(UroToday.com) The 2024 ESMO annual meeting included a session on prostate cancer, featuring a presentation by Dr. Cédric Pobel discussing phenotypic and genomic characterization of de novo metastatic prostate cancer from the phase 3 PEACE-1 trial. Recently, the addition of abiraterone acetate + prednisone to docetaxel and ADT became a standard of care for metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC) following results of PEACE-1:1

In this ancillary study, Dr. Pobel and colleagues aimed to identify prognostic and predictive biomarkers associated with radiographic progression-free survival and overall survival.
Immunochemistry analyses were performed using validated antibodies staining luminal components (AR, NKX3.1), neuroendocrine features (synaptophysin, CD56, chromogranin A), tumor suppressors (p53, Rb, pTEN), Ki67, and ERG. Five phenotype subgroups were defined using luminal and neuroendocrine status. A pre-specified statistical analysis plan was approved by the steering committee, and Cox models were fitted with each immunochemistry marker adjusted for age, tumor burden, Gleason score, ECOG status, and treatments received (radiotherapy, docetaxel and abiraterone acetate + prednisone) to evaluate their prognostic value. Interaction tests between abiraterone acetate + prednisone and biomarkers were performed to assess whether these factors were predictive of treatment benefit.
From the 1,172 de novo mCSPC patients randomized in PEACE-1 (NCT01957436), 595 patients had a paraffin-embedded sample collected and centrally reviewed. The distribution of clinical variables was similar between the full trial population and immunochemistry populations:
Among the 350 patients with an assessable phenotype, 150 (42.9%) were AR-high luminal, 97 (27.7%) AR luminal weak, 95 (27.1%) amphicrine, 3 (0.8%) double negative, and 5 (1.4%) neuroendocrine prostate cancer. No significant difference for radiographic progression-free survival or overall survival was found between these 5 subgroups but a trend from AR-high luminal (better prognosis) to neuroendocrine prostate cancer (worse prognosis), mainly driven by the neuroendocrine status:
Patients with at least one neuroendocrine positive marker had a shorter radiographic progression-free survival (HR 1.38, 95% CI 1.06-1.81, p = 0.017) and overall survival (HR 1.53, 95% CI 1.14-2.06, p = 0.005). ERG-positive patients had a longer radiographic progression-free survival (HR 0.71, 95% CI 0.53-0.94, p = 0.019):

None of the biomarkers were found to be predictive of response to abiraterone acetate + prednisone. With regards to genomics, multiple tumor suppressor gene alterations are also associated with worse prognosis. Specifically, < 2 alterations among TP53, PTEN, and RB1 had a median overall survival of 5.4 years (95% CI 4.34 – not reached) versus >= 2 alterations among TP53, PTEN, and RB1 with a median overall survival of 2.2 years (95% CI 1.88 – not reached; HR 2.63, 95% CI 1.10 – 6.30):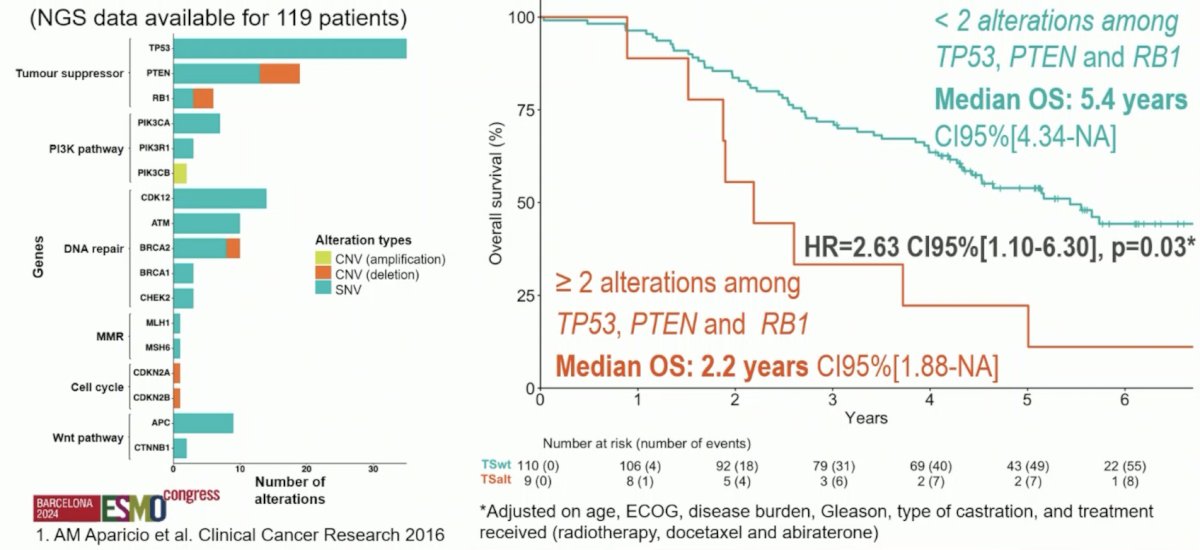
Dr. Pobel concluded his presentation discussing phenotypic and genomic characterization of de novo metastatic prostate cancer from the phase 3 PEACE-1 trial with the following take-home points:
- Combining AR and NE marker expression assessment allows the identification of mCSPC patient subgroups with different outcomes
- Both AR+ and NE+ expression is displayed in about 25% of mCSPC at baseline and predictors poor prognosis
- Alterations in at least two tumor suppressor genes (among TP53, PTEN, and RB1) also predict poor prognosis
- A predictive biomarker for abiraterone benefit remains to be established in mCSPC
Presented by: Cédric Pobel, MD, Medical Oncologist, Gustave Roussey Institute, Paris-Saclay University, Paris, France
Related content: PEACE-1 Trial Reveals Key Genomic Alterations Linked to Survival in Prostate Cancer Patients - Cédric Pobel
Written by: Zachary Klaassen, MD, MSc – Urologic Oncologist, Associate Professor of Urology, Georgia Cancer Center, Wellstar MCG Health, @zklaassen_md on Twitter during the 2024 European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Annual Meeting, Barcelona, Spain, Fri, Sept 13 – Tues, Sept 17, 2024.
References:


