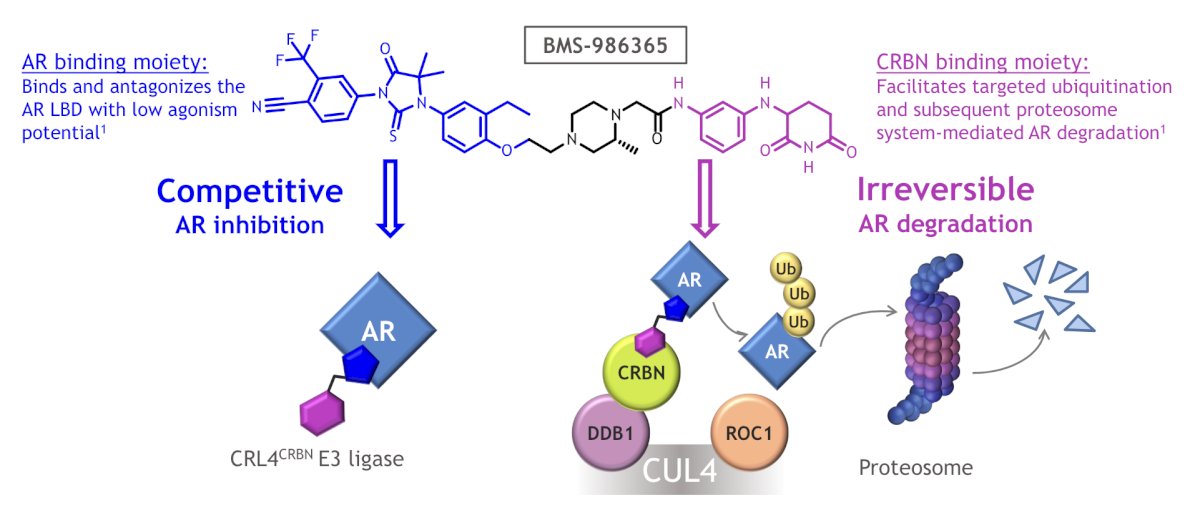
At ESMO 2024, Dr. Rathkopf and colleagues reported updated results from CC-94676-PCA-001 (NCT04428788), the first-in-human, multicenter study of BMS-986365 in patients with progressive mCRPC.
Patients with mCRPC who progressed on antiandrogen therapy including ≥ 1 AR pathway inhibitors (ie. enzalutamide, abiraterone) were enrolled. Patients had prior taxane chemotherapy unless ineligible or declined. Part A included dose escalation (n = 27), and data reported are from the Part B dose expansion at 400, 600, or 900 mg BID (n = 20 each). Median follow-up was 14.8 months (range: 9.6-24.3), and the primary objectives were safety and tolerability, as well as the recommended phase 2 dose.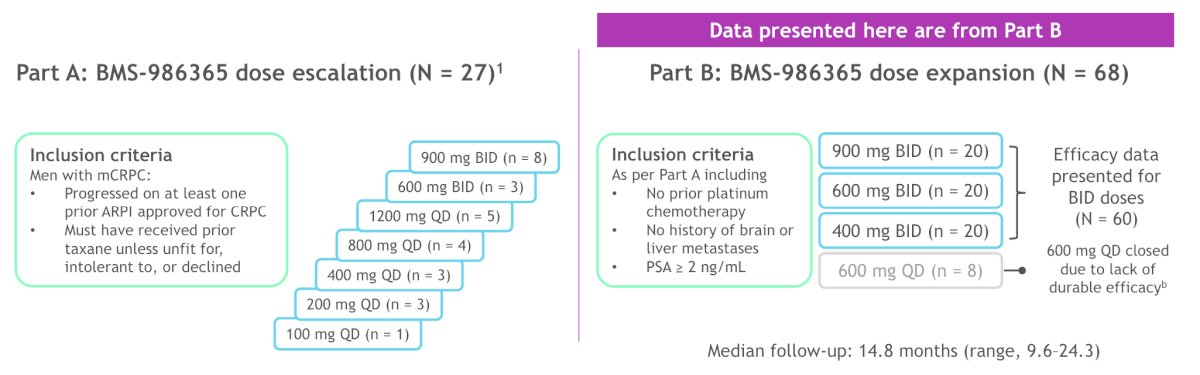
Among the 68 patients, prior therapy included chemotherapy (n = 31; 46%), enzalutamide (n = 51; 75%), and abiraterone (n = 44; 65%). Overall, 46% received both enzalutamide and abiraterone: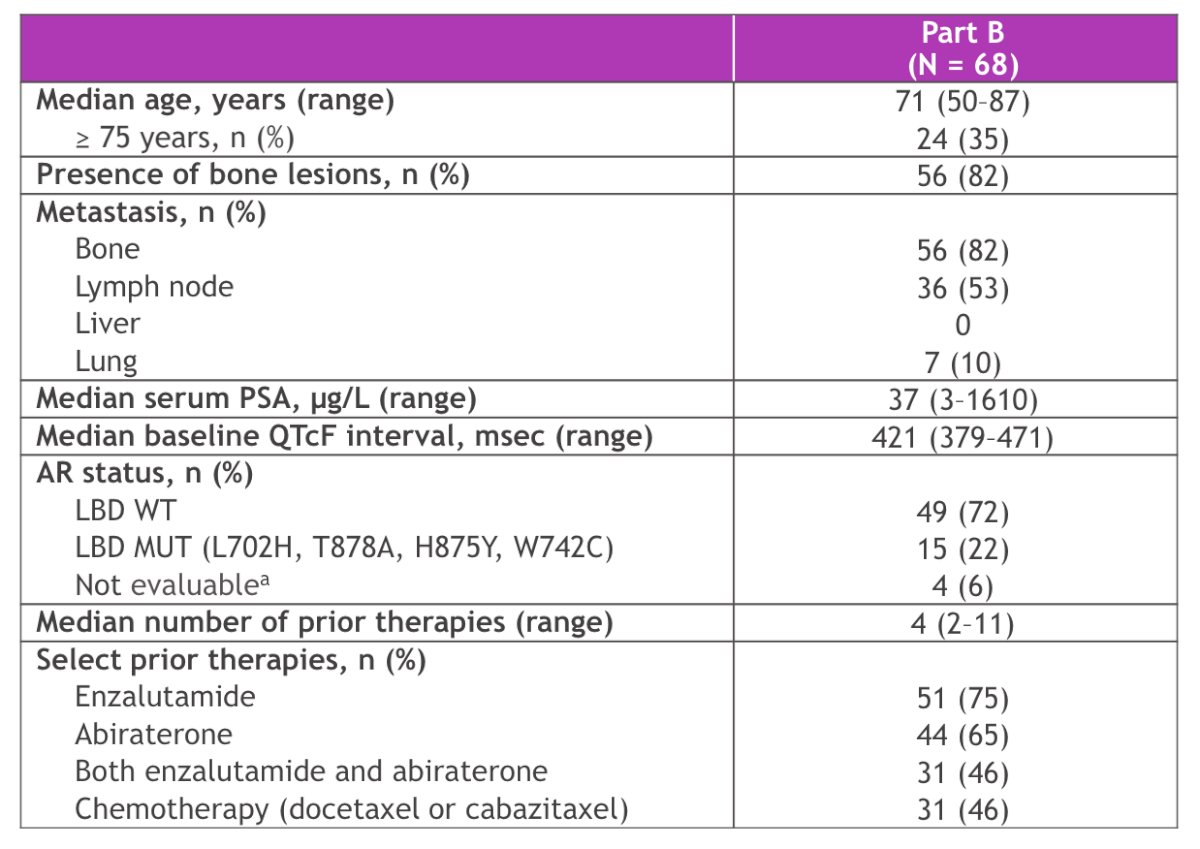
As of February 1, 2024, there were no ≥ grade 4 treatment-related adverse events or discontinuations due to treatment-related adverse events. The most common treatment-related adverse events were prolonged QTc (asymptomatic) (47%; grade 3 - 9%), bradycardia (34%; grade 3 - 0%), and fatigue (21%; grade 3 - 0%). Grade 3 QTc prolongation was successfully managed by dose reduction: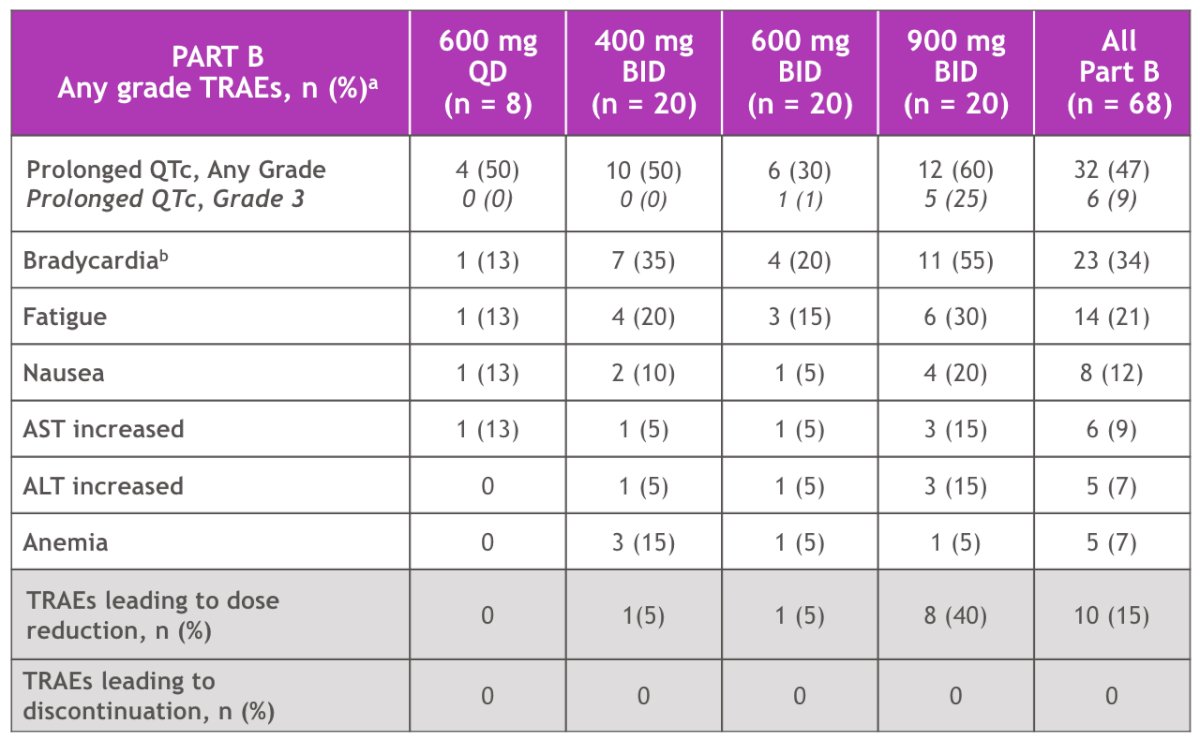
At the 400 mg BID dose, PSA30 was 30% and PSA50 was 25%, at the 600 mg BID dose, PSA30 was 45% and PSA50 was 20%, and at the 900 mg BID dose, PSA30 was 70% and PSA50 was 50%: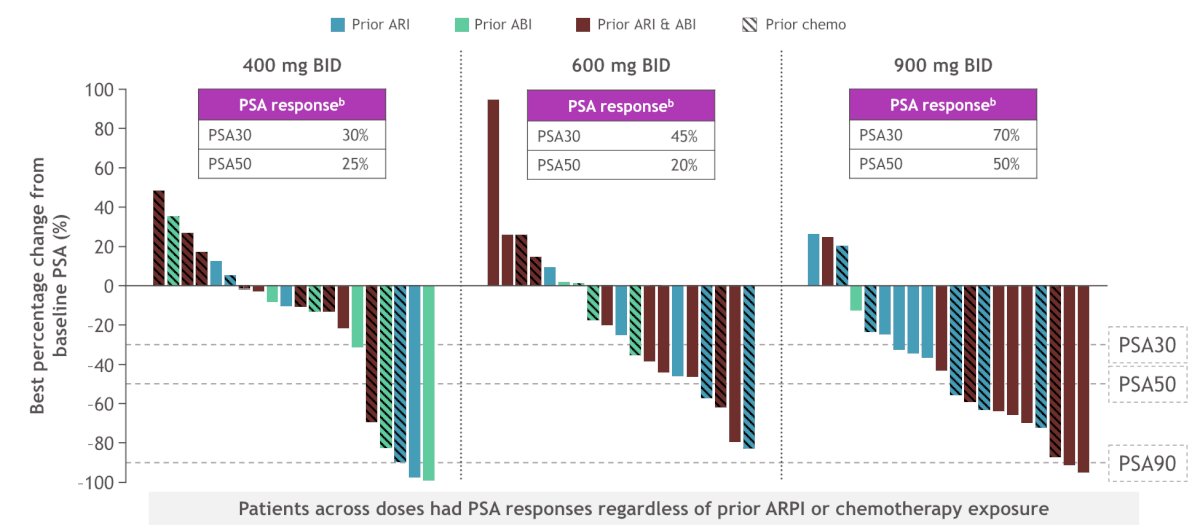
The median radiographic progression-free survival was 6.3 months (95% CI 5.3-10.5) and 42% of patients were free of radiographic progression or death at 6 months: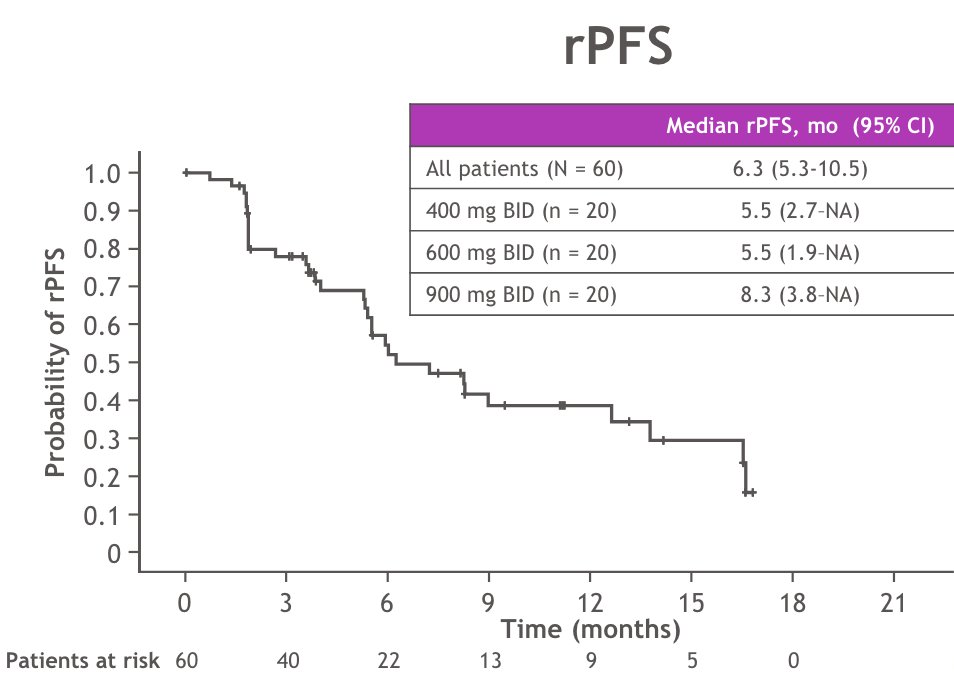
Patients with (n = 28) versus without (n = 32) prior chemotherapy had median radiographic progression-free survival of 5.5 versus 16.5 months, respectively: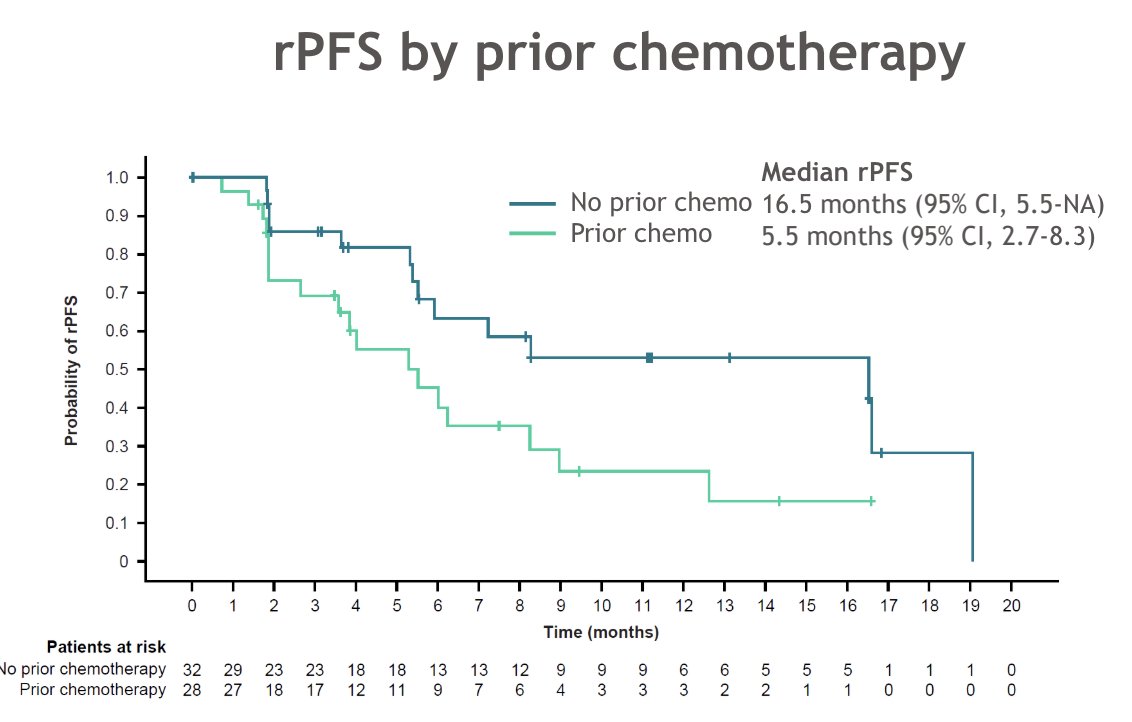
Clinical benefit was observed both in patients with AR ligand binding domain WT and mutant mCRPC: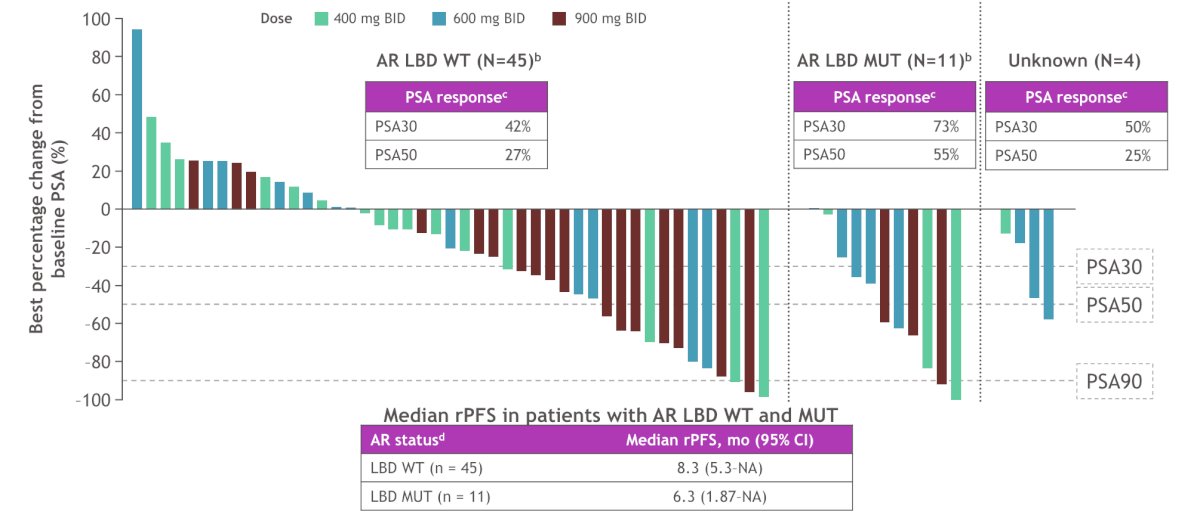
Dr. Rathkopf concluded her presentation discussing the clinical activity of BMS-986365 in heavily pretreated patients with mCRPC with the following take-home points:
- BMS-986365 was well tolerated with a manageable safety profile
- QTc prolongation was the most common treatment-related adverse event and did not lead to treatment discontinuation
- BMS-986365 is orally bioavailable and dose optimization is ongoing
- BMS-986365 demonstrated anti-tumor activity in heavily pre-treated mCRPC patients, all with progression on at least one prior androgen receptor pathway inhibitor
- Dose-dependent PSA responses were observed.
- Median radiographic progression-free survival was longer in chemotherapy-naïve patients compared to chemotherapy-exposed patients.
- Clinical benefit was seen both in patients with AR ligand binding domain wild type and AR ligand binding domain mutation mCRPC
- BMS-986365 is a first-in-class, dual AR degrader and antagonist with potential to overcome androgen receptor inhibitor-resistant mCRPC regardless of AR ligand binding domain mutational status
- Planning for a pivotal phase 3 study in 2025 of BMS-986365 in patients with mCRPC is underway.
Presented by: Dana Rathkopf, MD, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
Related content: First-in-Class AR Degrader Shows Promise in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer - Dana Rathkopf


